Roman temple found in France may have been dedicated to war god Mars
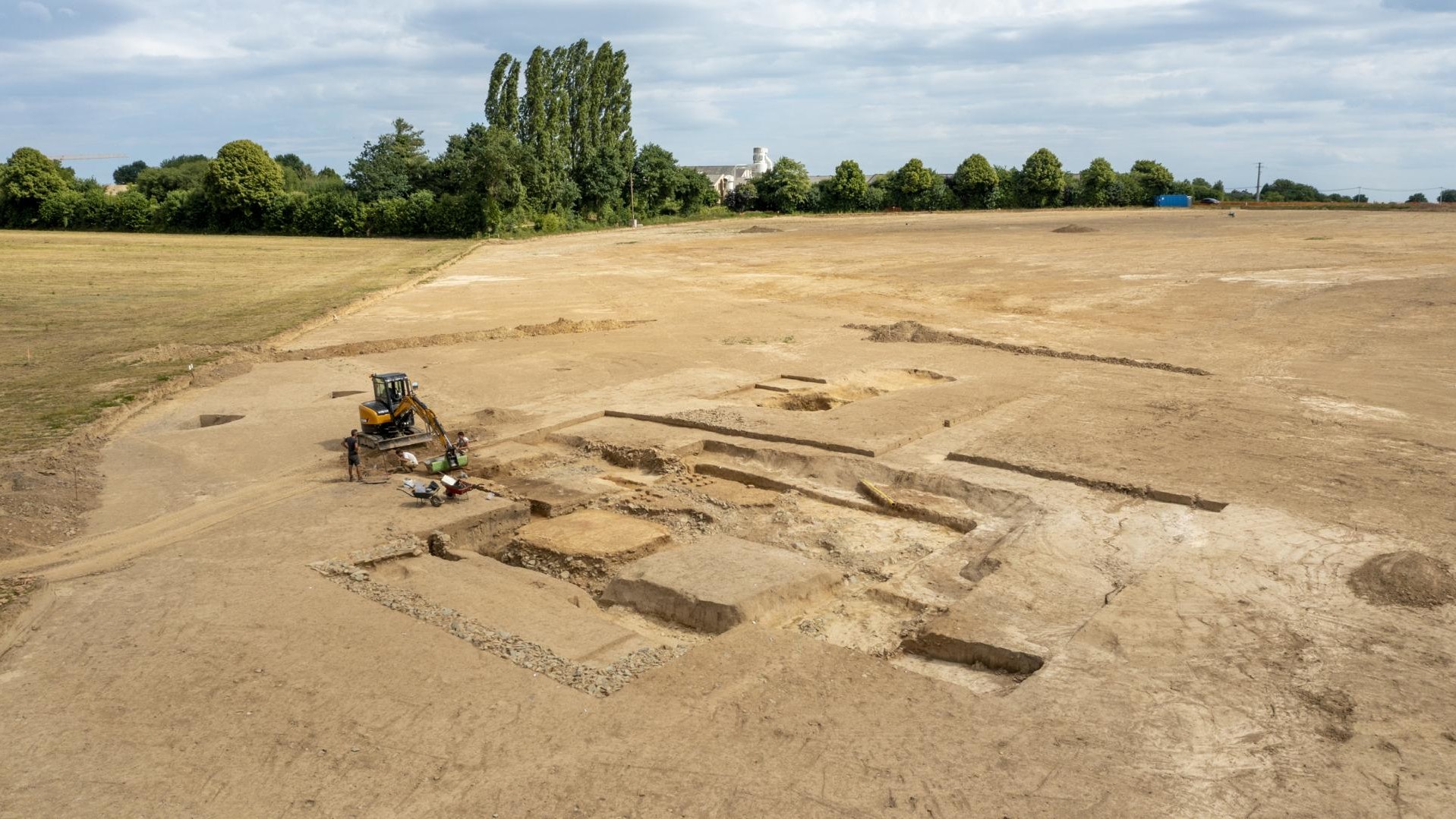
A large temple possibly used by Roman soldiers for hundreds of years has been unearthed by archaeologists in northwest France.
