Wreck of WWII 'Hit 'Em Harder' submarine, which sank with 79 crew on board, discovered in South China Sea
The U.S. wreck is the grave site of the 79 crew who died when the sub was sunk in battle in 1944.
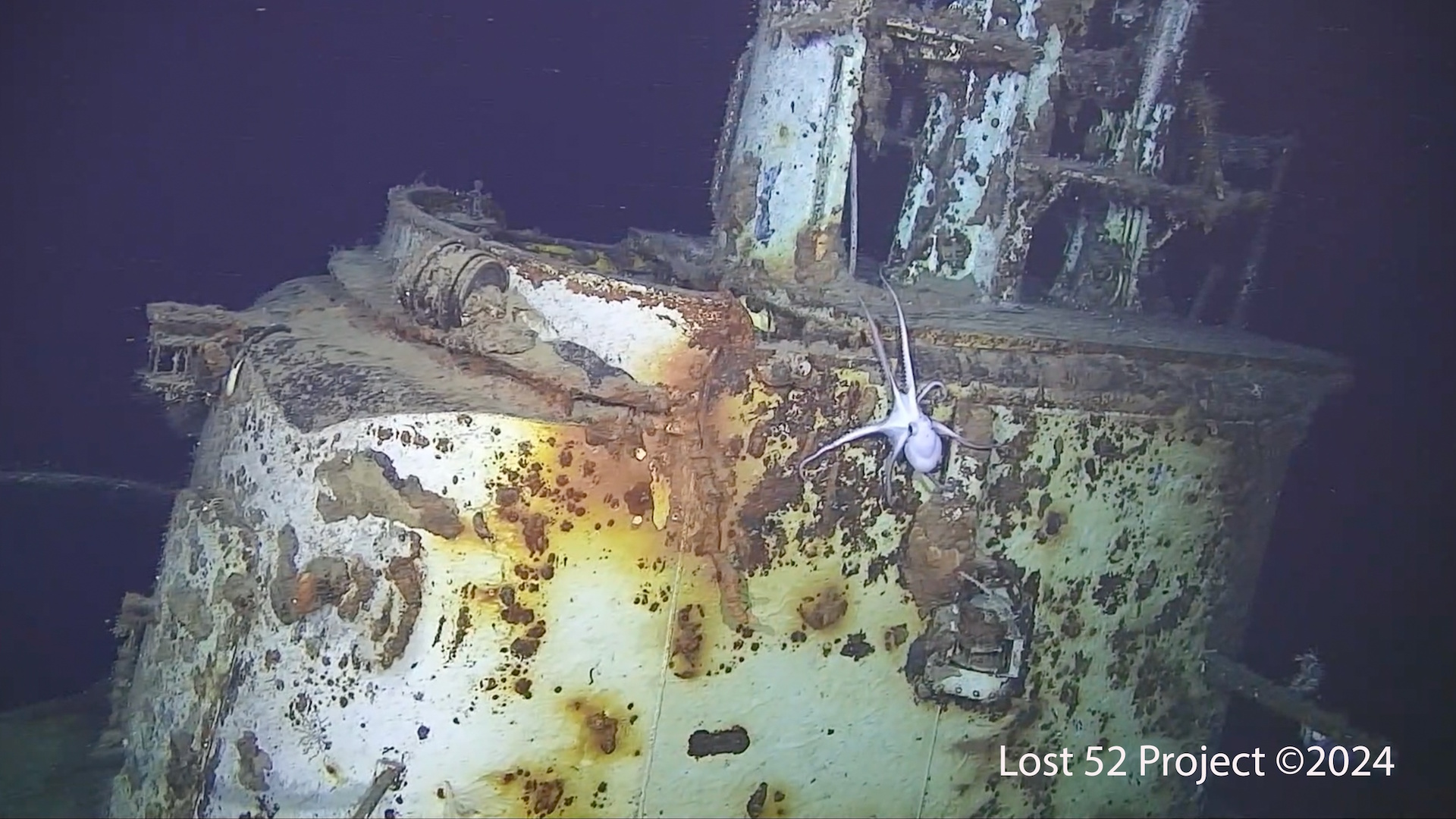

Shipwreck hunters have discovered the remains of a famous American submarine that sank with 79 crew on board while fighting a Japanese warship near the Philippines in 1944.
