Emily Cooke
Emily is a health news writer based in London, United Kingdom. She holds a bachelor's degree in biology from Durham University and a master's degree in clinical and therapeutic neuroscience from Oxford University. She has worked in science communication, medical writing and as a local news reporter while undertaking NCTJ journalism training with News Associates. In 2018, she was named one of MHP Communications' 30 journalists to watch under 30. (emily.cooke@futurenet.com)
Latest articles by Emily Cooke
Deadly amoeba brain infection can result from unsafe nasal rinsing, CDC warns
By Emily Cooke published
A CDC report describes 10 patients infected by an amoeba after conducting a nasal rinse, three of whom died from a nervous-system infection.
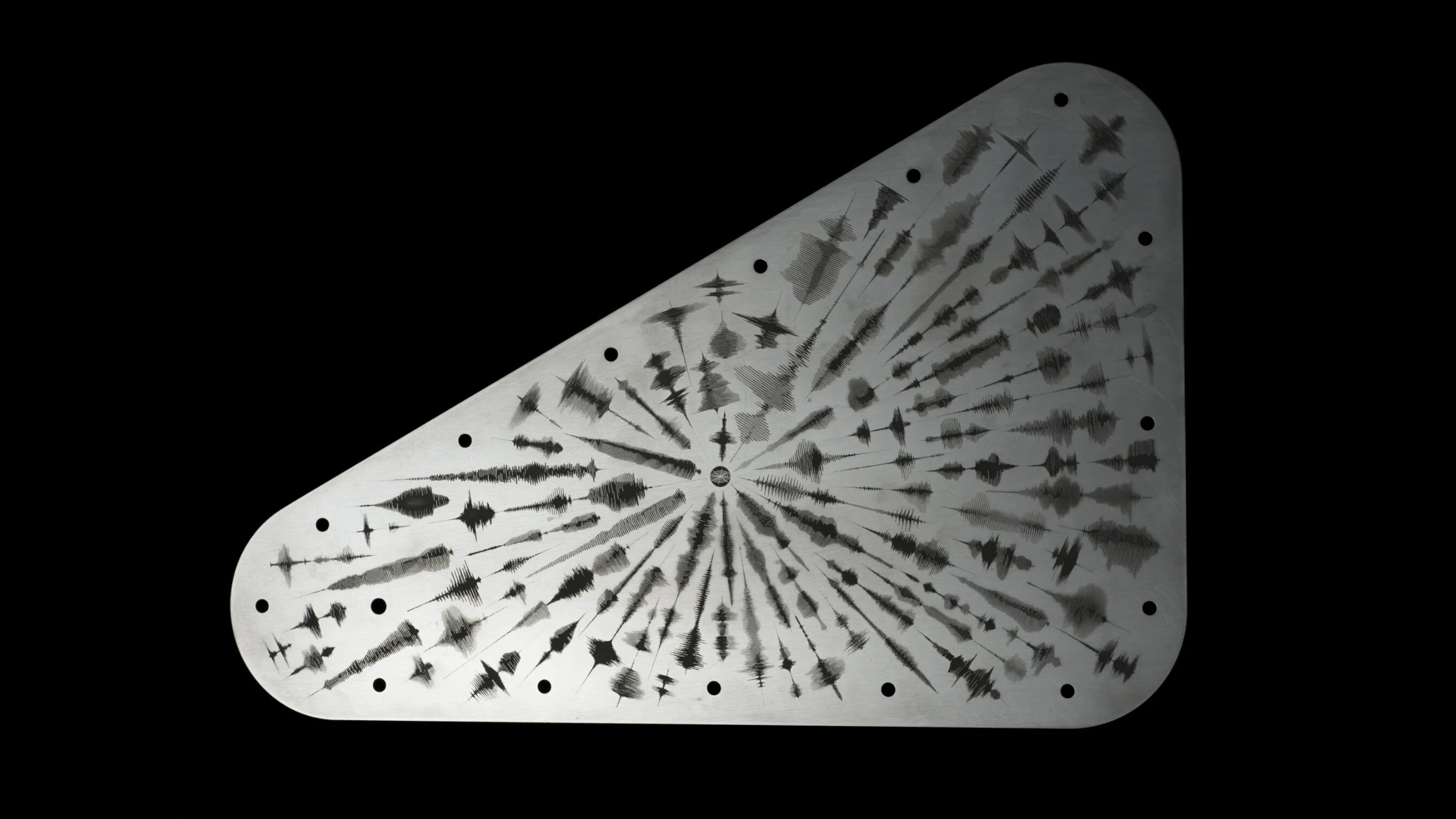
NASA unveils cryptic message from Earth to be sent to Jupiter's icy ocean moon Europa
By Emily Cooke published
From a poem written by a U.S. Poet Laureate to millions of stenciled names, NASA's Clipper spacecraft's trip to Europa will be marked with a human touch.
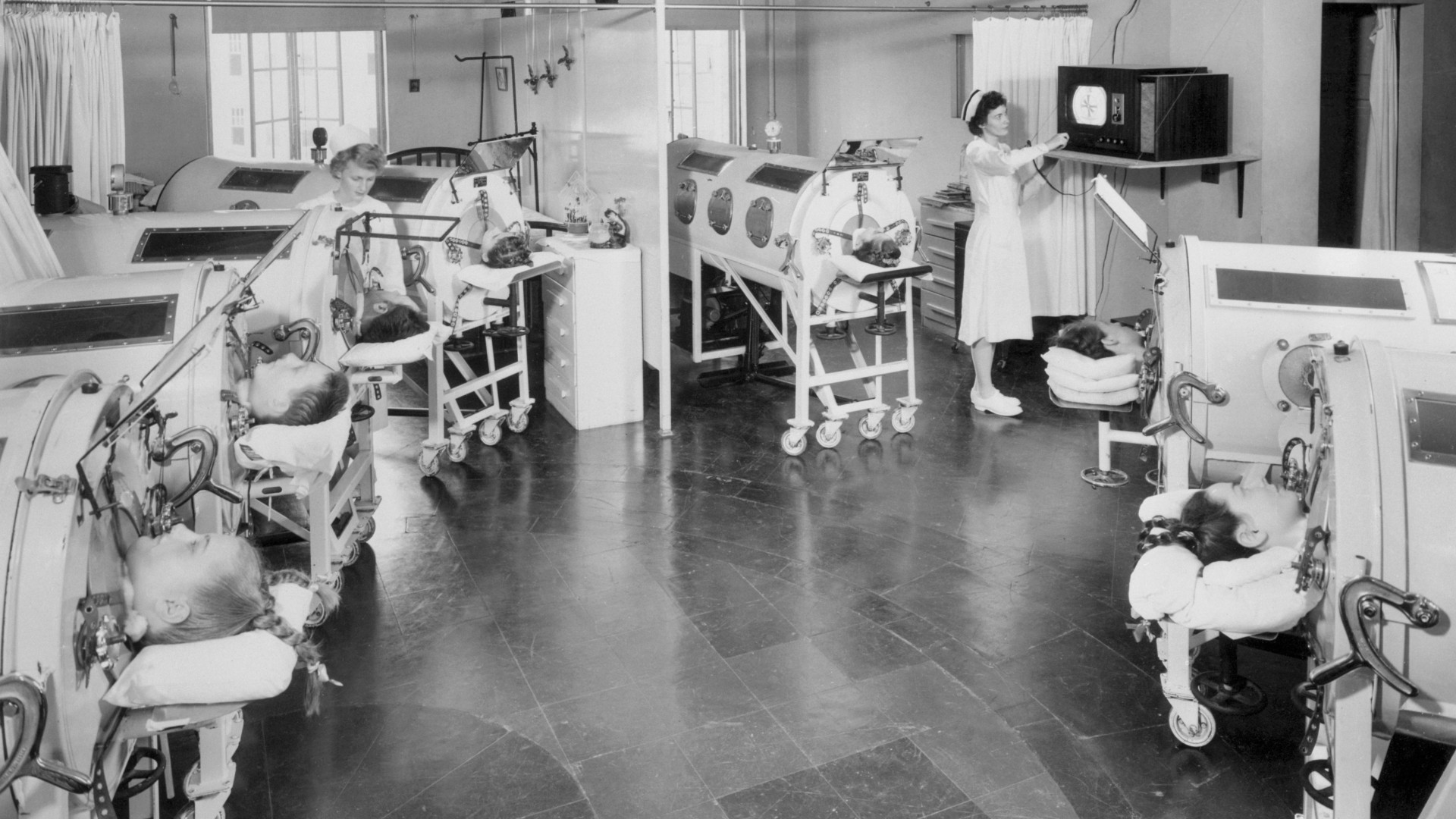
Paul Alexander, polio survivor who lived in iron lung for 70 years, dies age 78
By Emily Cooke published
Paul Alexander was one of the last people to use an iron lung, having been left unable to breathe on his own after catching polio in the 1950s.