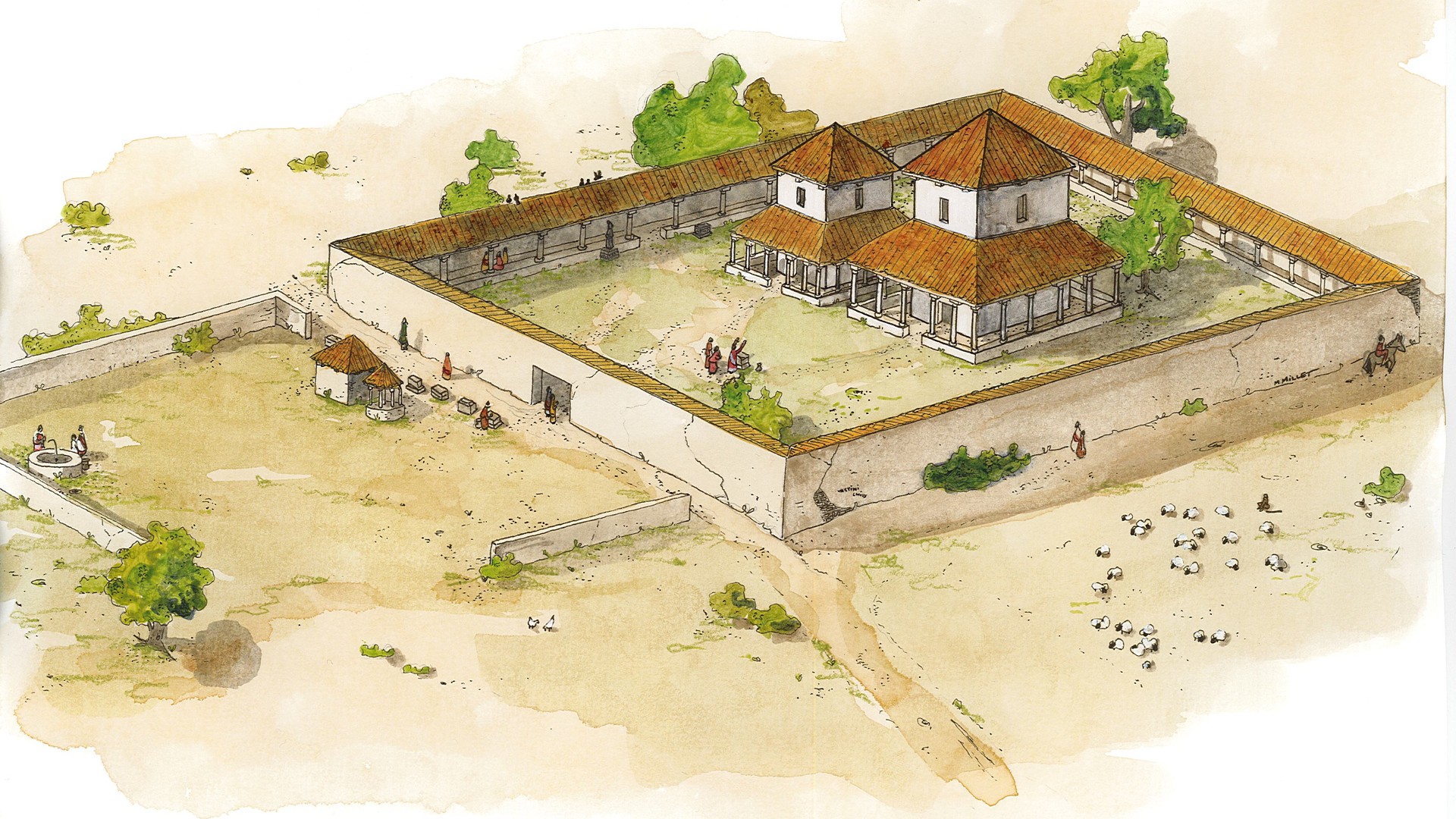
Archaeologists in northwest France have unearthed what may have been a temple to the Roman war god Mars, dating to the first century B.C.
The temple, or sanctuary, is part of a Roman complex spread over more than 17 acres (7 hectares) that was discovered last year at La Chapelle-des-Fougeretz, Brittany, and was probably visited by Roman soldiers posted to the region.
"The size of the sanctuary indicates it was an important place for religion," Françoise Labaune-Jean, one of the directors of the excavations and an archaeologist at the National Institute of Preventive Archaeological Research (INRAP), told Live Science.
Related: 31 ancient temples from around the world, from Göbekli Tepe to the Parthenon
La Chapelle-des-Fougeretz has been recognized for its wealth of archaeological remains since the 1970s, and it was first excavated in the 1990s, Labaune-Jean said. The latest excavations started in 2022.
