
Emily Cooke
Emily is a health news writer based in London, United Kingdom. She holds a bachelor's degree in biology from Durham University and a master's degree in clinical and therapeutic neuroscience from Oxford University. She has worked in science communication, medical writing and as a local news reporter while undertaking NCTJ journalism training with News Associates. In 2018, she was named one of MHP Communications' 30 journalists to watch under 30. (emily.cooke@futurenet.com)
Latest articles by Emily Cooke

Science of sleep quiz: How much do you know about sleep and dreams?
By Nicoletta Lanese, Emily Cooke published
Test your knowledge of how sleeping and dreaming work.
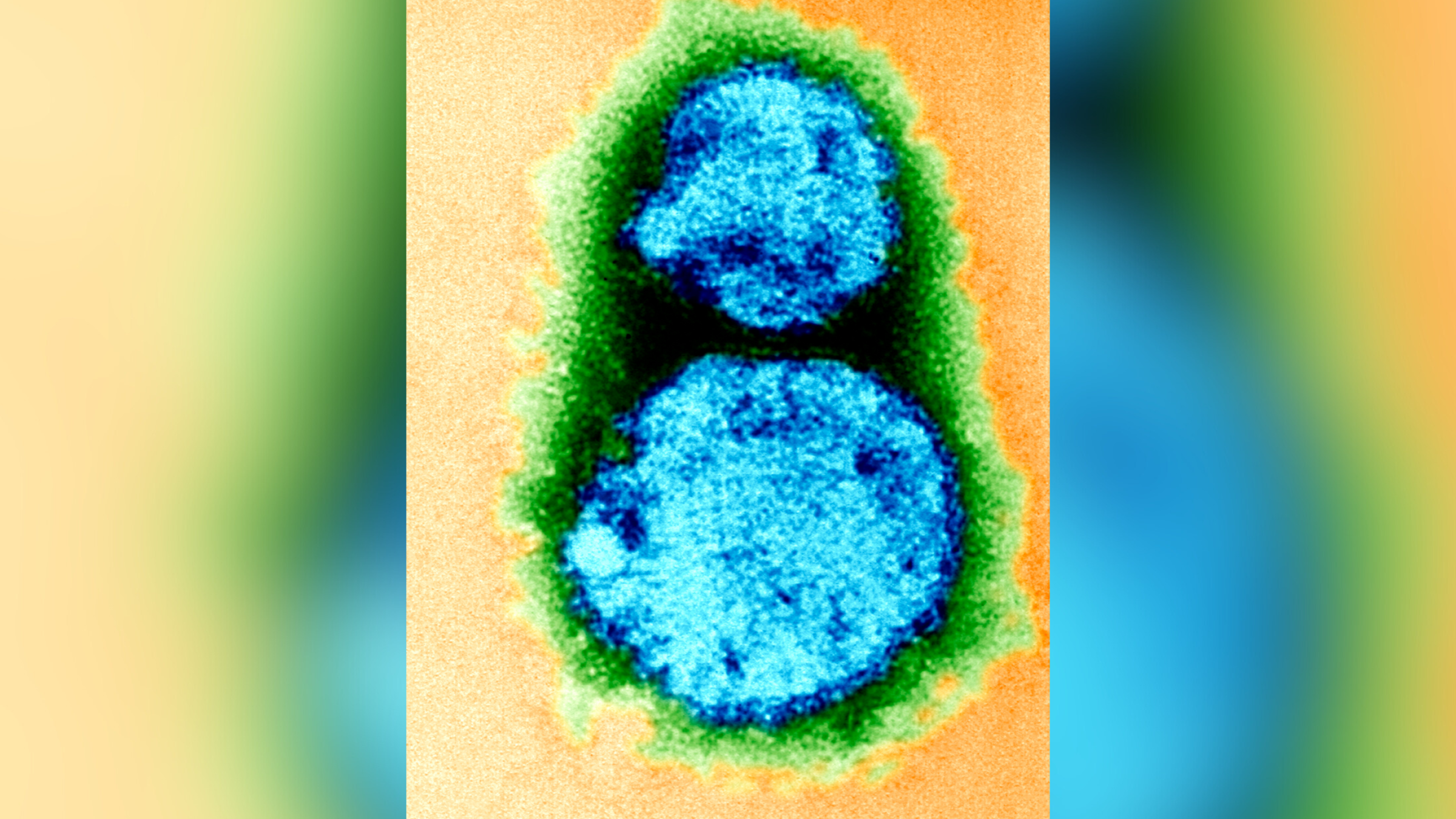
What is hantavirus? The rare but deadly respiratory illness spread by rodents
By Emily Cooke published
Hantaviruses are spread by rodents and can cause deadly respiratory and kidney illnesses in humans. It recently killed Betsy Arakawa, actor Gene Hackman's wife, in a widely covered case.