Every 2.4 million years, Mars tugs on Earth so hard it changes the ocean floor
By Emily Cooke published
A new geological study suggests that Mars' gravitational field pulls the Earth closer to the sun over cycles lasting millions of years, warming our climate.
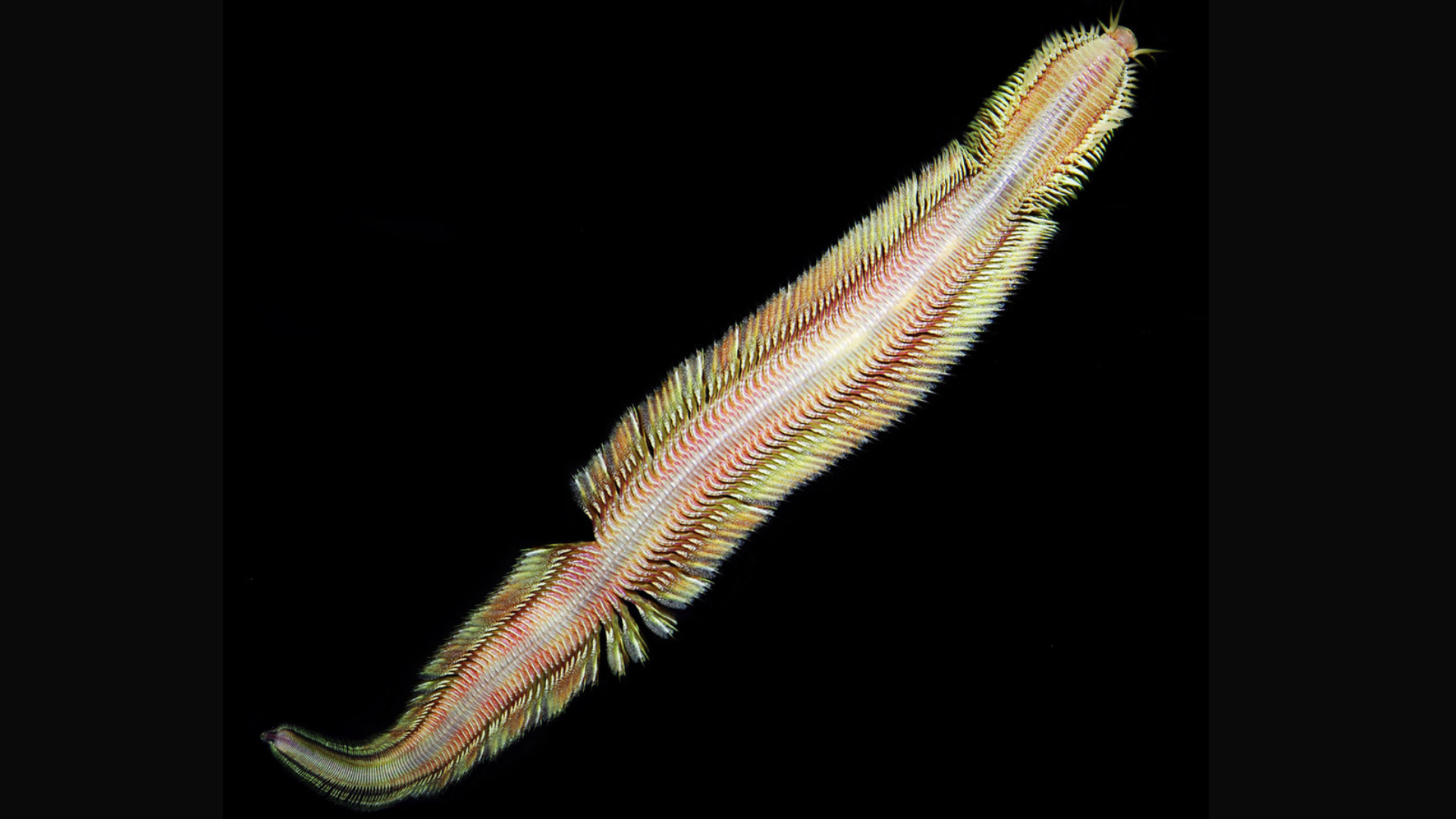

Technicolor 'living magic carpet' deep-sea worm discovered near methane seep off Costa Rica
By Emily Cooke published
The rosy-colored, segmented worms appeared to swim through water like a "living magic carpet," scientists say.
300 people possibly exposed to measles at California hospital
By Emily Cooke published
Officials are trying to contact around 300 people who may have been exposed to measles at the UC Davis Medical Center Emergency Department on March 5, when an infected child was treated there.