The site is slightly elevated, with a commanding view of the Rennes basin. This viewpoint makes it "likely that religious ceremonies gathered here from Condate [the Roman city in the basin] and the surrounding area,” Labaune-Jean said in an email.



Roman war god
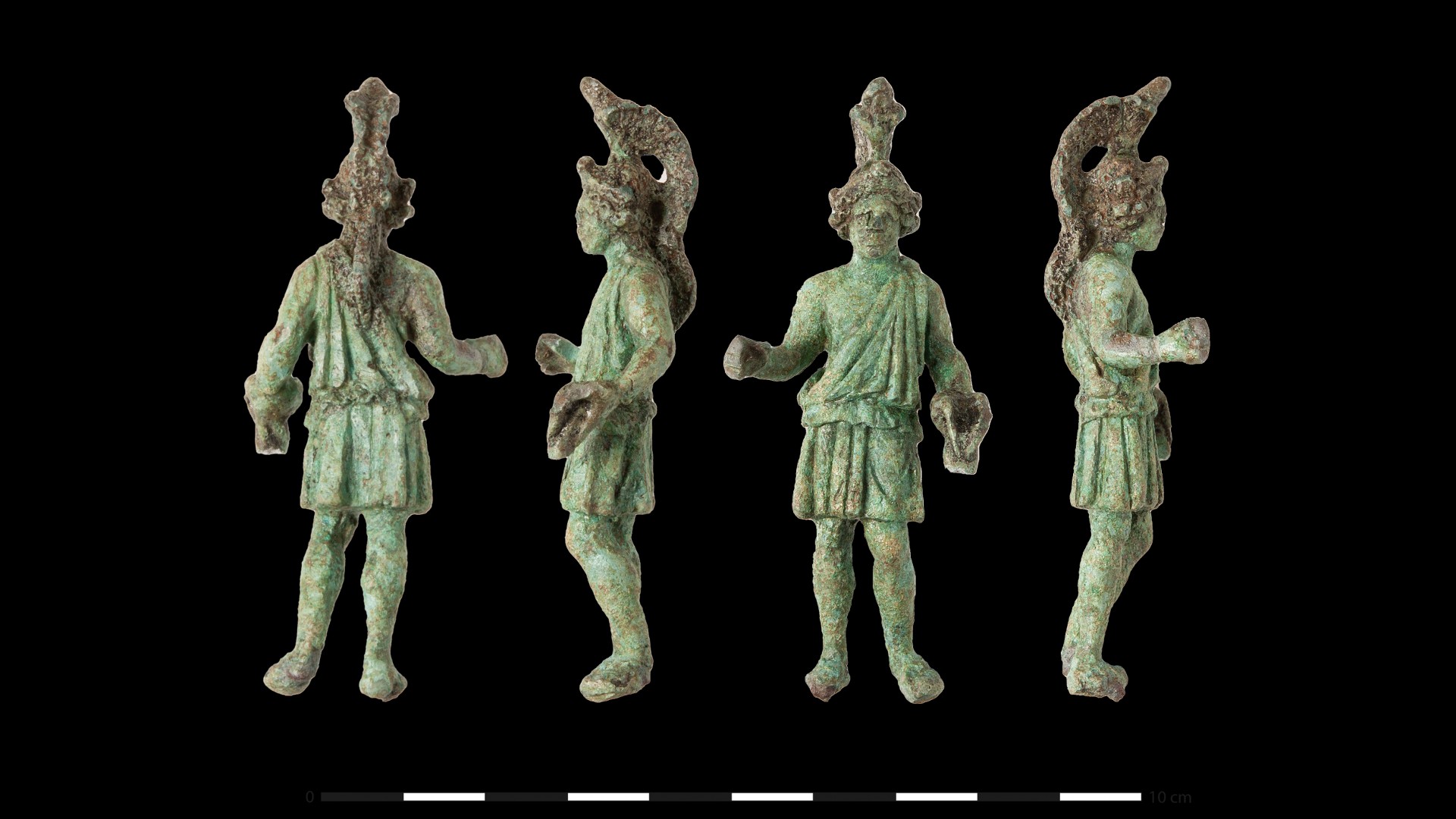
Archaeologists believe the site was dedicated to Mars after discovering a bronze statuette of the Roman war god in 2022, while iron weapons deposited in a ditch around the sanctuary also suggest that it was frequented by soldiers.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

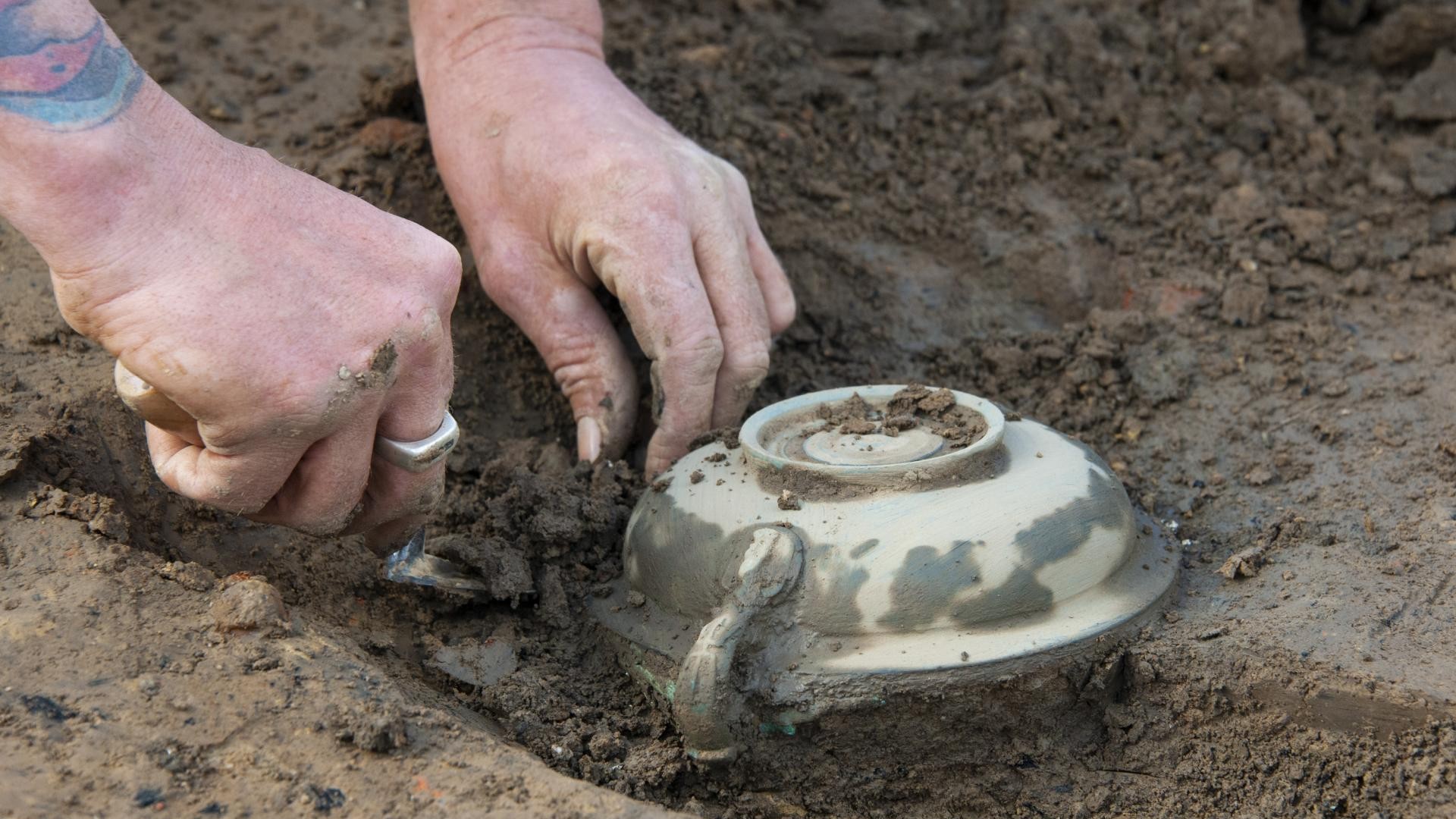
But a large number of terracotta figurines, perhaps representing Venus and mother goddesses, were also found in a nearby pit.