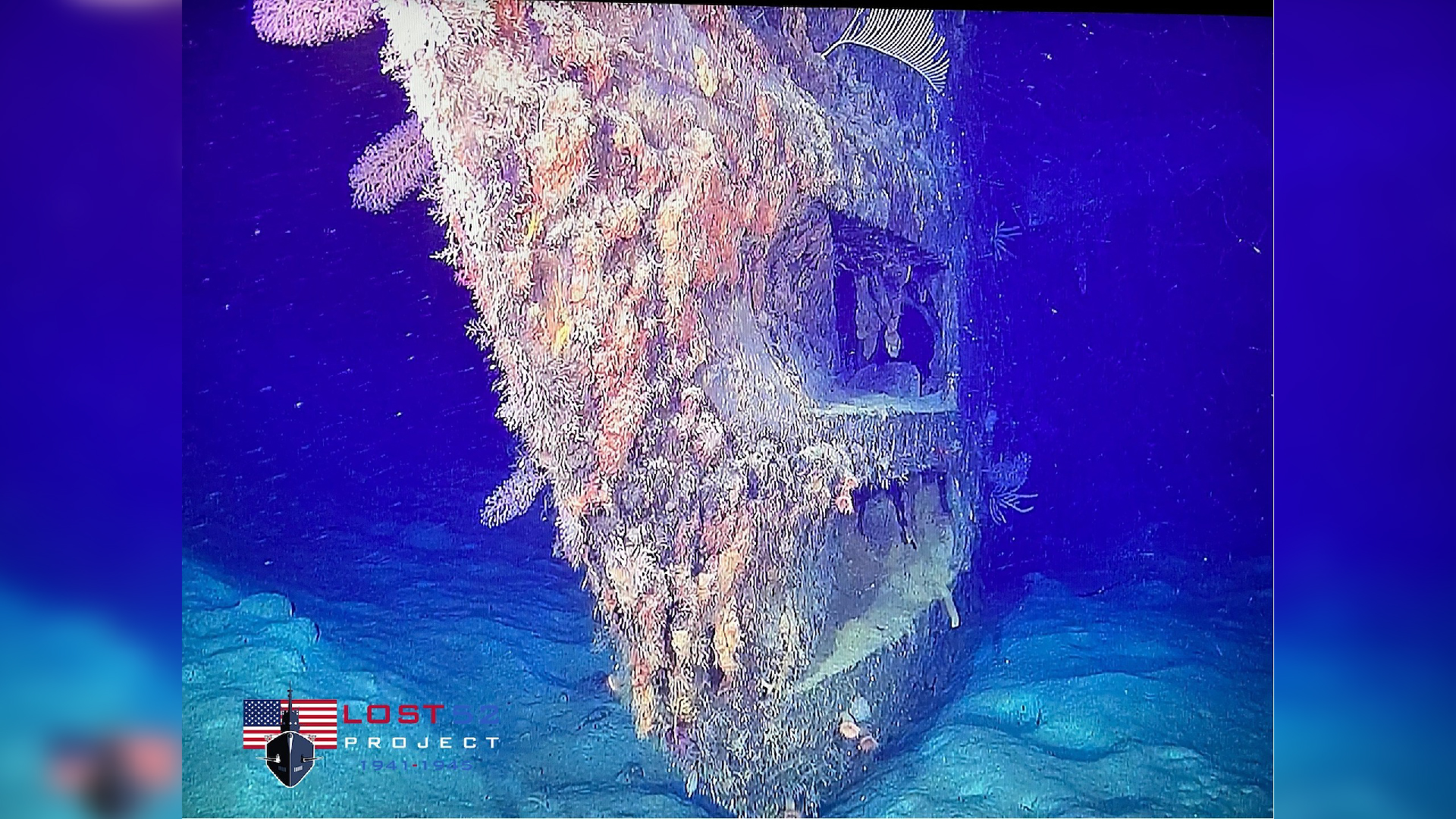
According to the New York-based Lost 52 Project, which made the discovery, the wreck of USS Harder now lies on its keel on the bottom of the South China Sea near the northern Philippine island of Luzon at a depth of around 3,750 feet (1,140 meters).
Naval reports of the sub's final mission say the Harder — a Gato-class sub named after a type of fish (the harder mullet) and nicknamed the "Hit 'Em Harder" — sank with all crew on Aug. 24, 1944 after it was heavily damaged by depth charges in a battle with a Japanese destroyer.
The Harder was one of the most famous American submarines of World War II. U.S. Navy records report that it torpedoed and sank five Japanese destroyers and several other enemy ships during six successful patrols in the Pacific war theater.
"This is one of the most celebrated WWII submarines and an historic naval discovery," Tim Taylor, the founder of the Lost 52 Project, told Live Science in an email.