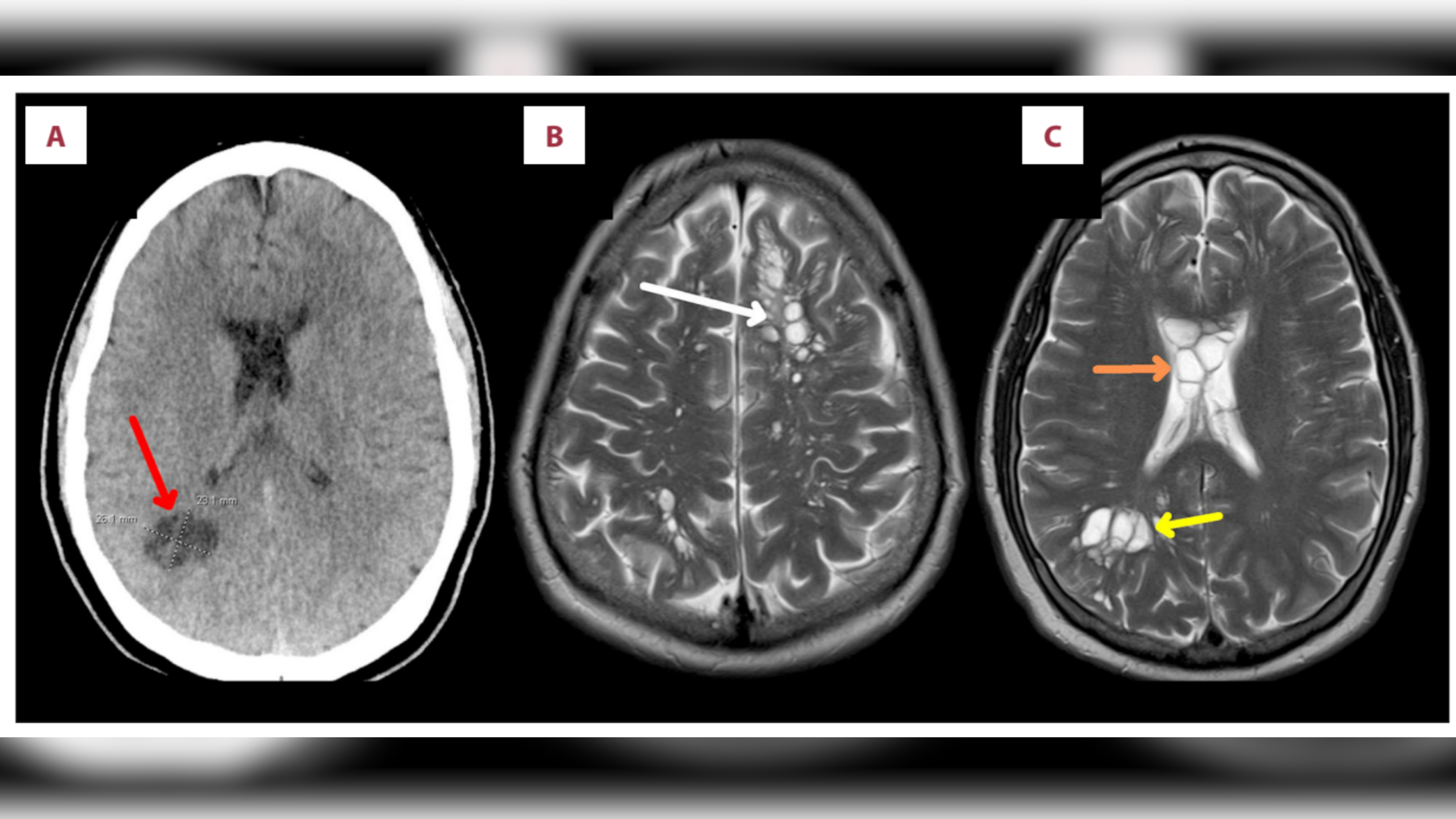
Parasitic worms found in man's brain after he likely ate undercooked bacon
By Emily Cooke published
A middle-aged man in the U.S. developed a parasitic infection in his brain after eating undercooked bacon.

India's evolutionary past tied to huge migration 50,000 years ago and to now-extinct human relatives
By Emily Cooke published
Modern Indians inherited genes from what is now Tajikistan and a diverse set of DNA from Neanderthals and Denisovans, new research reveals.
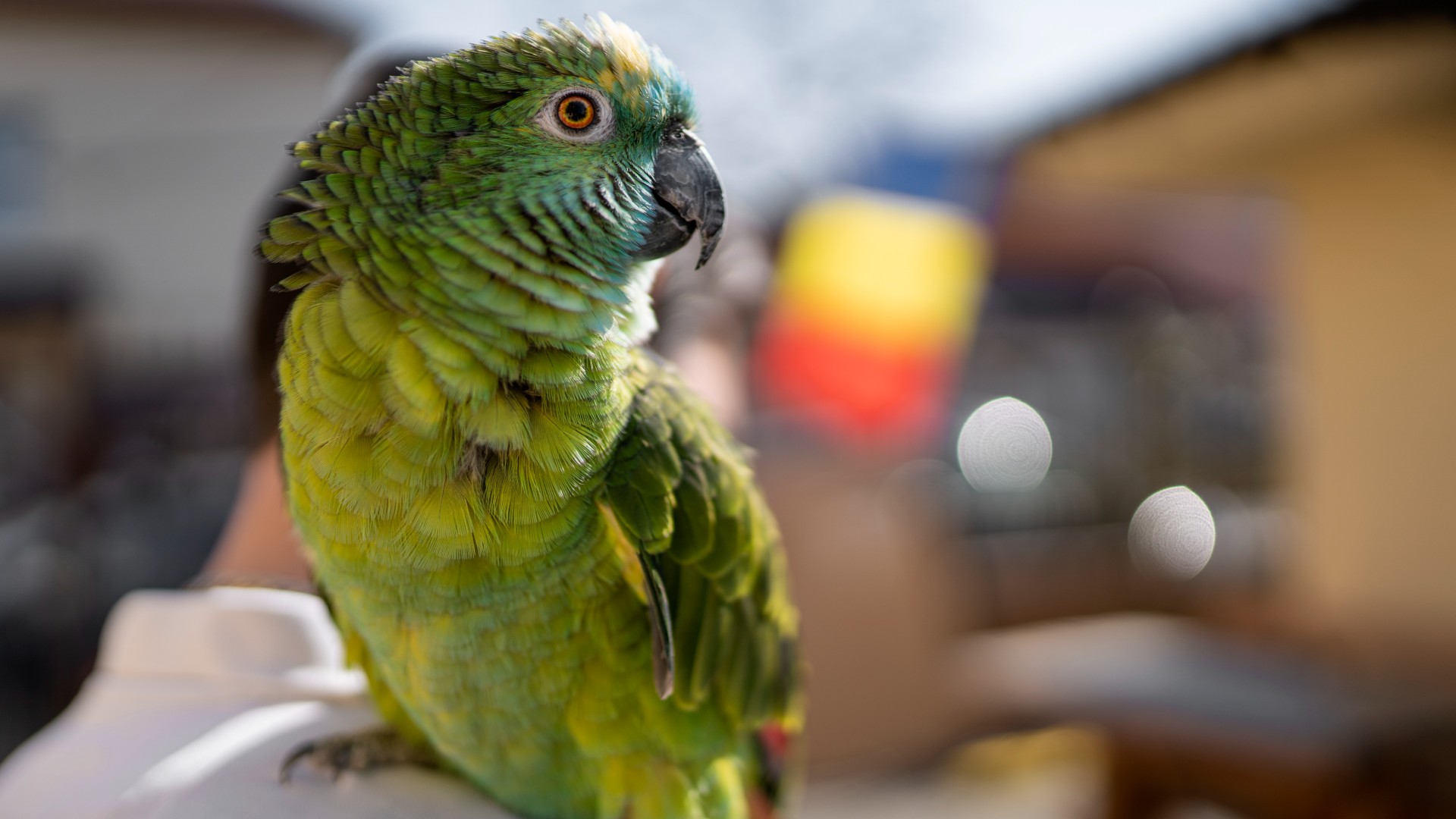

'Parrot fever' outbreak in 5 European countries kills 5 people
By Emily Cooke published
Most people involved in the current parrot fever outbreak developed the disease after being exposed to infected wild or pet birds, the WHO said.