"As is often the case with religious buildings of antiquity, it is difficult to know which deity they may have been dedicated to," Labaune-Jean said, noting that no inscriptions or large statues have been found at the site. "When the study of the objects discovered there is more advanced, it will perhaps be possible to propose other complementary deities."
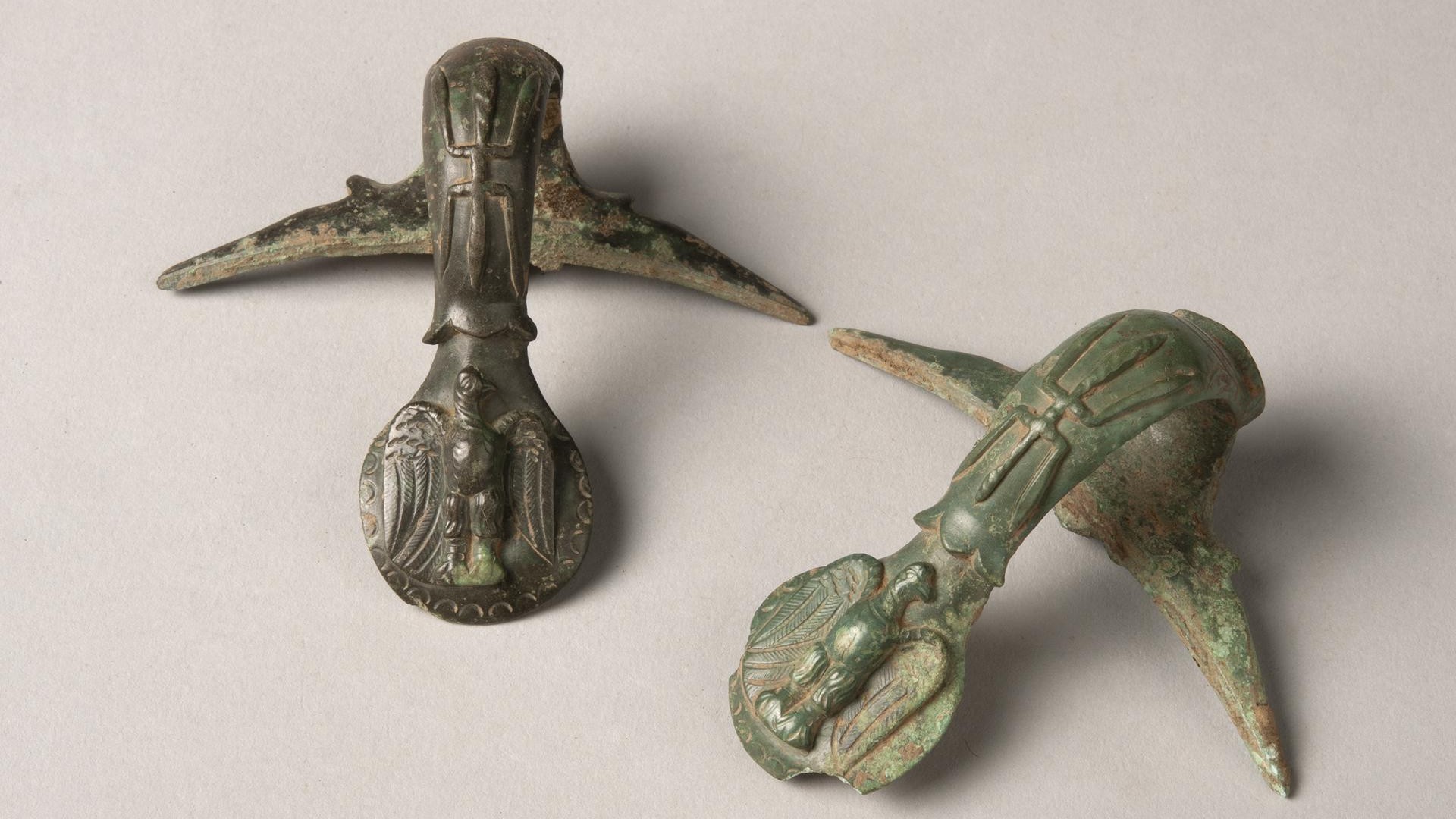

Julius Caesar conquered Brittany — called “Armorica” by the Romans — in 56 B.C.