When will the US measles outbreak end?
By Emily Cooke published
A public health official in Texas recently warned that the state's ongoing measles outbreak could last a year. Why are cases expected to keep rising?

'Fingerprints of cancer' found after scientists flash infrared light pulses at blood samples
By Emily Cooke published
A new, AI-powered test can detect the molecular "fingerprints" of cancer in a patient's blood using flashes of infrared light.
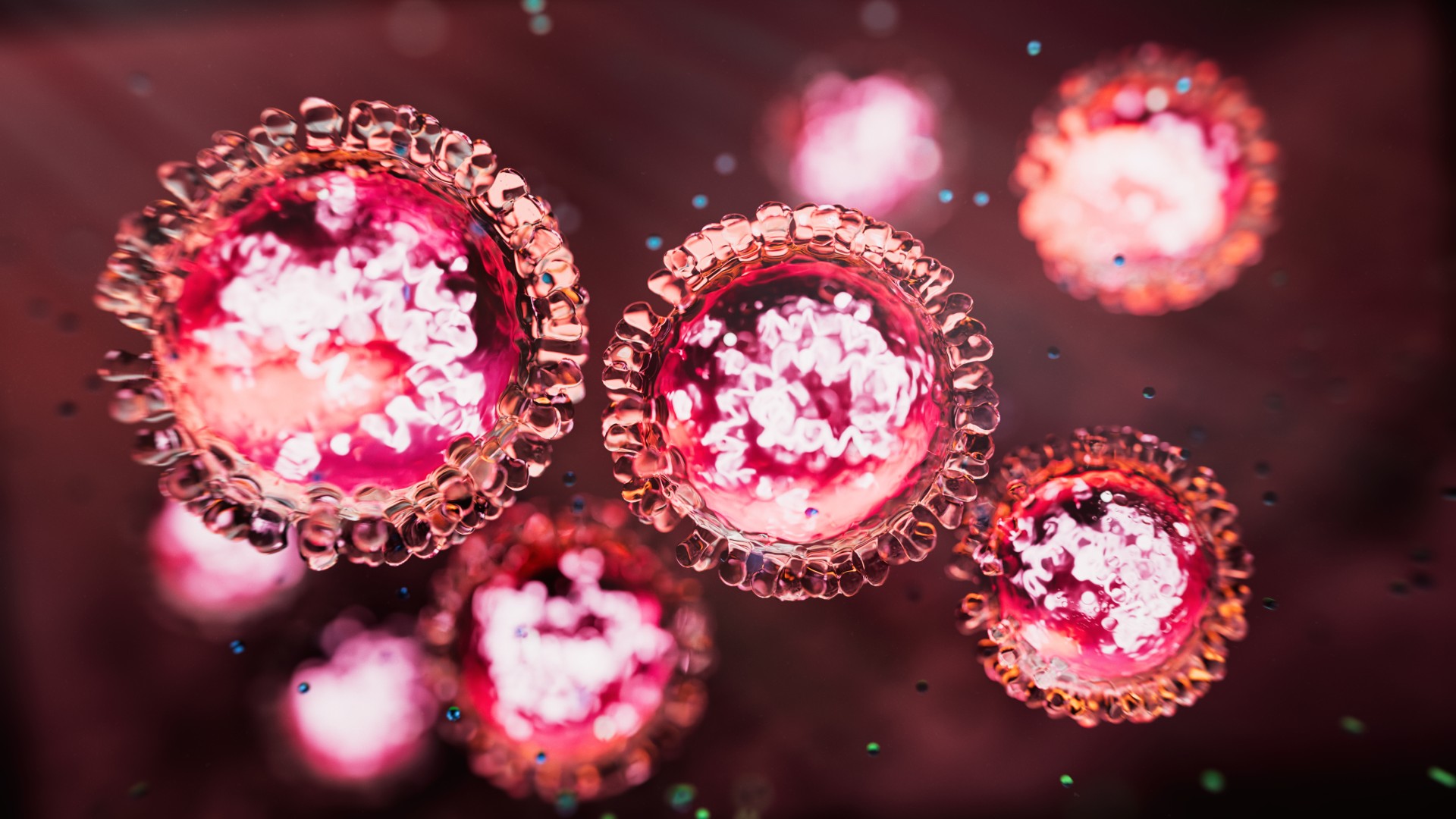
US measles outbreak tops 600 cases — what to know about the disease
By Emily Cooke last updated
As measles outbreaks in the U.S. continue, here's what to know about how the disease spreads, what its symptoms are, and how to protect yourself and community from the illness.

