'Octagonal' sword from Bronze Age burial in Germany is so well preserved, it shines
Archaeologists in Germany have unearthed a sword in a three-person burial dating to the late 14th century B.C.
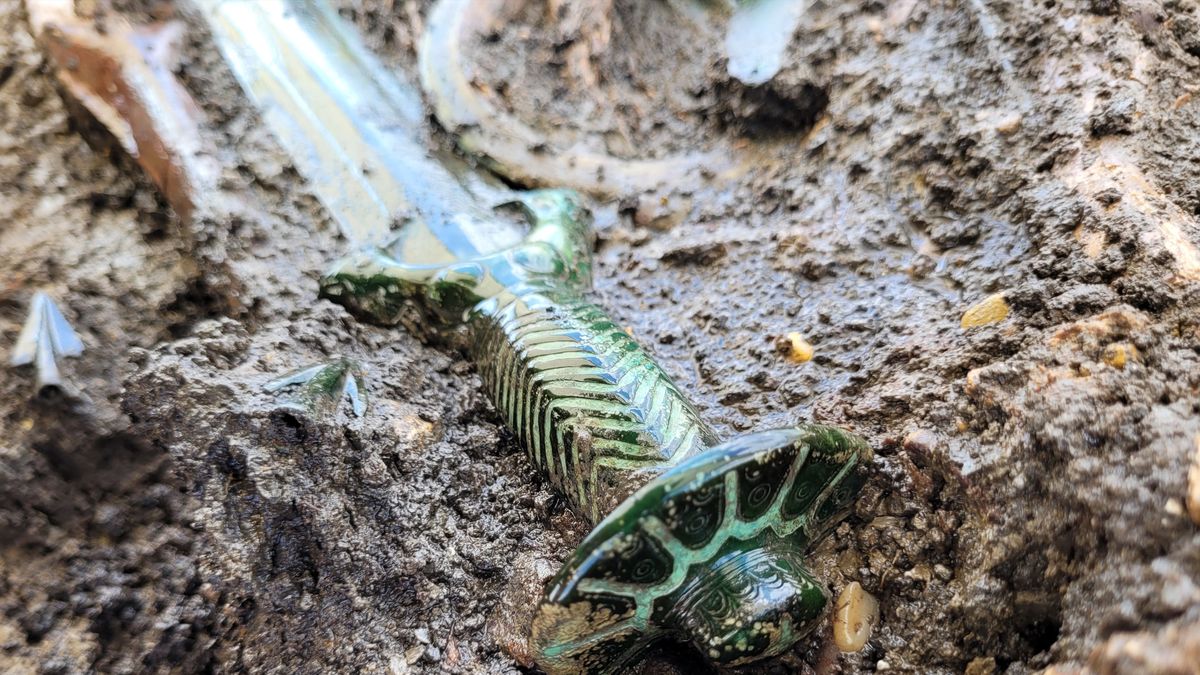

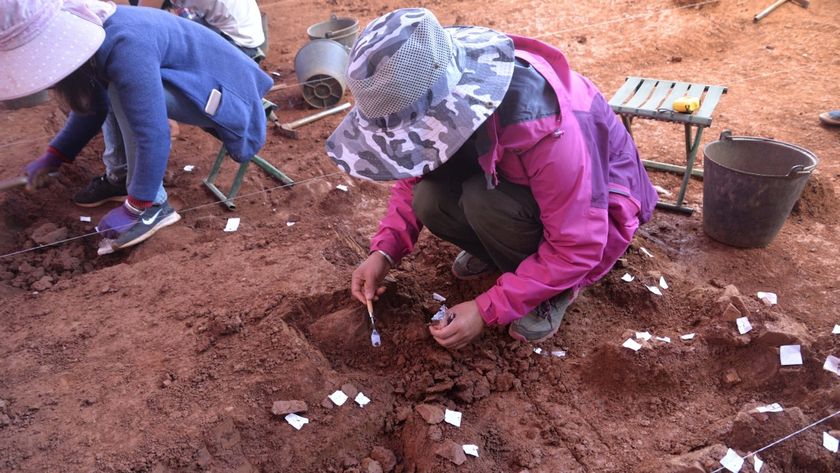
Archaeologists in Germany have unearthed a sword from a Bronze Age burial, and the weapon is in such good condition that it still gleams.
The 3,000-year-old sword, discovered in the town of Nördlingen in Bavaria, was found in the burial of a man, woman and child. It appears that the trio were buried in quick succession, but it's unclear if they are related to one another, according to a statement the Bavarian State Office for Monument Protection released on Wednesday (June 14).

The sword is so well preserved, "it almost still shines," according to the translated statement. The weapon has an ornate octagonal hilt crafted from bronze that now has a greenish tinge, as bronze contains copper, a metal that oxidizes when exposed to air and water.
Related: 10 stunning swords and other ancient weapons uncovered in 2021

Archaeologists dated the sword to the end of the 14th century B.C. Sword discoveries from this time and region are rare, as many middle Bronze Age graves were looted over the millennia, the team said.
Only skilled smiths could make octagonal swords. The handle, which has two rivets, was cast over the blade in a technique known as overlay casting. However, the blade doesn't have any visible cut marks or signs of wear, suggesting that it had a ceremonial or symbolic purpose, according to the statement. Even so, the sword could have easily served as an active weapon, as the center of gravity on the blade's front end suggests that it could have effectively slashed opponents.
Researchers know of two manufacturing areas for octagonal swords in Germany. One region, a local one, was in southern Germany, while the other hailed from northern Germany and Denmark, according to the statement. It's unknown where the newfound sword was cast.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"The sword and the burial still have to be examined so that our archaeologists can classify this find more precisely," Mathias Pfeil, head of the Bavarian State Office for Monument Protection who is involved with the sword's conservation, said in the statement. "But it can already be said: the condition is exceptional! A find like this is very rare!"

Laura is the archaeology and Life's Little Mysteries editor at Live Science. She also reports on general science, including paleontology. Her work has appeared in The New York Times, Scholastic, Popular Science and Spectrum, a site on autism research. She has won multiple awards from the Society of Professional Journalists and the Washington Newspaper Publishers Association for her reporting at a weekly newspaper near Seattle. Laura holds a bachelor's degree in English literature and psychology from Washington University in St. Louis and a master's degree in science writing from NYU.