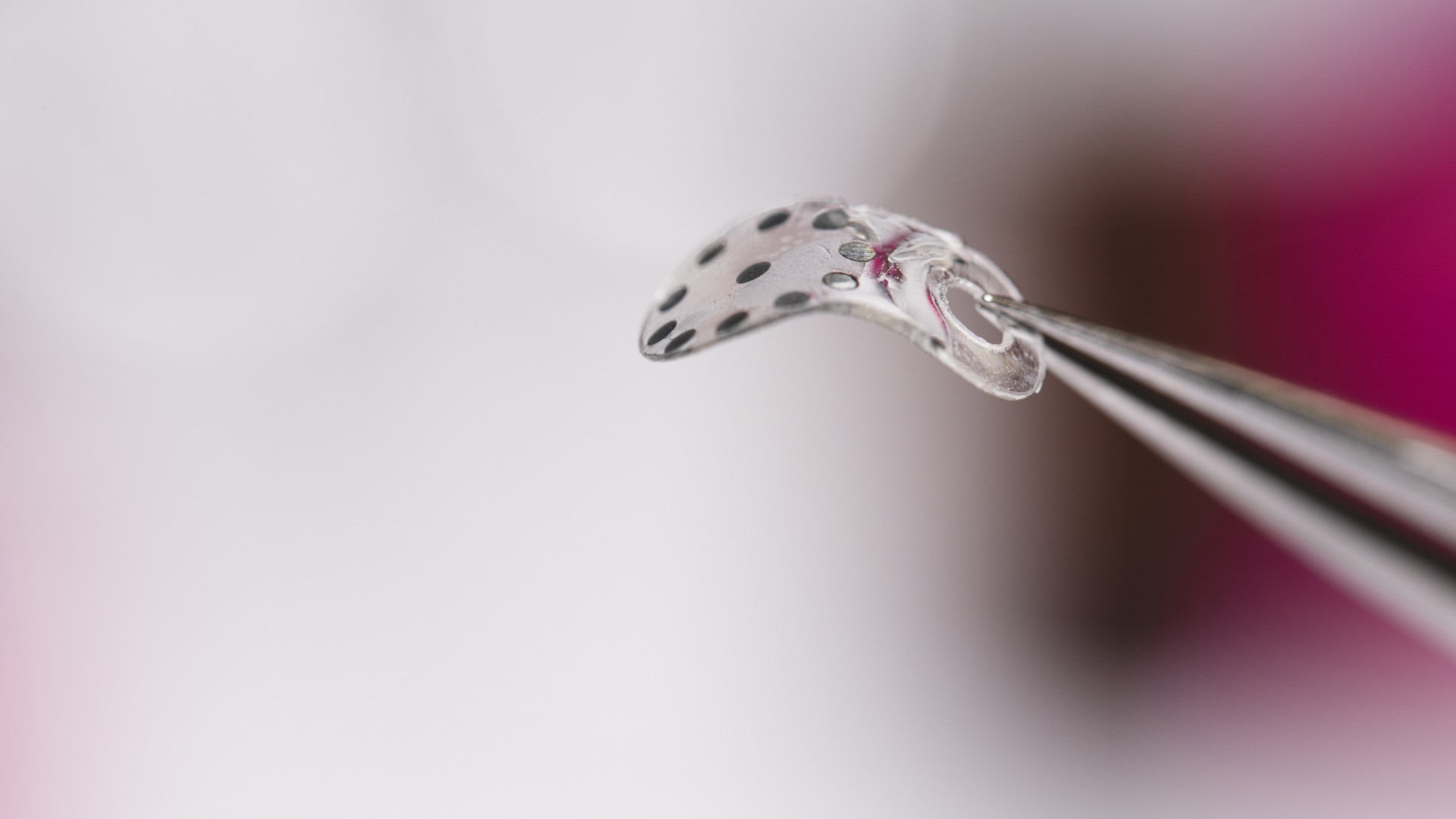

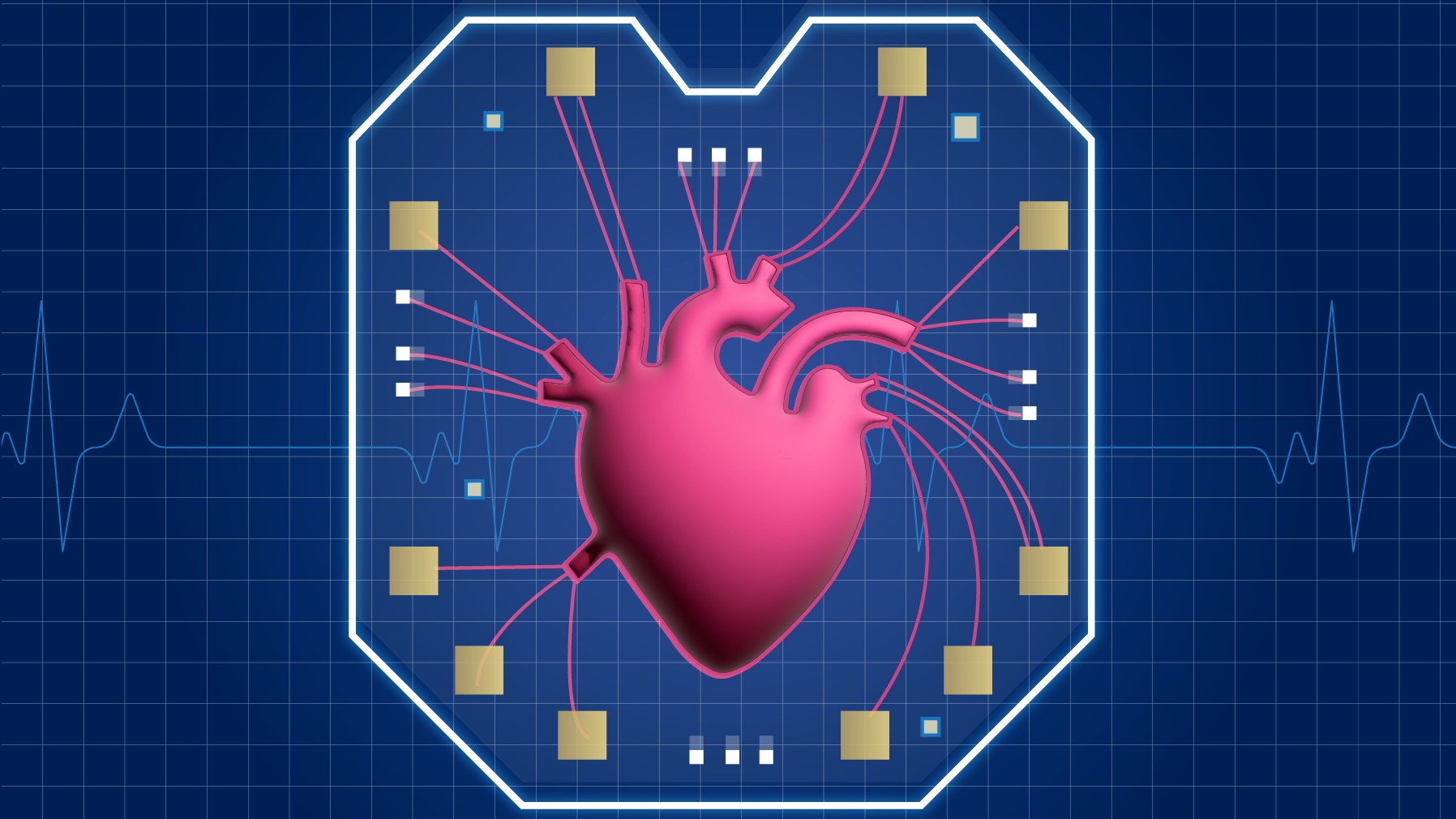
Life-threatening 'leaks' after surgery could be flagged faster with tiny new device
By Emily Cooke published
A new implantable device, so far tested in rats and pigs, could soon be trialed in humans to help detect harmful post-surgery leaks in the body.

