Space Rock Leaves 'Evil' Splat on Mars' Surface
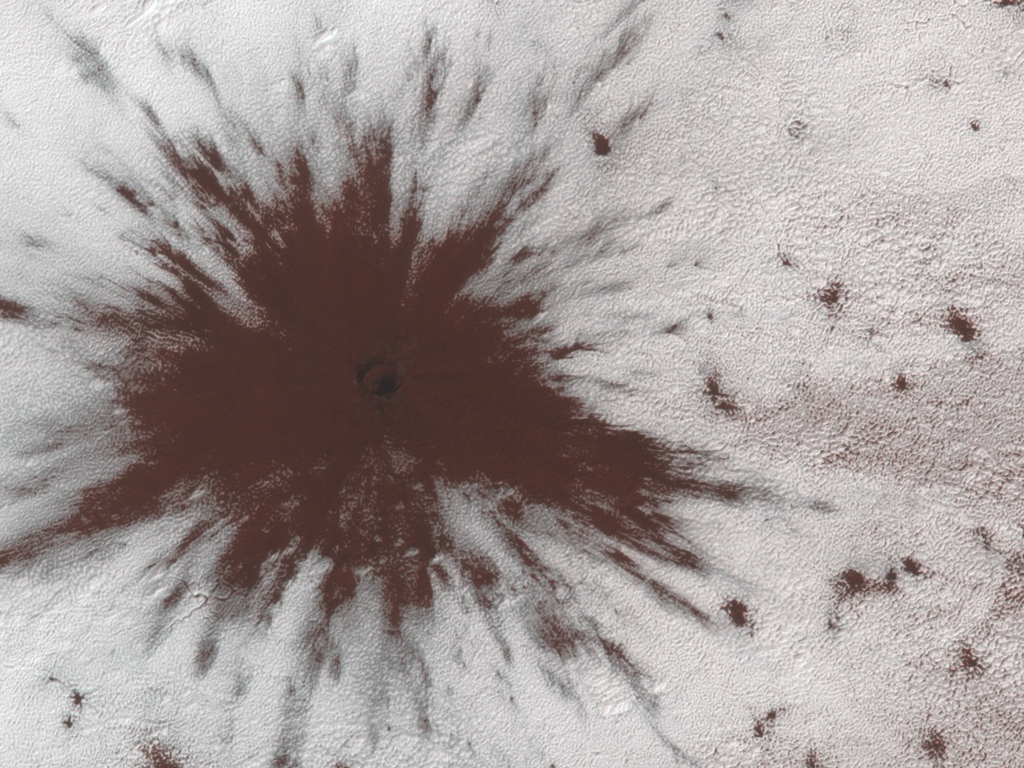

Something punched through ice on Mars, leaving behind what looks like the indent from an evil character in a cartoon movie: a dark splat.
The impact crater, less than 0.62 miles (1 kilometer) across, resulted when a space rock such as a meteoroid, asteroid or comet hit the southern ice cap of the Red Planet between July and September of last year, according to a statement from the University of Arizona.
What resulted was a two-toned splat: a dark inner tone, surrounded by a lighter shade. When the impactor hit the planet, it punctured the thin ice, launching dark sand from below it in all directions. The lighter color surrounding the splat could have resulted from the "scouring by winds from the impact shockwave," according to the statement. [5 Mars Myths and Misconceptions]
Scientists have found only about 120 impact craters on our planet, whereas on Mars they estimate that there are more than 43,000 with diameters over 3 miles (5 km), according to NASA. Though many of these craters are ancient — they don't get erased as much as they do on our planet because Mars doesn't have geological phenomena like plate tectonics — some, like this splat, are new.
The splat was captured by the HiRISE, or High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment, a large camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter that's been imaging the surface of Mars since 2006.
- Photos: The Search for Water on Mars
- Mars InSight Photos: A Timeline to Landing on the Red Planet
- Seeing Things on Mars: A History of Martian Illusions
Originally published on Live Science.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Yasemin is a staff writer at Live Science, covering health, neuroscience and biology. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Science and the San Jose Mercury News. She has a bachelor's degree in biomedical engineering from the University of Connecticut and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.