$3 million Breakthrough Prize awarded to developers of Ozempic-style drugs
By Emily Cooke published
Five researchers have been jointly awarded one of this year's Breakthrough Prizes in Life Sciences for their contributions to the development of Ozempic-style drugs.

Drug makes blood toxic to malaria-spreading mosquitoes
By Emily Cooke published
Nitisinone, a drug that is already used to treat two genetic diseases, could be repurposed to control the spread of malaria, according to new research.

This rare bacterial infection triggers pus-filled sores in the lungs and brain
By Emily Cooke published
Nocardiosis is a rare bacterial infection that attacks the lungs, skin and brain.

Staring at the March 29 solar eclipse can cause eye damage in seconds — and you won’t even feel it happening
By Emily Cooke published
Experts explain damage that can happen to your eyes if you stare at the partial eclipse without using adequate protection.

New cells discovered in eye could help restore vision, scientists say
By Emily Cooke published
A new study suggests that never-seen-before stem cells in the human retina can restore vision in mice with a common eye disorder. But more work is needed to translate the treatment to people.

'Fish odor syndrome': A rare metabolic condition that makes sweat smell like rotten fish
By Emily Cooke published
Patients with trimethylaminuria, or "fish odor syndrome," make too much of a chemical with a strong fishy smell.

HIV-funding cuts could lead to nearly 3 million extra deaths by 2030, study suggests
By Nicoletta Lanese, Emily Cooke published
A modeling study looked at how anticipated cuts to international HIV funding would affect the rate of new cases and HIV-related deaths in low- and middle-income countries.

Why don't we remember being babies?
By Benjamin Shouse, Emily Cooke last updated
The inability to remember your first few years of life is called infantile amnesia. But why does it happen?

In a 1st, trial finds vitamin D supplements may slow multiple sclerosis. But questions remain.
By Emily Cooke published
A new clinical trial has shown for the first time that taking high doses of vitamin D could stave off the progression of multiple sclerosis. However, much more research is warranted to confirm these findings.

Simple blood tests could be the future of cancer diagnosis
By Emily Cooke published
Blood tests that detect early cancer are coming to market. Could they lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment?