PFAS 'forever chemicals' to officially be removed from food packaging, FDA says
By Emily Cooke published
New food packaging products sold in the U.S., such as takeout boxes and fast-food wrappers, will no longer contain harmful "forever chemicals" known as PFAS.
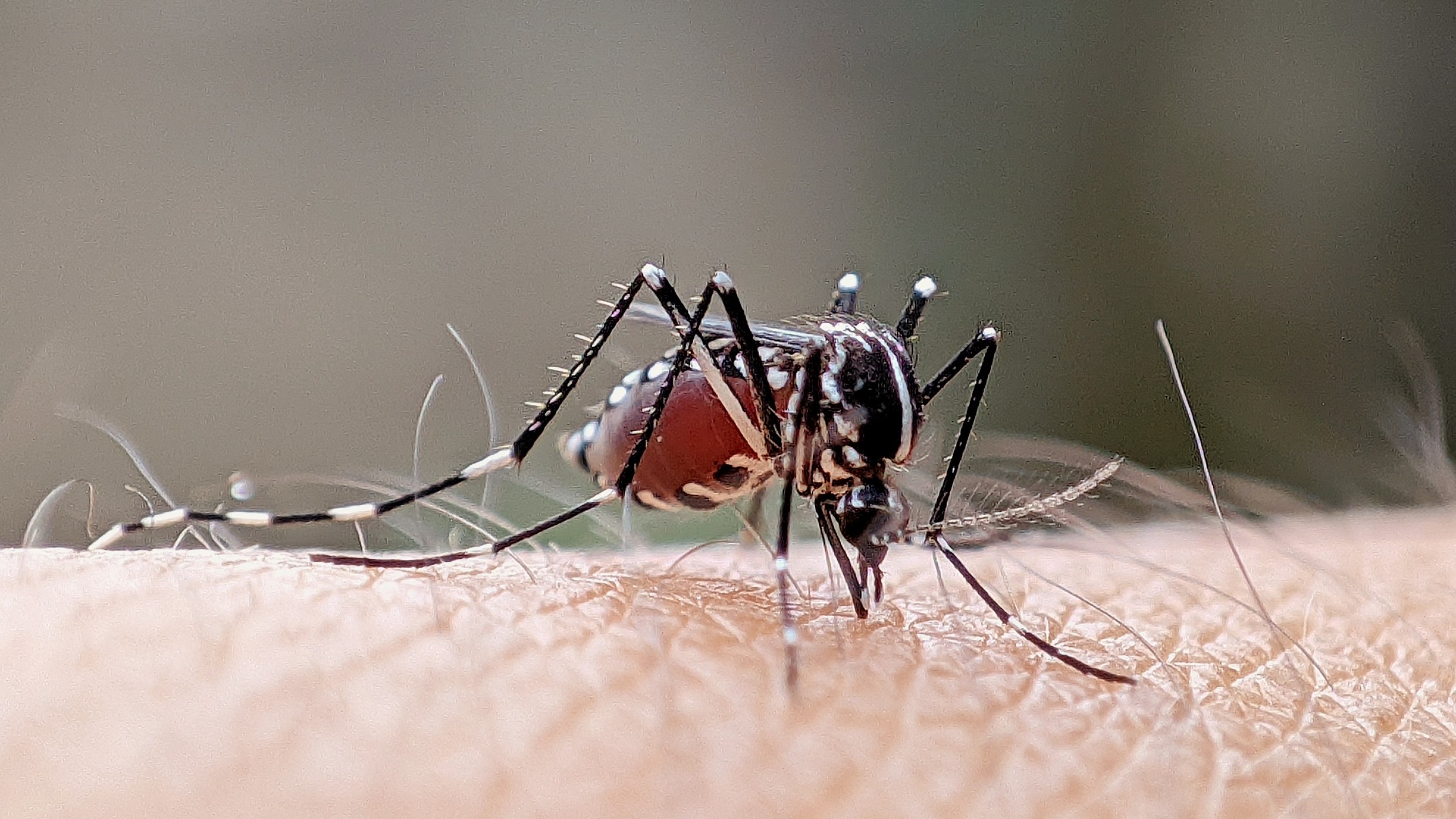
Scientists release genetically modified mosquitoes to fight dengue in Brazil
By Emily Cooke published
Genetically modified mosquitoes are being released in Brazil to reduce the spread of the viral infection dengue fever.
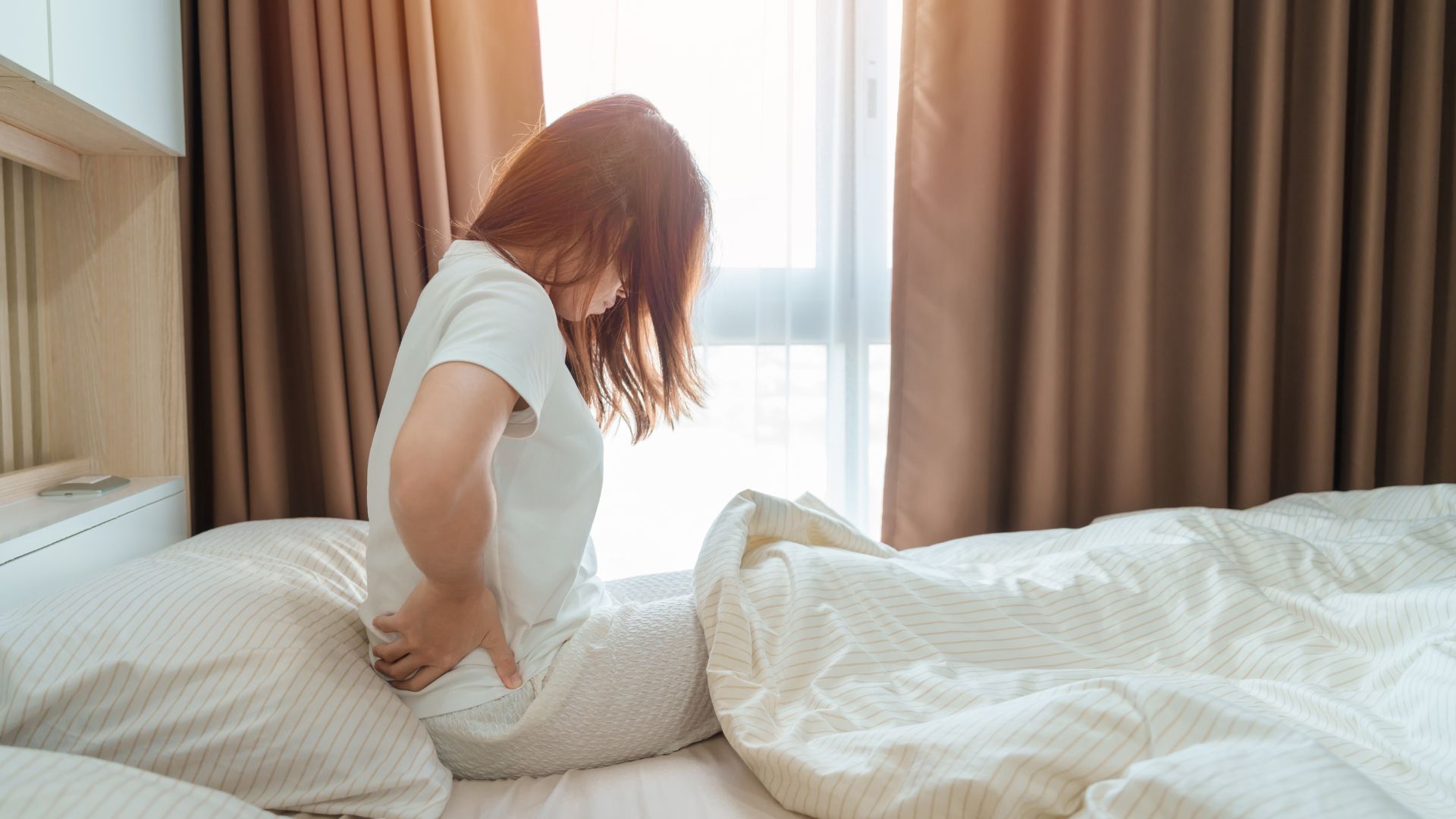

Pain can linger even after a UTI is gone — haywire nerve growth may explain it
By Emily Cooke published
A new study in mice and human tissue samples suggests that UTI symptoms may persist after the infection has been treated due to an overgrowth of neurons in the bladder.