Related: 30 incredible sunken wrecks from WWI and WWII
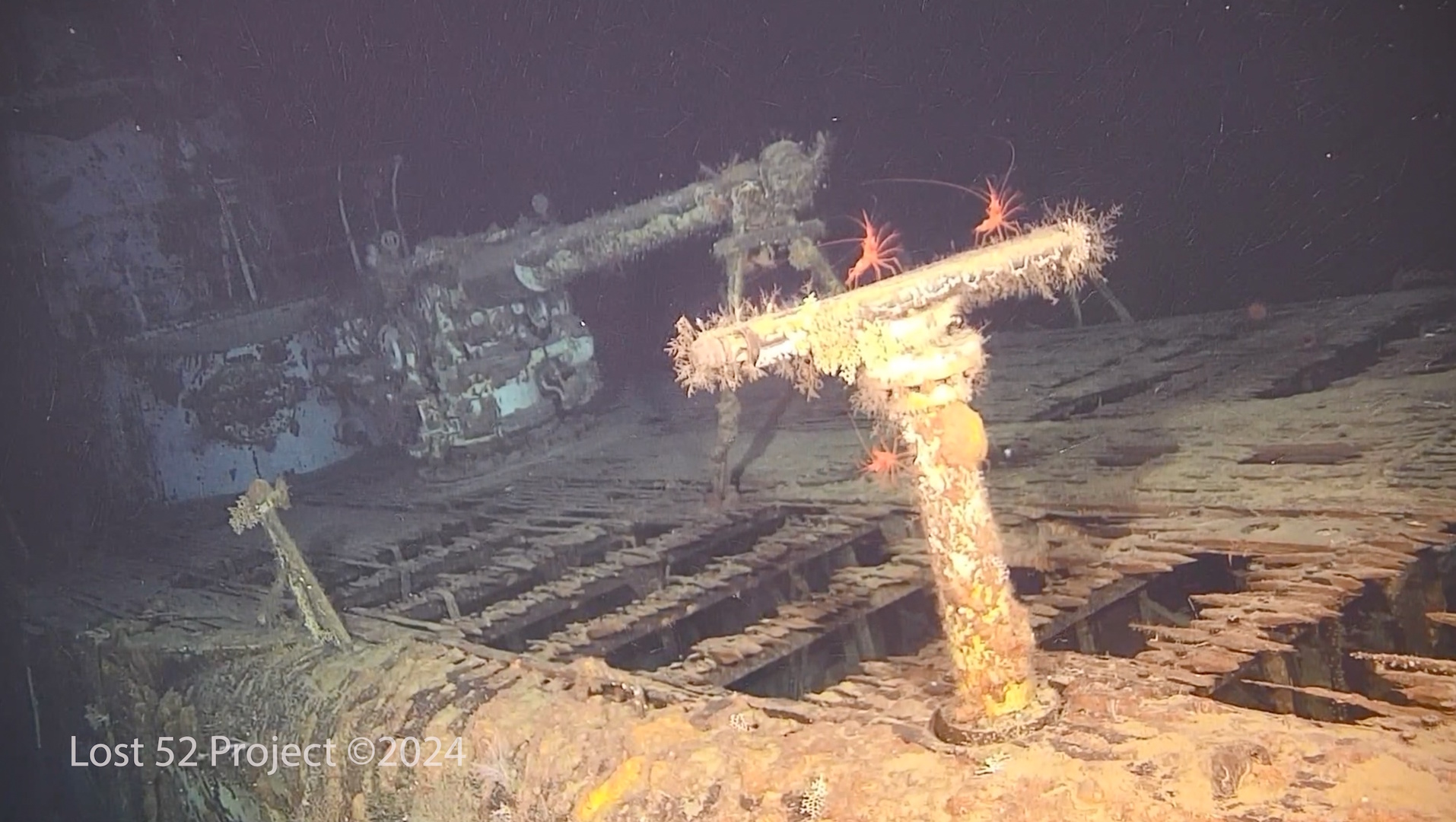
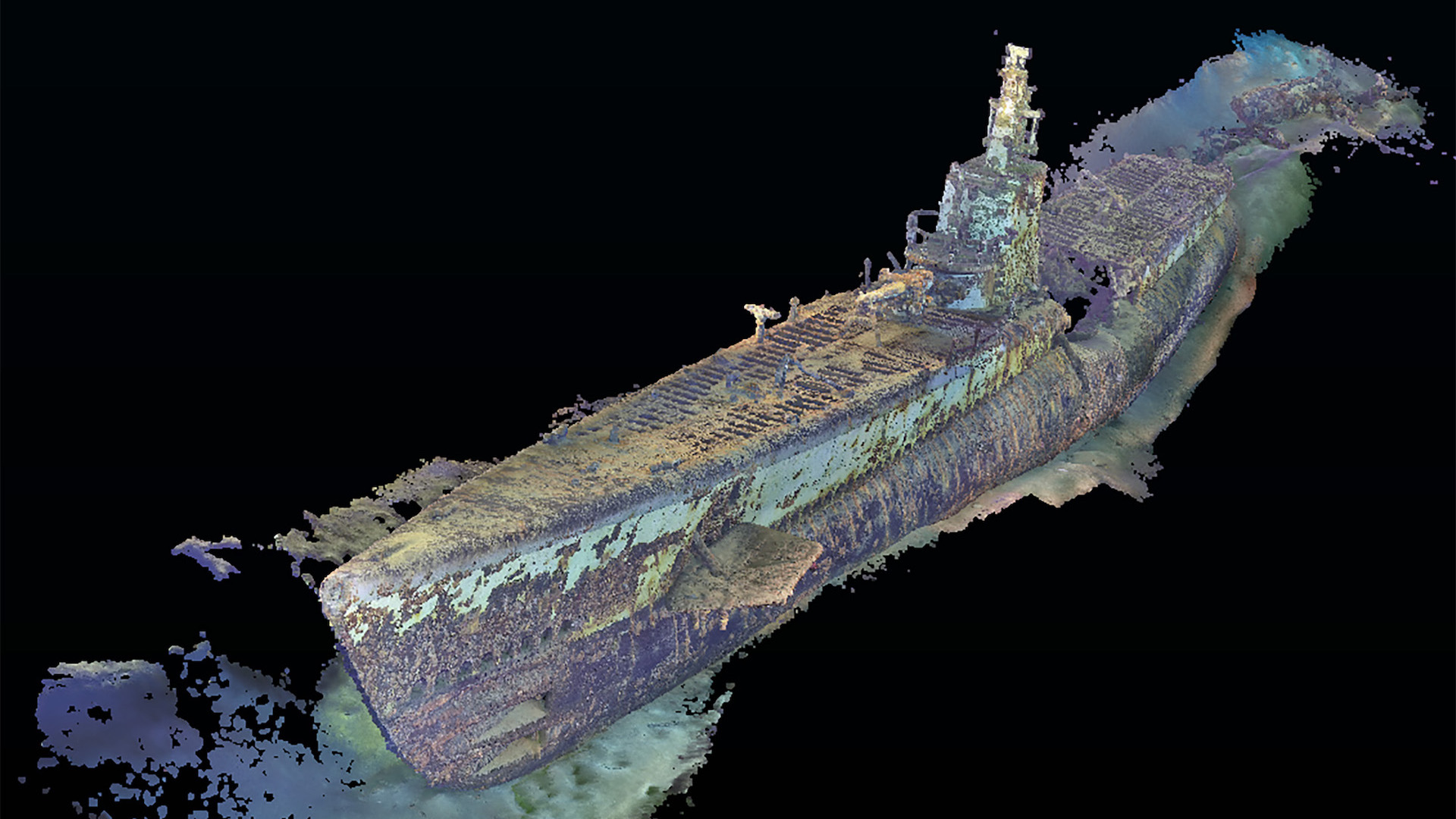


War grave
Taylor is the CEO of a company called Tiburon Subsea, which uses autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and other technologies to collect data at underwater sites. He also leads the Lost 52 Project, which aims to locate the wrecks of the 52 American submarines lost at sea during World War II and four lost during the Cold War.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The group has already located the wrecks of eight vessels, making the wreck of USS Harder their ninth discovery, Taylor said. Each of the underwater wrecks is also a war grave for the crewmembers who died when it sank, and the missing crew of the Harder were remembered for their service when the wreck was found.
"We have a protocol that, when we locate a submarine, we memorialize the crew," Taylor said. "We observe a minute of silence, ring the bell for every member of the crew and have a prayer service led by a deacon who is part of our expedition team."
The team located the wreck by studying reports of its final battle and then searching suitable areas with shipboard sonar, which can reveal objects on the seafloor, and AUVs, which can go much deeper than human divers.
But even after they take steps to make the search patterns as efficient as possible, "It is a long and arduous process, like looking for a needle in a haystack," Taylor said.