What is babesiosis? The parasitic infection that 'eats' your red blood cells
By Emily Cooke published
Most people exposed to the parasites behind babesiosis don't get sick, but for others, the infection can be deadly.
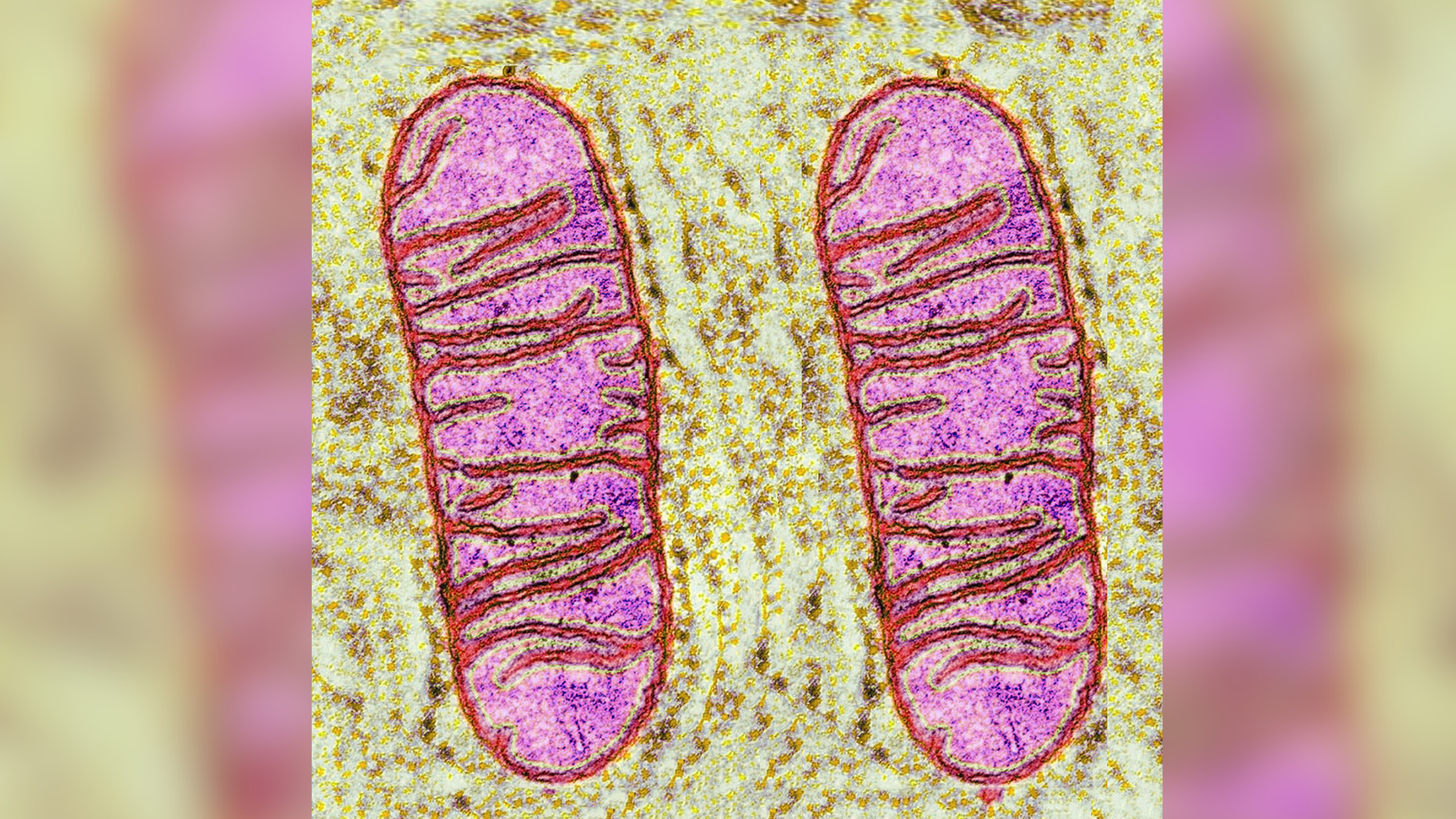
POLG diseases: Rare genetic conditions that starve cells of energy and afflicted the late Prince of Luxembourg
By Emily Cooke published
POLG-related diseases disrupt the function of the mitochondria, or "powerhouses" of the cell — starving them of energy.

Diagnostic dilemma: Growing weed with bat poop left 2 men with deadly infections
By Emily Cooke published
Using bat poop to fertilize plants like cannabis can sometimes have deadly consequences. A report highlights two fatal cases that affected men in New York.

East Asians who can digest lactose can thank Neanderthal genes
By Emily Cooke published
Unique versions of the lactase gene found in the genomes of East Asian people may have increased in prevalence within the population over time because they bolstered immune responses against pathogens, new data reveal.