The sanctuary at La Chapelle-des-Fougeretz seems to date from close to that time and was used until the fifth century A.D., according to a statement from INRAP.
The archaeologists aren't sure why the complex was abandoned, but it may be linked with the collapse of the Western Roman Empire at about that time.
Temple complex
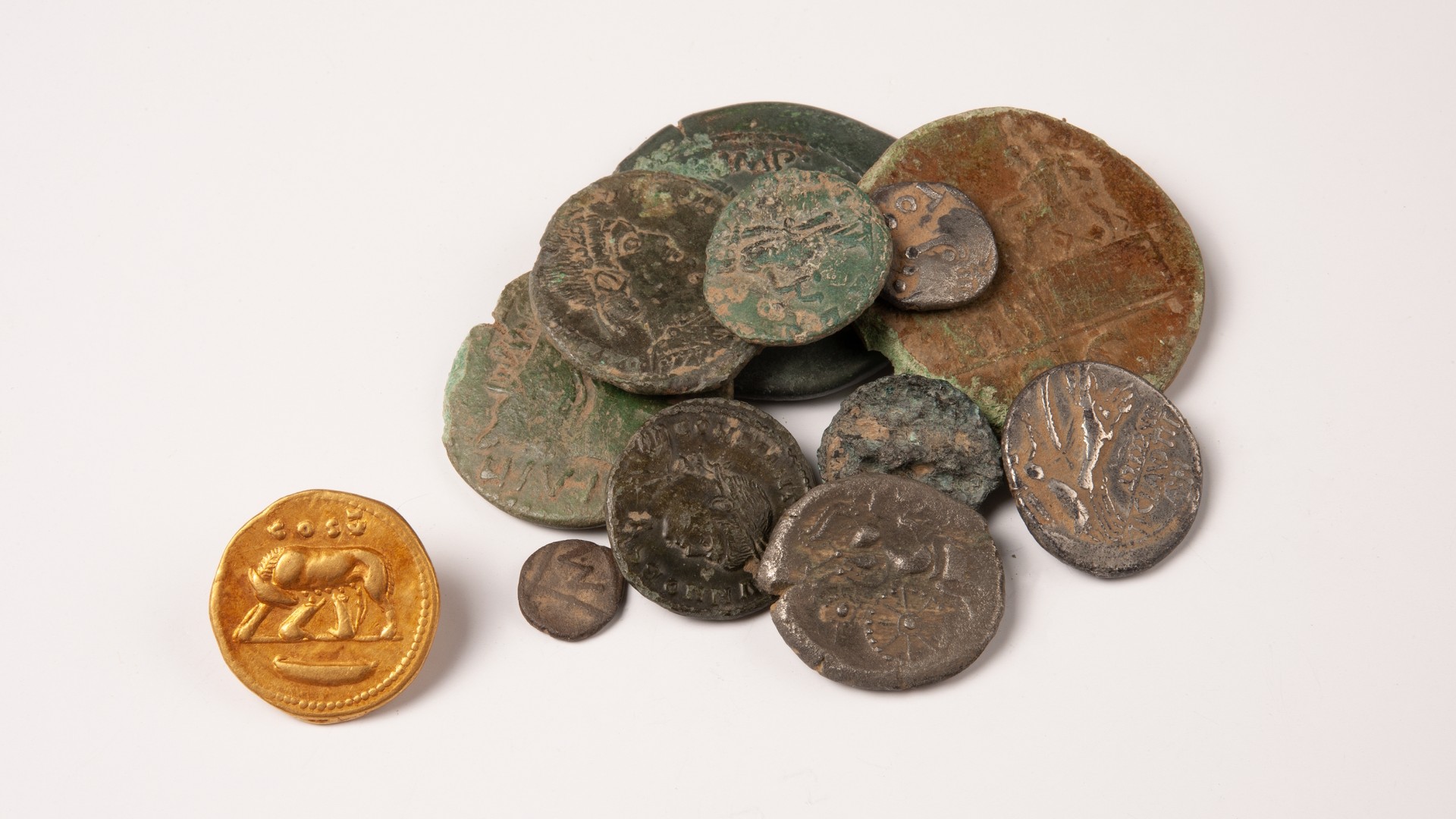

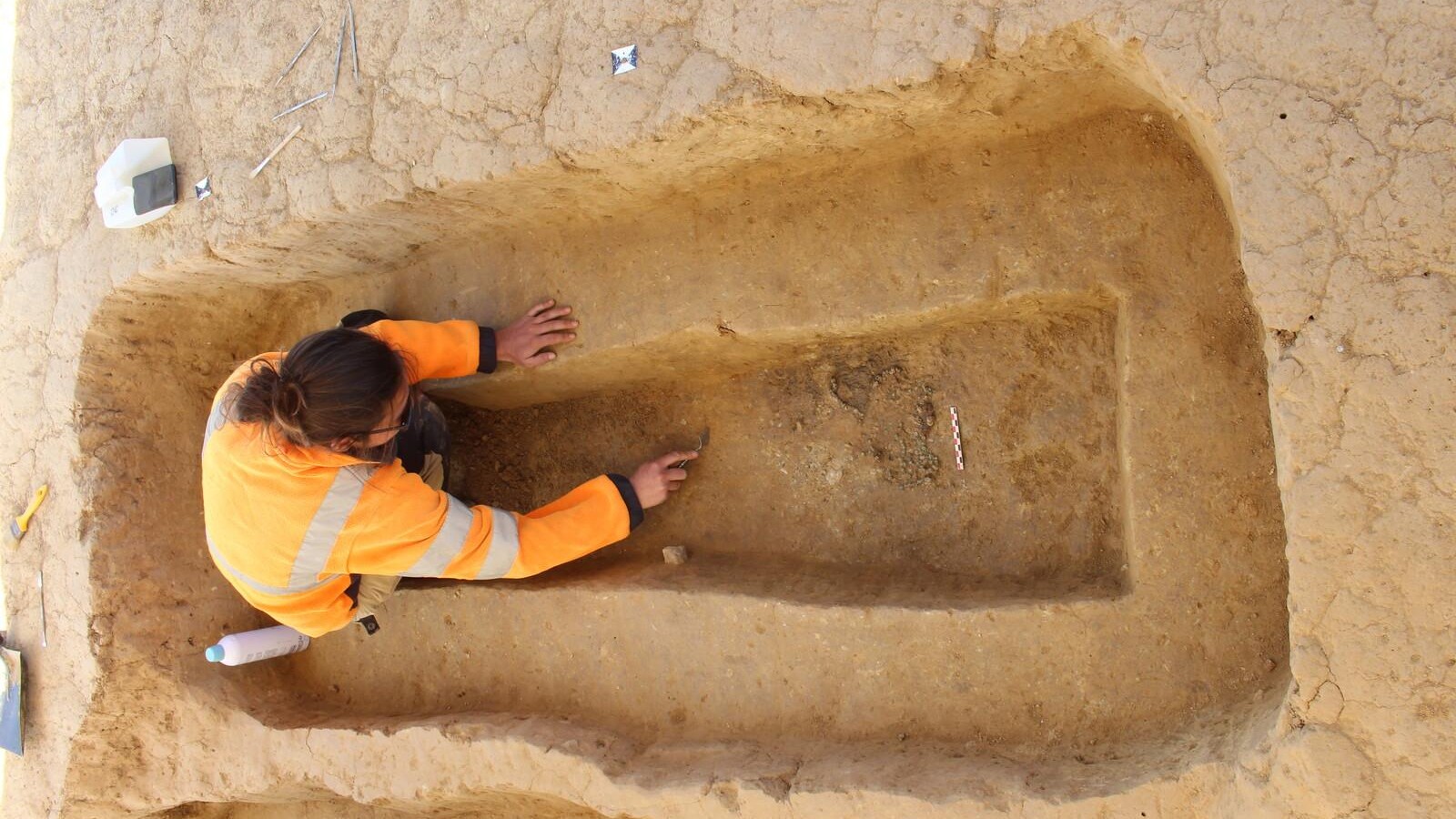
The temple complex expanded over time to include a small town with public baths and a cemetery containing about 40 tombs.
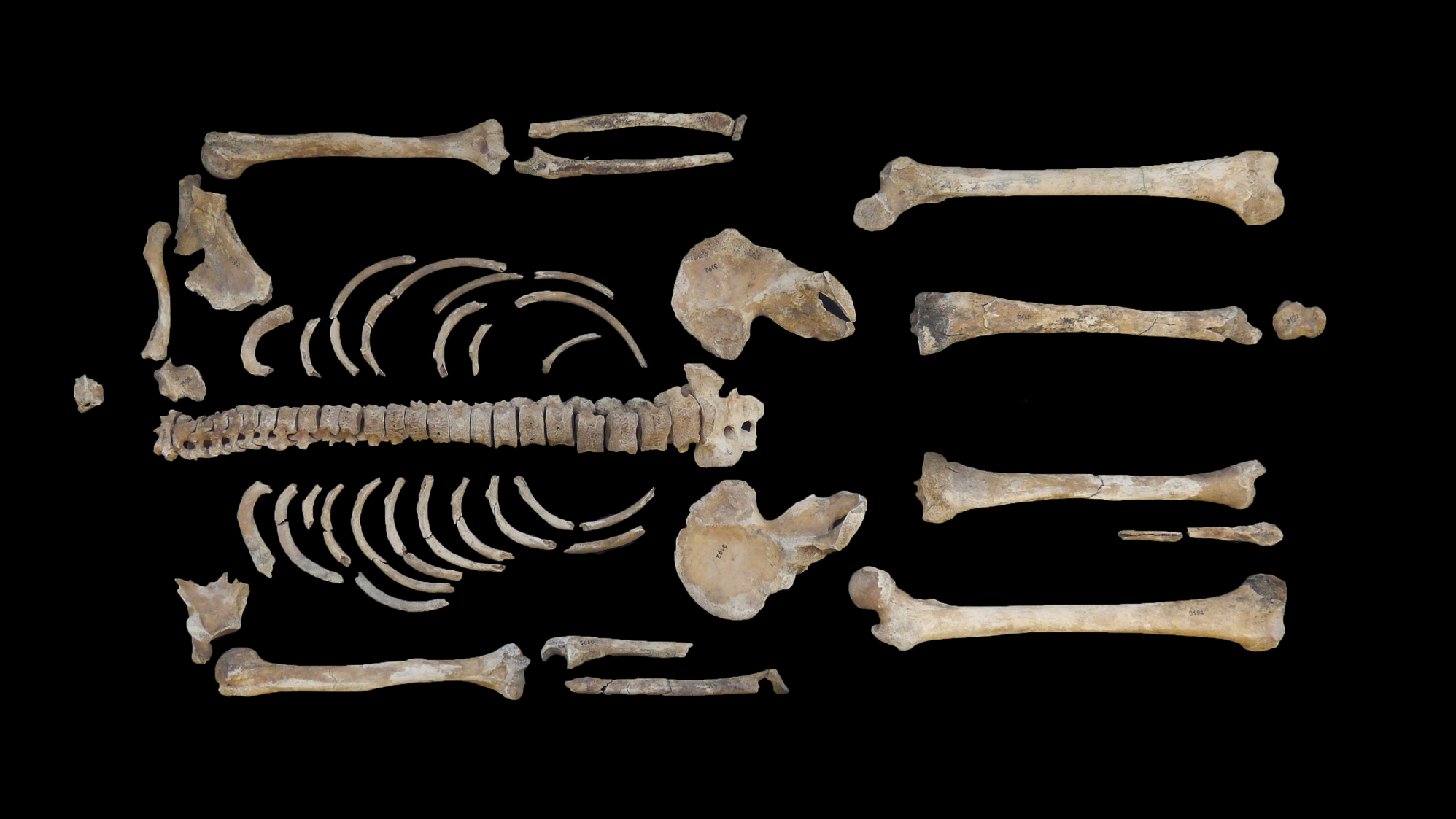