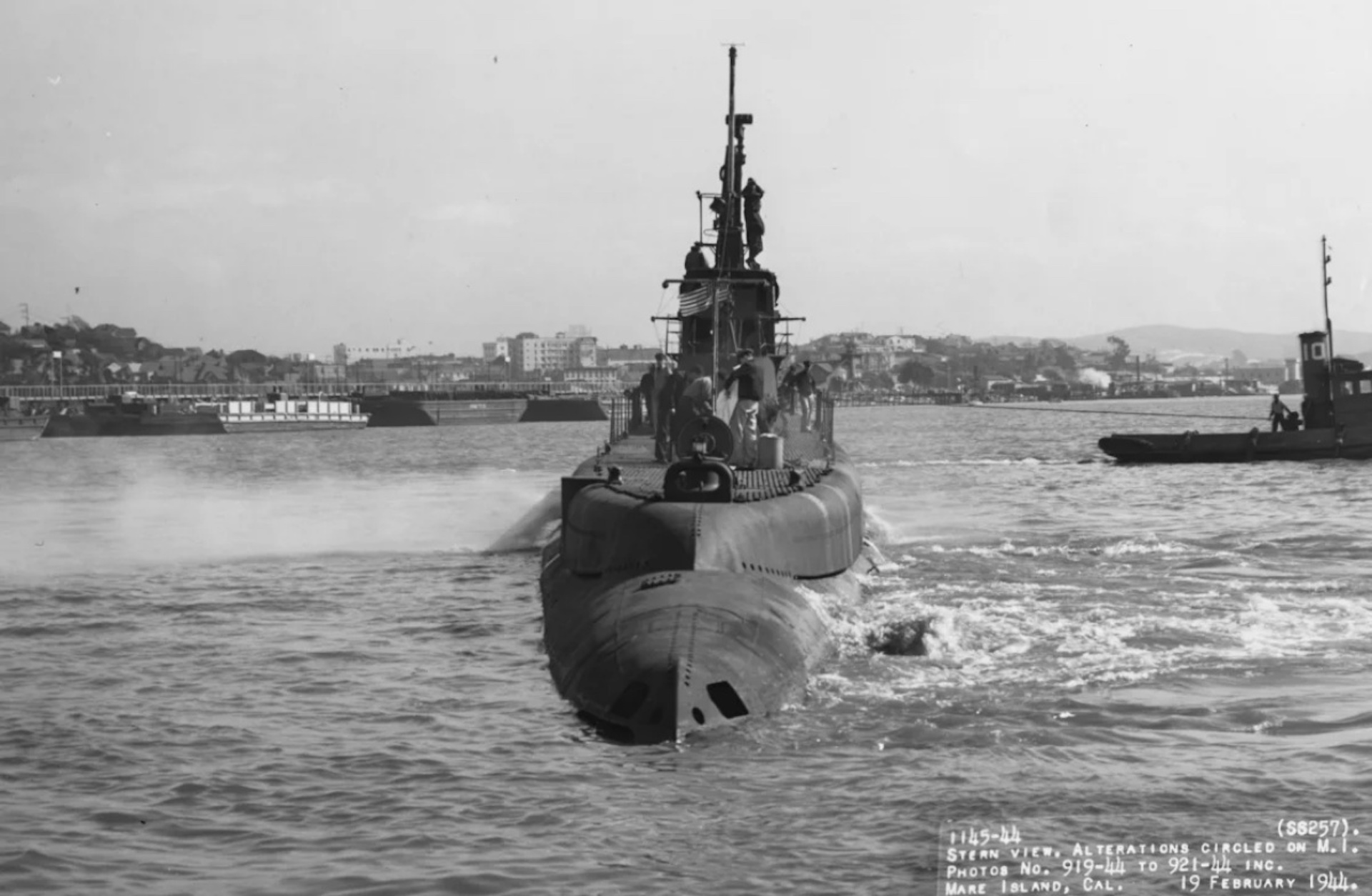

Sunken sub
The extreme depth of the wreck meant that AUV searches were essential, although a period of relatively good weather in recent weeks made the search easier.
The Harder wreck is too deep to be visited by divers, and the U.S. Navy has designated the wreck as a protected site. "The wreck represents the final resting place of sailors that gave their life in defense of the nation and should be respected by all parties as a war grave," the Navy said in a statement.
Taylor added that the AUV images show that the vessel appears to be in good condition. "The submarine is relatively intact, minus the damage done by the depth charges," he said.
And now, after 80 years under the waves, the wreck seems to be a thriving home for sea life, including an octopus that Taylor saw in the AUV images.
"It is a protected gravesite for 79 US WWII sailors, but there is a lot of life on the submarine," he said. "It's quite extraordinary."
Tom Metcalfe is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor who is based in London in the United Kingdom. Tom writes mainly about science, space, archaeology, the Earth and the oceans. He has also written for the BBC, NBC News, National Geographic, Scientific American, Air & Space, and many others.