Skeleton with 4 prosthetic metal fingers unearthed from centuries-old grave in Germany
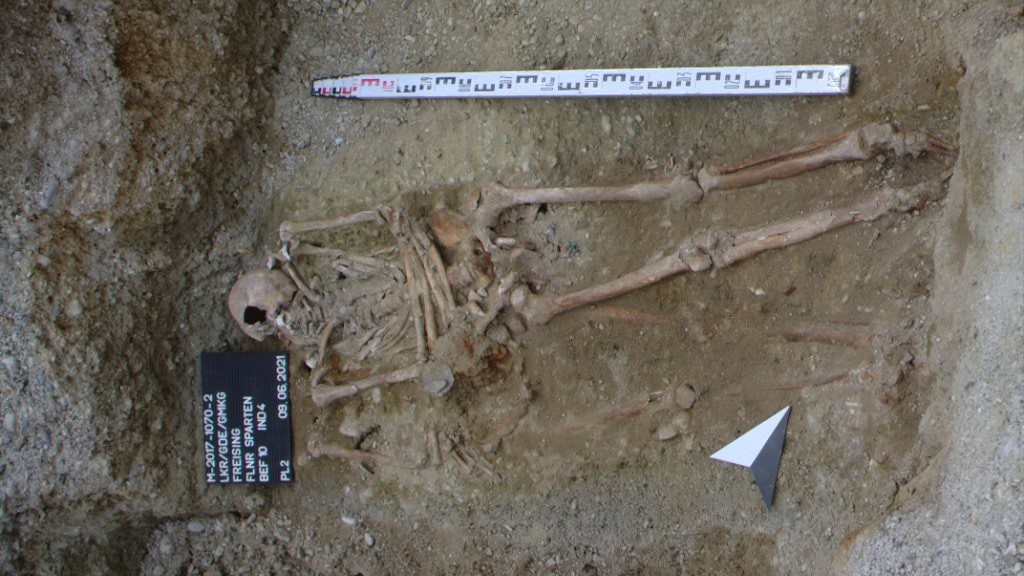
The skeleton of a middle-aged man who died between 1450 and 1620 was found with a prosthetic hand still attached to his left arm, which replaced four fingers he likely lost through amputation.
Archaeologists in Germany have unearthed a skeleton with a metal prosthetic hand still attached to its left arm, replacing fingers that had likely been amputated.
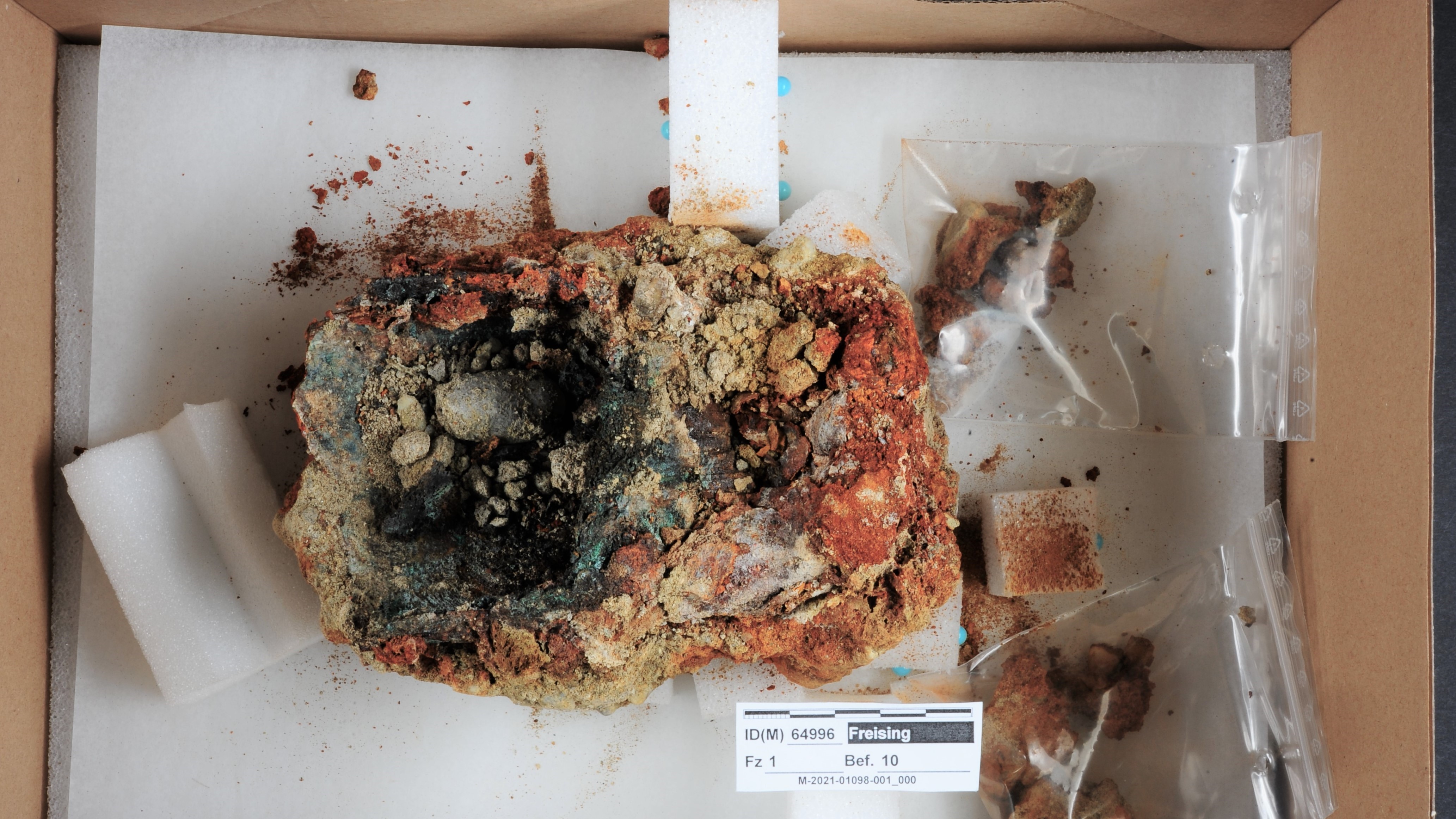
An analysis revealed the prosthetic contraption was once covered in leather and strapped to the individual's arm with bandages. The skeleton, discovered in the southern town of Freising, belonged to a man aged 30 to 50 who died between the years 1450 and 1620, government officials announced in a translated statement on Oct. 27.
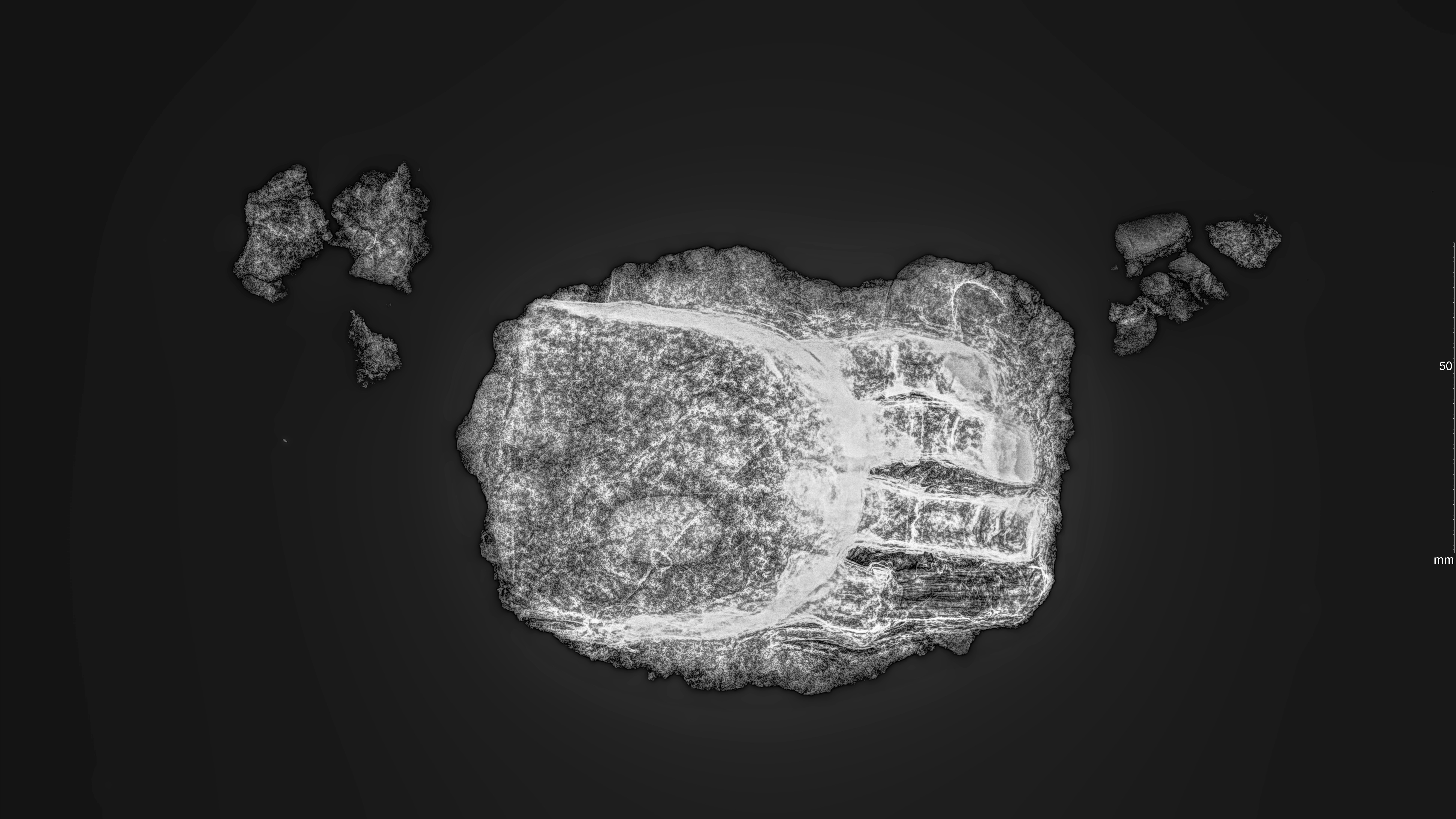
"The hollow prosthetic on the left hand replaced four fingers," Walter Irlinger, deputy of the general conservator at the Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation, said in the statement. "The index, middle, ring and little fingers are individually molded out of sheet metal and are immobile."