Some of the tombs held items made of silver, such as bracelets, pins and belt buckles, while another had a dagger and parts of a harness for horses. Hundreds of everyday artifacts have also been unearthed there, including furniture and pieces of pottery, glass and metal.
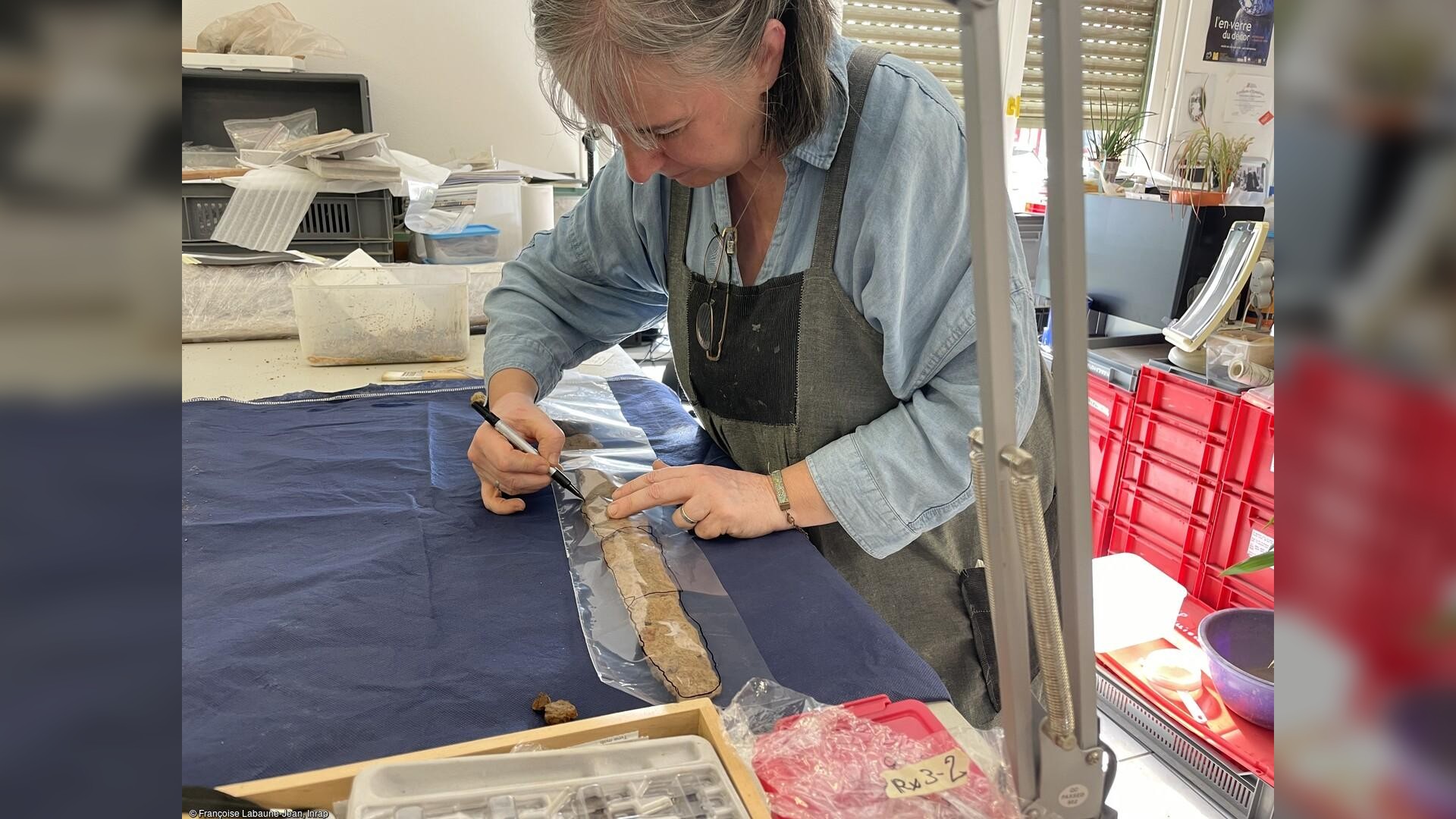
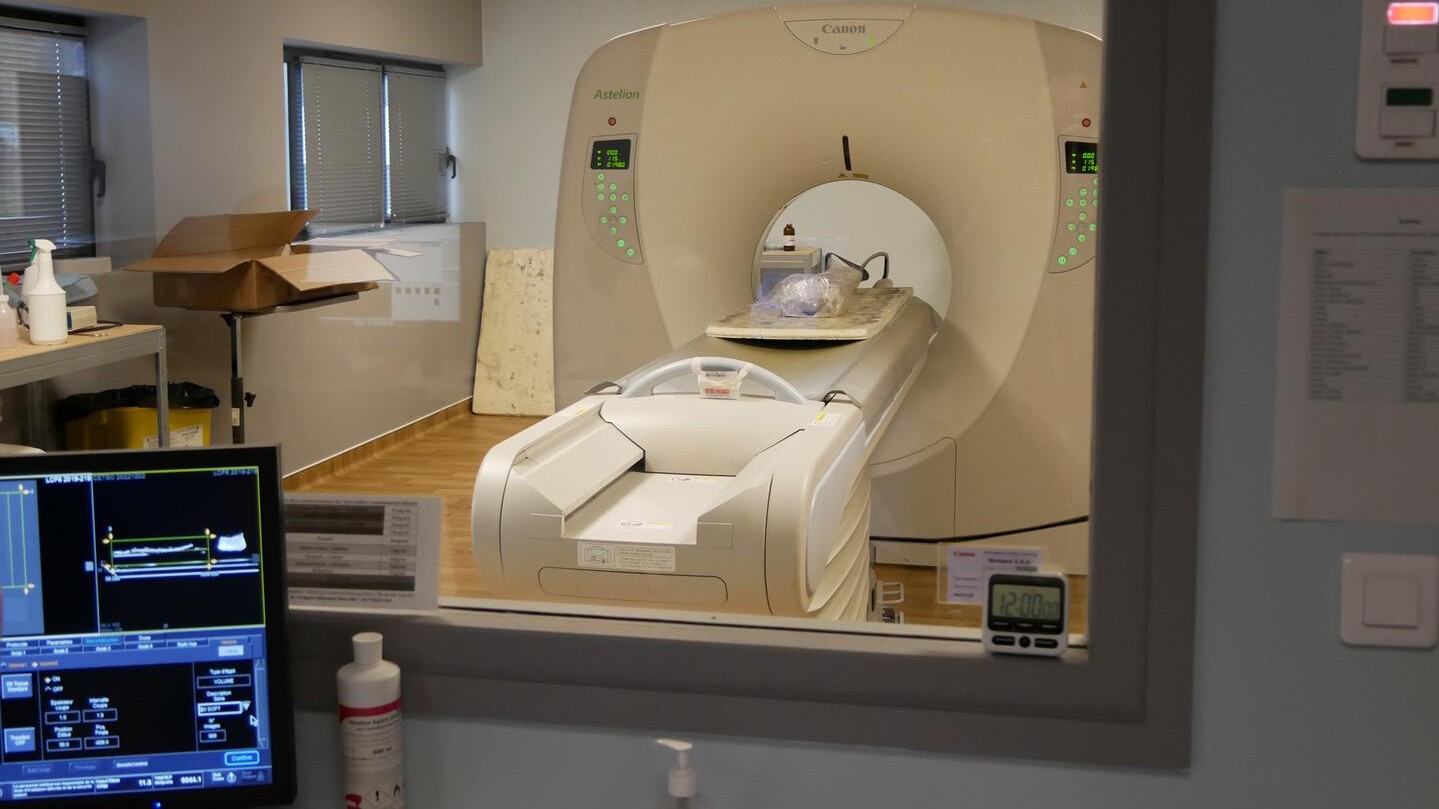

Labaune-Jean role is to quickly preserve and study artifacts unearthed during the excavations, which might otherwise deteriorate quickly when exposed to air or light. X-rays and computerized 3D imaging are also being used to document the discoveries, she said.
Eric Norde, an archaeologist with the Dutch archaeological agency RAAP, who is excavating a sanctuary used by Roman soldiers near Zevenaar, Netherlands, said he's.cautious about assigning the sanctuary at La Chapelle-des-Fougeretz to Mars alone.
That's because the Zevenaar sanctuary shows that Roman temples were often associated with several deities. "When you look only at the sculptures and the weapons and military equipment, one would conclude only Hercules was venerated," he told Live Science.
But careful research shows instead that several different gods were worshiped there. "It is quite dangerous to assign a deity to a sanctuary based only on the finds," and not inscriptions or texts, he said.
Tom Metcalfe is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor who is based in London in the United Kingdom. Tom writes mainly about science, space, archaeology, the Earth and the oceans. He has also written for the BBC, NBC News, National Geographic, Scientific American, Air & Space, and many others.