When is cancer considered cured, versus in remission?
By Emily Cooke published
Experts explain the difference between what it means to experience cancer remission versus being cured of the disease.
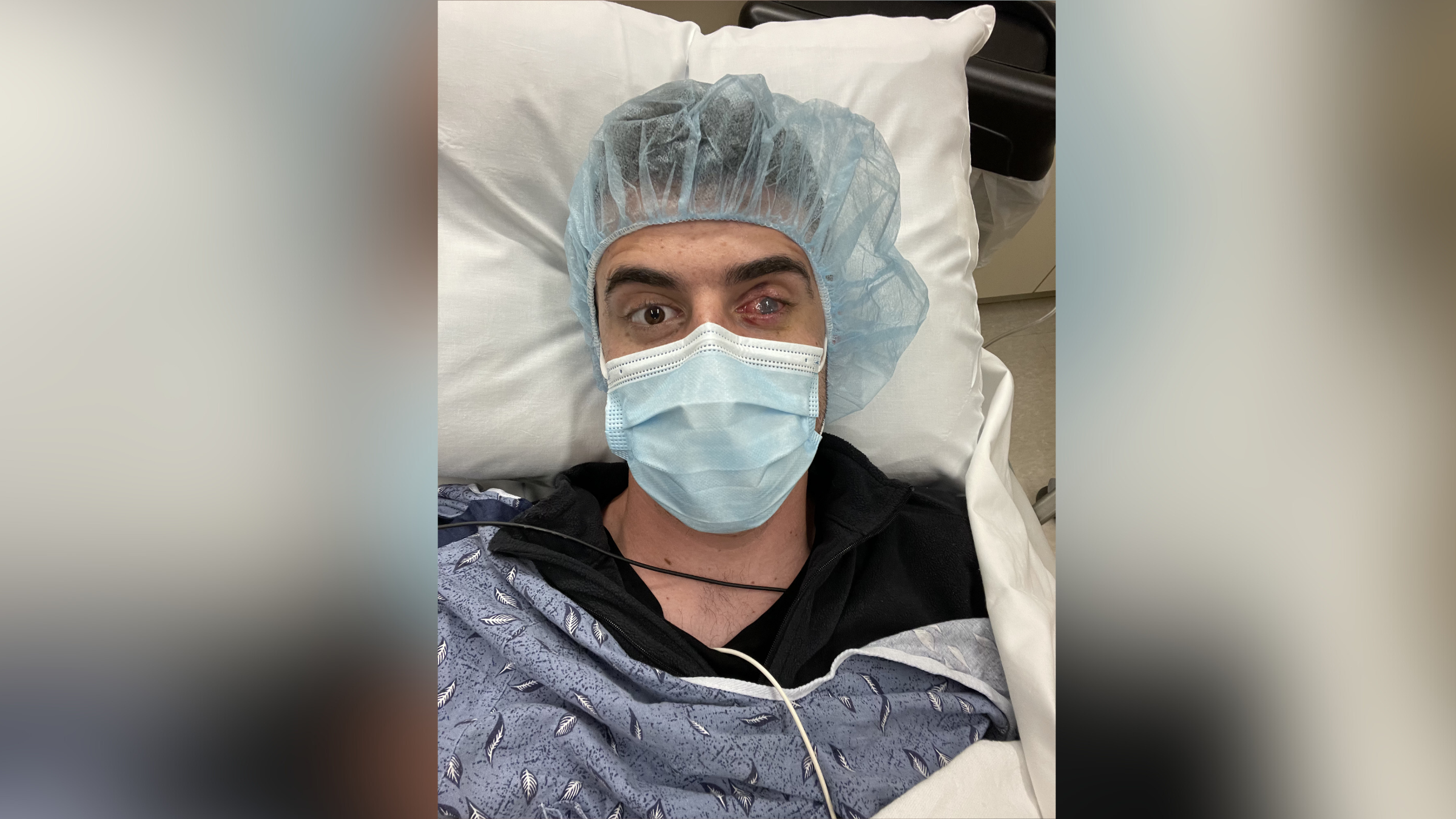
'In that moment, that was everything to me': Patient describes joy of regaining vision in 1 eye after new stem cell therapy
By Emily Cooke published
A first-of-its-kind stem cell transplant has changed the life of a man who was left blind in one eye following a firework accident.
The rare genetic disorder that causes severe itchiness and liver failure
By Emily Cooke published
Patients with PFIC develop liver failure as a result of a buildup of a digestive fluid known as bile.
CDC data reveal plummeting rate of cervical precancers in young US women — down by 80%
By Emily Cooke published
New CDC data on falling rates of precancerous cervical lesions in the U.S. underscore the benefits of HPV vaccination.

New stem cell therapy could repair 'irreversible' and blinding eye damage, trial finds
By Emily Cooke published
A new therapy repairs corneal damage to a patient's eye using stem cells from their other, healthy eye.

Scientists discover never-before-seen type of brain cell
By Emily Cooke published
A new study has pinpointed cells in the brains of mice that have the unique ability to proliferate and may help to repair damaged tissue. Scientists now need to determine if similar cells exist in human brains.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