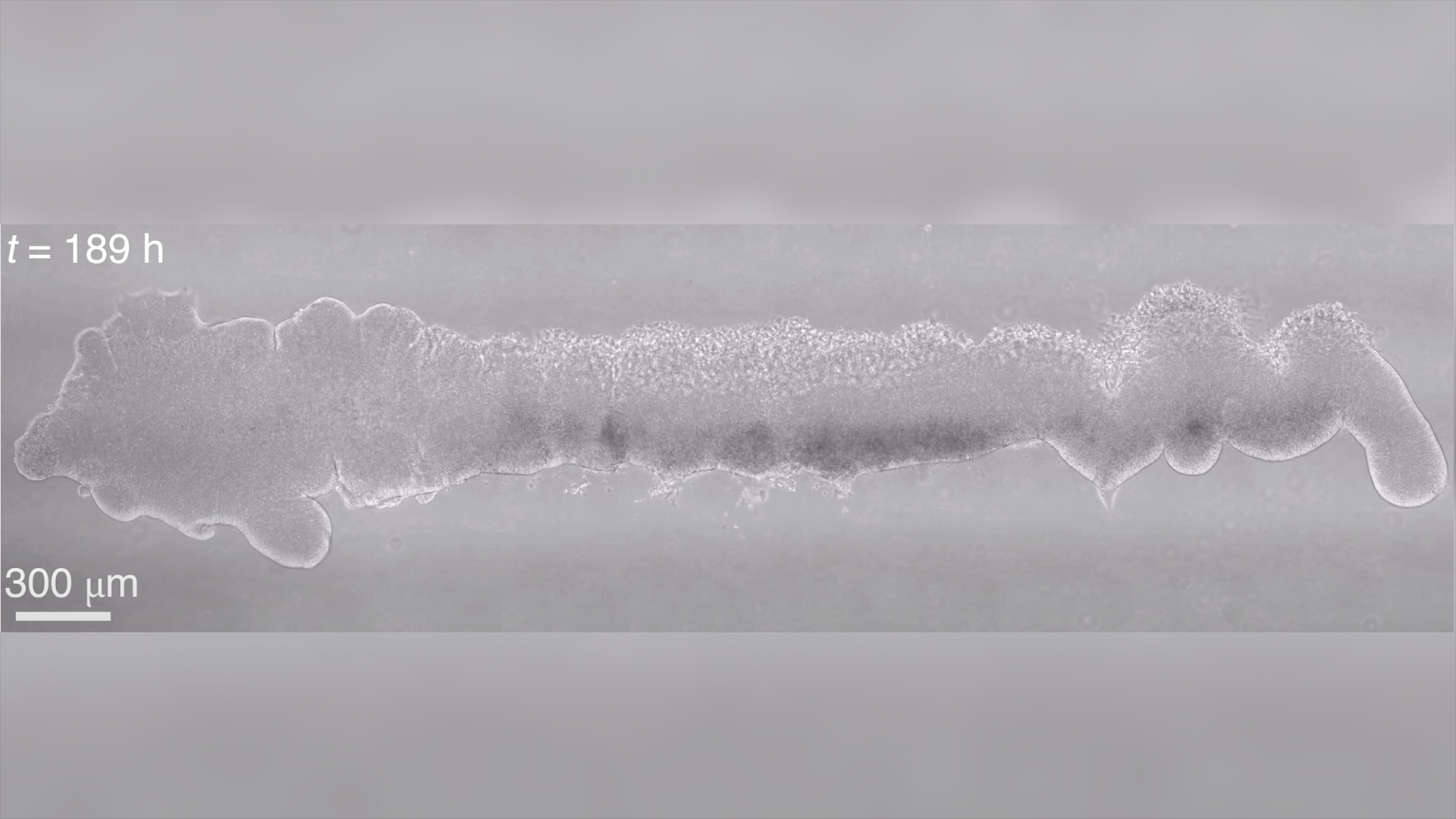
Mini model of human embryonic brain and spinal cord grown in lab
By Emily Cooke published
The new organoids were grown in the lab for up to 40 days, and they mimicked the central nervous system of an 11-week-old human embryo.
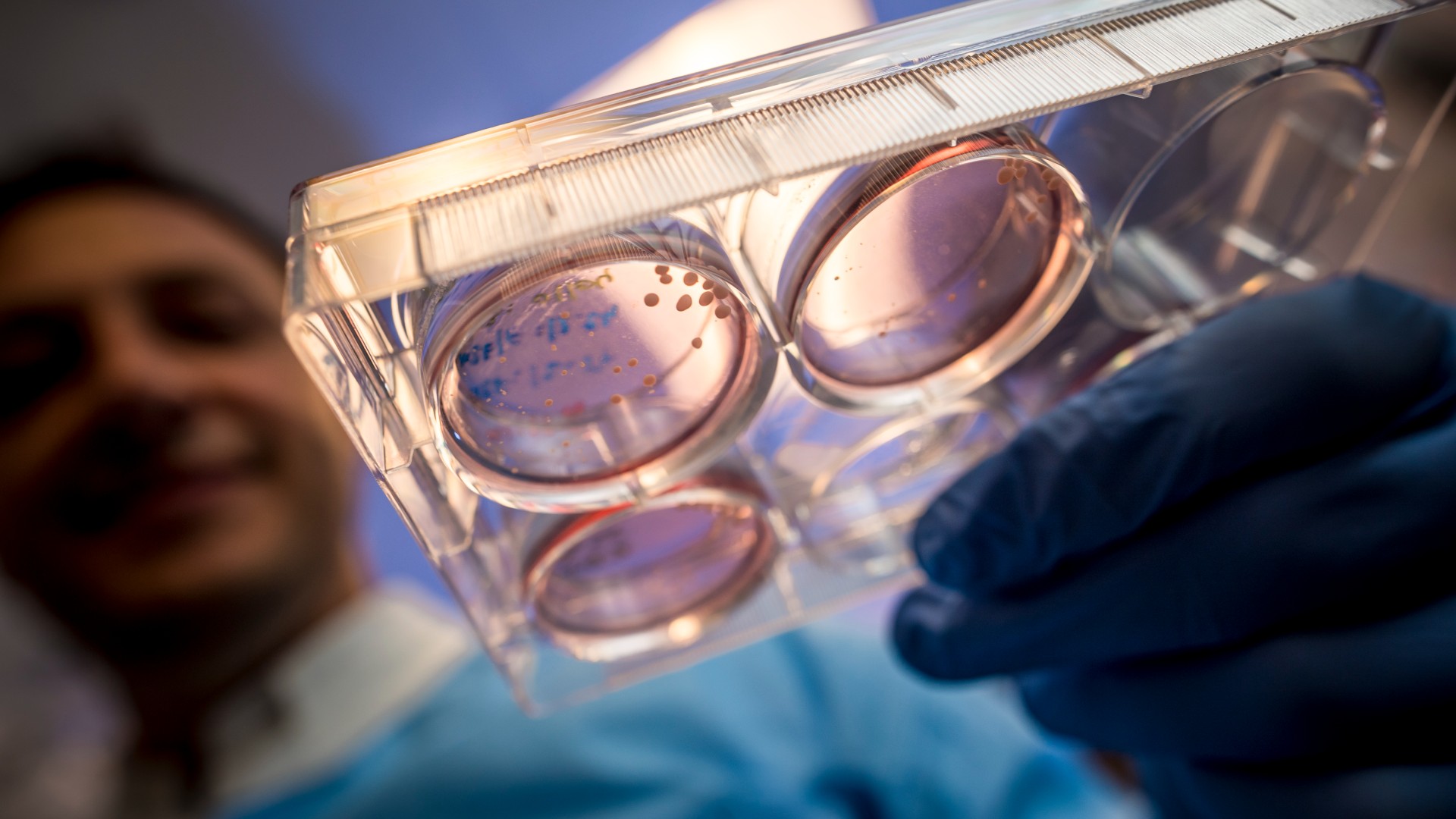
Could mini space-grown organs be our 'cancer moonshot'?
