Real Doc Ock: New Robot Has Robotic Tentacles
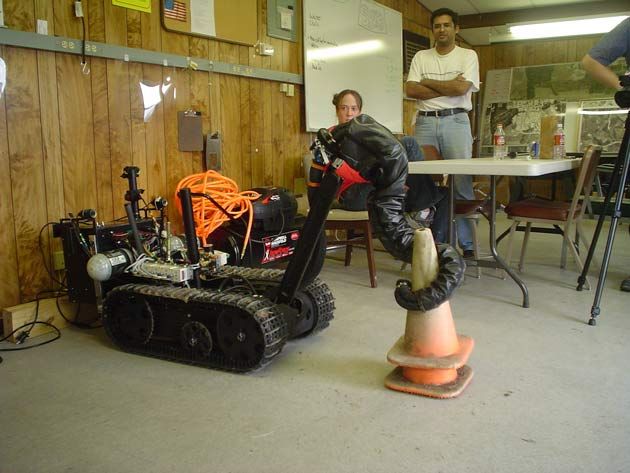

Octarms, developed in the OCTOR project (sOft robotiC manipulaTORs), are robotic tentacles that can grasp a variety of differently shaped objects. Octarm development is funded by DARPA, under their BIODYNOTICS (Biologically Inspired Multifunctional Dynamic Robots) program.
An Octarm is powered by compressed air; pressure sensors on the surface of the tentacle, positional sensors and a camera on the tip provide the functionality. Octarms have explored the interior of pipes and picked up irregularly shaped objects. [See one in the OCTOR project lab.]
Manipulation of fragile objects has also been accomplished.
One of the problems with most robot "manipulators" or mechanical claws for grasping is the difficulty in grasping objects with irregular shapes (like many natural objects), or objects that are fragile (like eggs or tomatoes).
In his classic 1898 story, War of the Worlds, H.G. Wells referred to the "glittering tentacles" that enabled the Martian Tripods to both walk and grasp objects:
Seen nearer, the Thing was incredibly strange, for it was no mere insensate machine driving on its way. Machine it was, with a ringing metallic pace, and long, flexible, glittering tentacles (one of which gripped a young pine tree) swinging and rattling about its strange body. (Read more about H.G. Wells steel tentacle)
For additional information on how robots can pick up fragile objects, see this article on pressure-sensitive skin for robots. The RISE six-legged robot is another result of DARPA's BIODYNOTICS program. The original article was found here. Thanks to Adi for the tip on this story.
(This Science Fiction in the News story used with permission from Technovelgy.com - where science meets fiction.)
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
- Real Robots: Vote for Your Favorite
- Oddly, Octopuses Have Ephemeral Elbows
- Octopus Doesn't Give Up on Motherhood
- Rare White Octopus