Related: See the stunning facial approximation of a medieval man with dwarfism
Marks on the remaining left hand bones suggest the fingers were amputated while the man was alive, but it remains unclear why surgeons had to perform the procedure. A thumb bone found cemented to the corroded metal prosthetic indicates the patient kept his thumb.
Archaeologists removed the hand wearing the prosthetic from the skeleton for restoration work and analysis. Scans revealed it was a simple metal contraption with scraps of fabric and leather stuck to the finger replicas, showing the outside of the prosthetic hand was at least partially covered, according to the statement. Remains of a gauze-like material inside the hollow fingers indicate the prosthetic device may have been padded to protect the hand stump from the metal.
The fingers were slightly curved and lay parallel to each other to imitate the natural resting position of a hand, Irlinger said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The discovery suggests medicine at this time was concerned with the wellbeing of amputees and found solutions to make life easier for them, officials said in the statement. The skeleton dates to a period marked by military conflicts that may have led to a high number of injuries and amputations, which likely heightened the demand for prosthetics in and around Freising.
The prosthetic hand is not the first of its kind to be unearthed. Archaeologists have described around 50 similar medical devices found across Central Europe and dating from the late Middle Ages (1300 to 1500) to the early modern period (1500 to 1800). Unlike the stiff contraption discovered in Freising, some of these prosthetic limbs had sophisticated, movable parts, the statement said.
One of the oldest prosthetics on record is a 3,000-year-old wooden toe discovered on an ancient Egyptian mummy.

Sascha is a U.K.-based staff writer at Live Science. She holds a bachelor’s degree in biology from the University of Southampton in England and a master’s degree in science communication from Imperial College London. Her work has appeared in The Guardian and the health website Zoe. Besides writing, she enjoys playing tennis, bread-making and browsing second-hand shops for hidden gems.