By Emily Cooke published
Scientists say they're growing "organoids" in space to better understand cancer, neurological diseases and aging, and to hopefully uncover treatments.
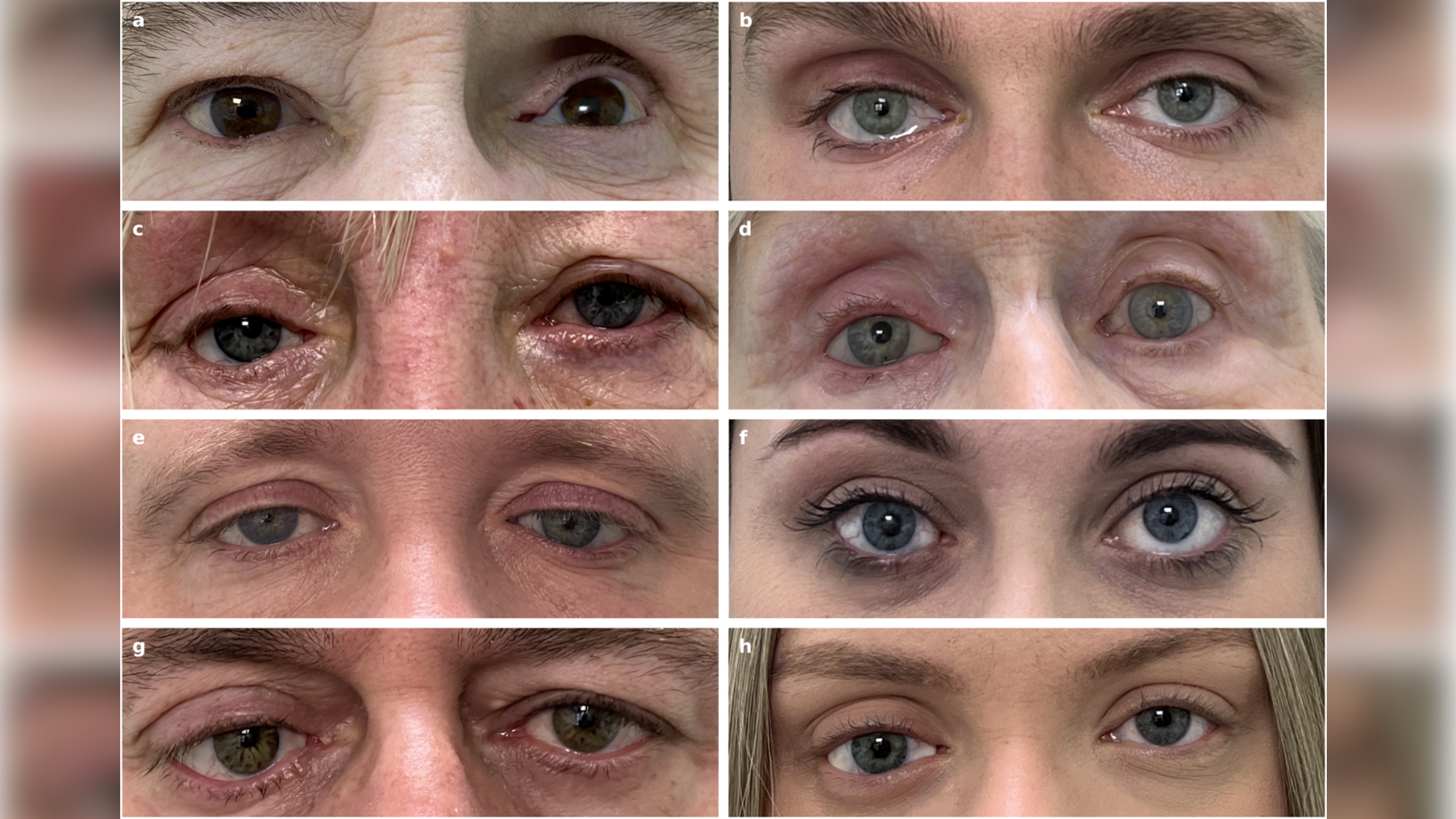
Super-realistic prosthetic eyes made in record time with 3D printing
By Emily Cooke published
Scientists can now 3D print more-realistic prosthetic eyes in a fraction of the time and effort required by traditional approaches.
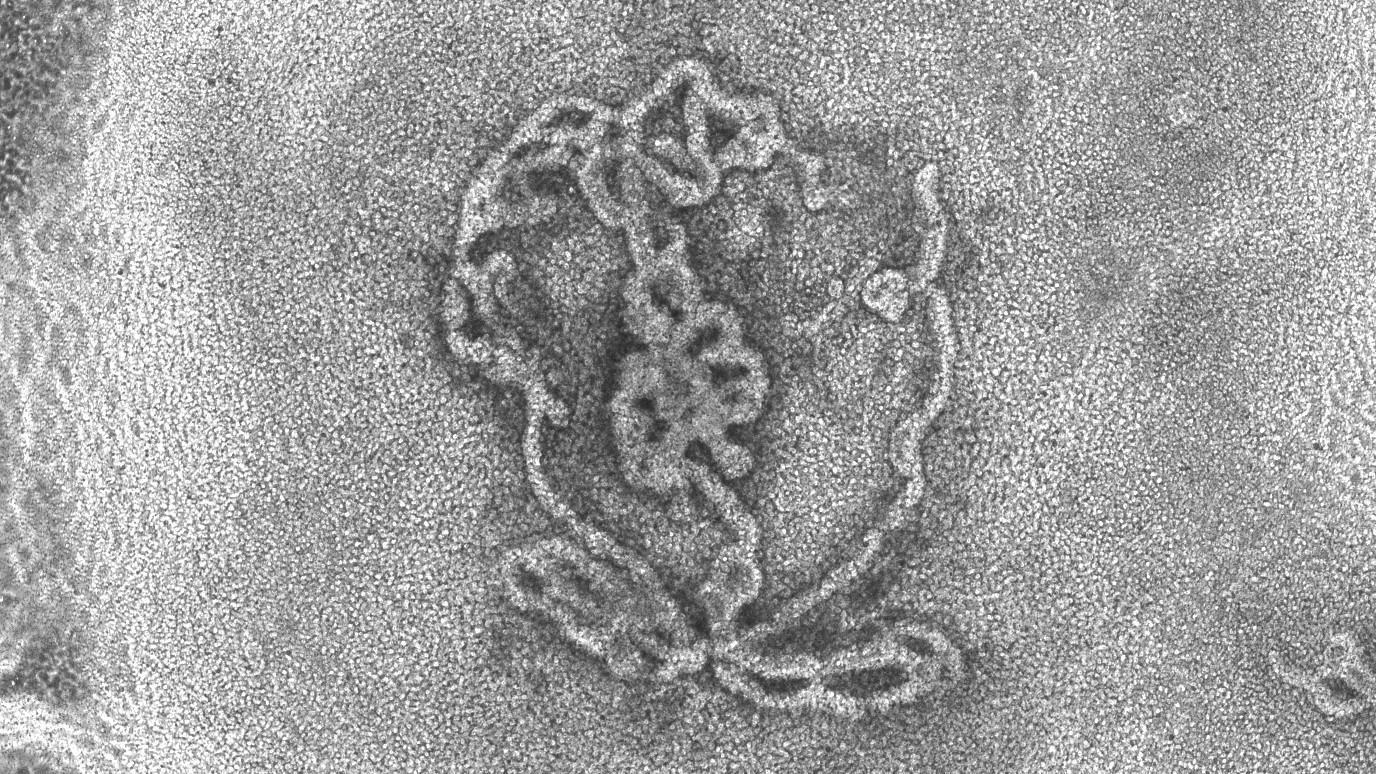
Tiny lab-grown testicles look remarkably like the real thing under the microscope
By Emily Cooke published
The first-ever 3D model of testicles, made using mouse cells, could improve our understanding of sex development disorders and male infertility.

Casimir Funk: What is the biochemist celebrated in today's Google Doodle famous for?
By Emily Cooke published
In 1912, biochemist Casimir Funk discovered vitamins, and more than a century later his legacy lives on.

One-third of trans people taking testosterone may still ovulate, raising chance of pregnancy
By Emily Cooke published
In a small study of transgender men and gender-diverse people who take testosterone, scientists found that one-third of the participants still ovulate and could therefore potentially become pregnant.

4 genes' activity could be key to faster appendicitis diagnosis
By Emily Cooke published
An analysis of children's gene activity suggests that more severe forms of appendicitis can be distinguished from milder cases based on the activity of four genes.

1st frostbite drug approved by FDA after successful clinical trial
By Emily Cooke published
A drug called Aurlumyn has been approved to treat severe frostbite in the U.S. after a successful clinical trial.

More than 275 million never-before-seen gene variants uncovered in US population
By Emily Cooke published
The newly uncovered gene variants were identified as part of an analysis of the DNA of more than 400,000 people in the U.S. who agreed to participate in the All of Us Research Program.
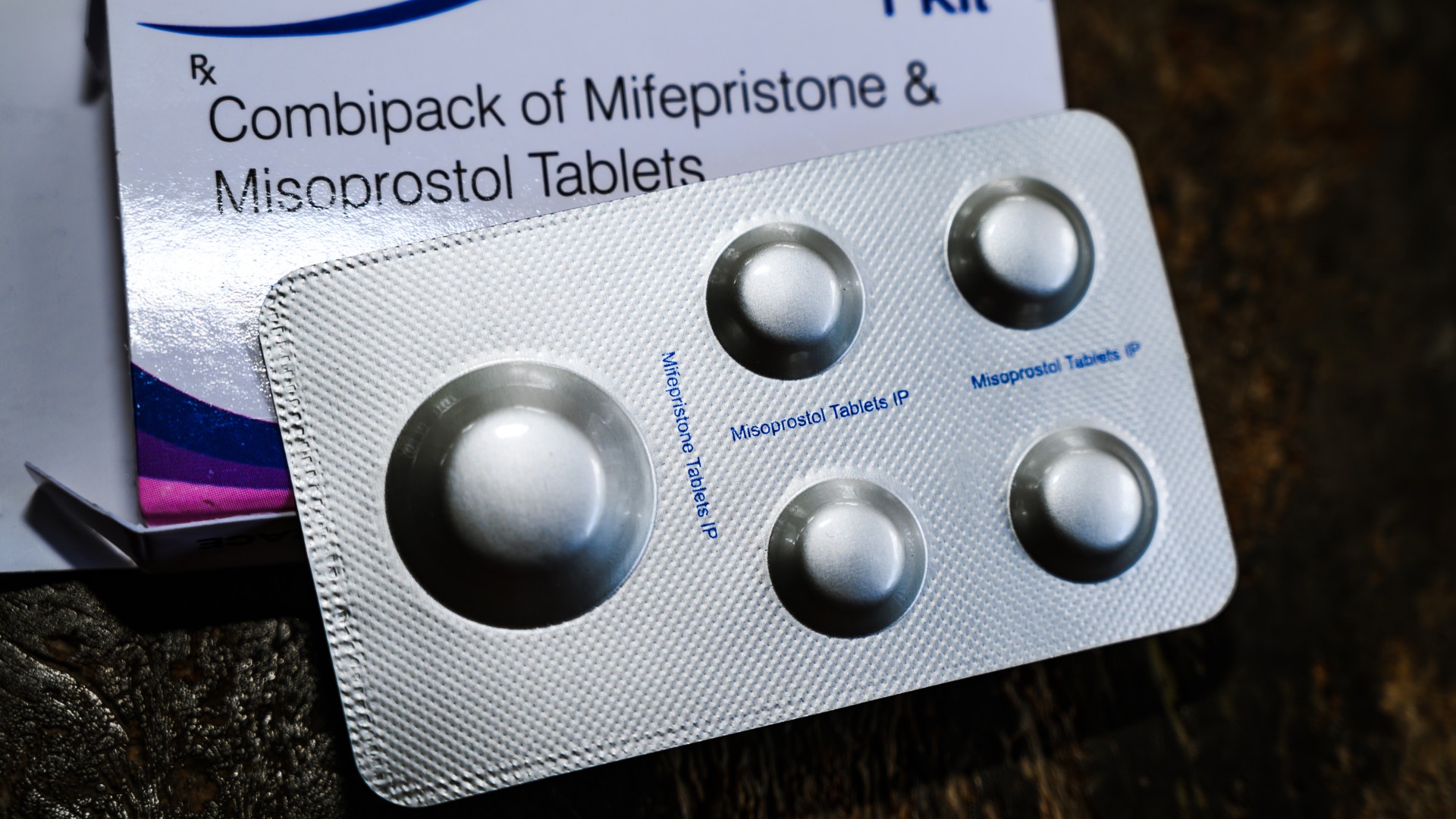
Telehealth abortions are as safe and effective as in-person, large study shows
By Emily Cooke published
An analysis of more than 6,000 telehealth abortion recipients in the U.S. suggests that receiving the abortion drugs via a virtual doctor's appointment is as safe and effective as doing so in person.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.