Jim Lucas
Latest articles by Jim Lucas

What are centrifugal and centripetal forces?
By Jim Lucas last updated
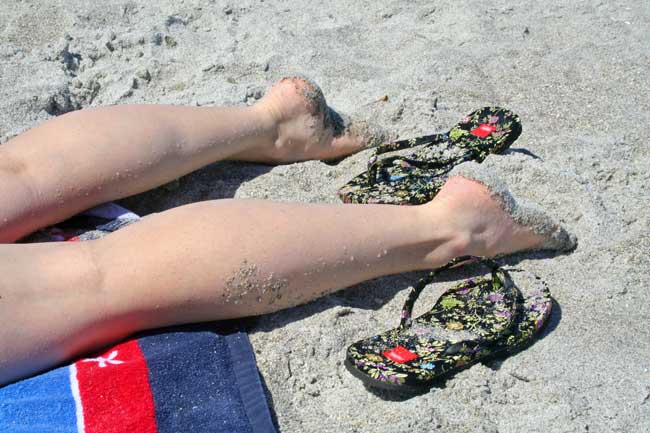
reference Centrifugal and centripetal are two closely related forces that describe circular motion, but the meanings are often mixed up.

What is the strong force?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference The strong force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Learn how it fits into the Standard Model of particle physics.
What is the third law of thermodynamics?
By Jim Lucas last updated
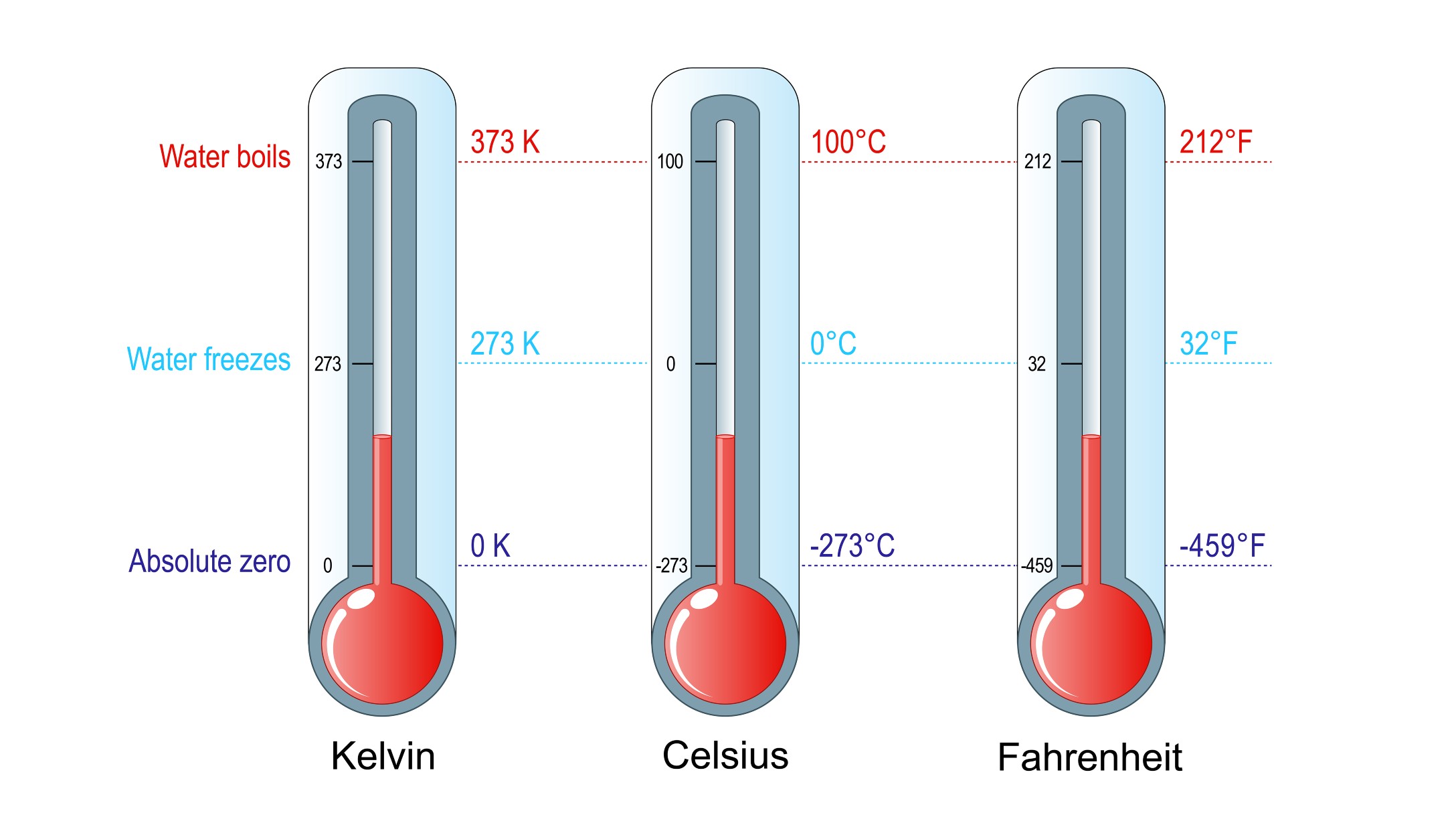
Reference According to the third law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a perfect crystal is zero when the temperature of the crystal is equal to absolute zero (0 kelvin).
What is visible light?
By Jim Lucas published
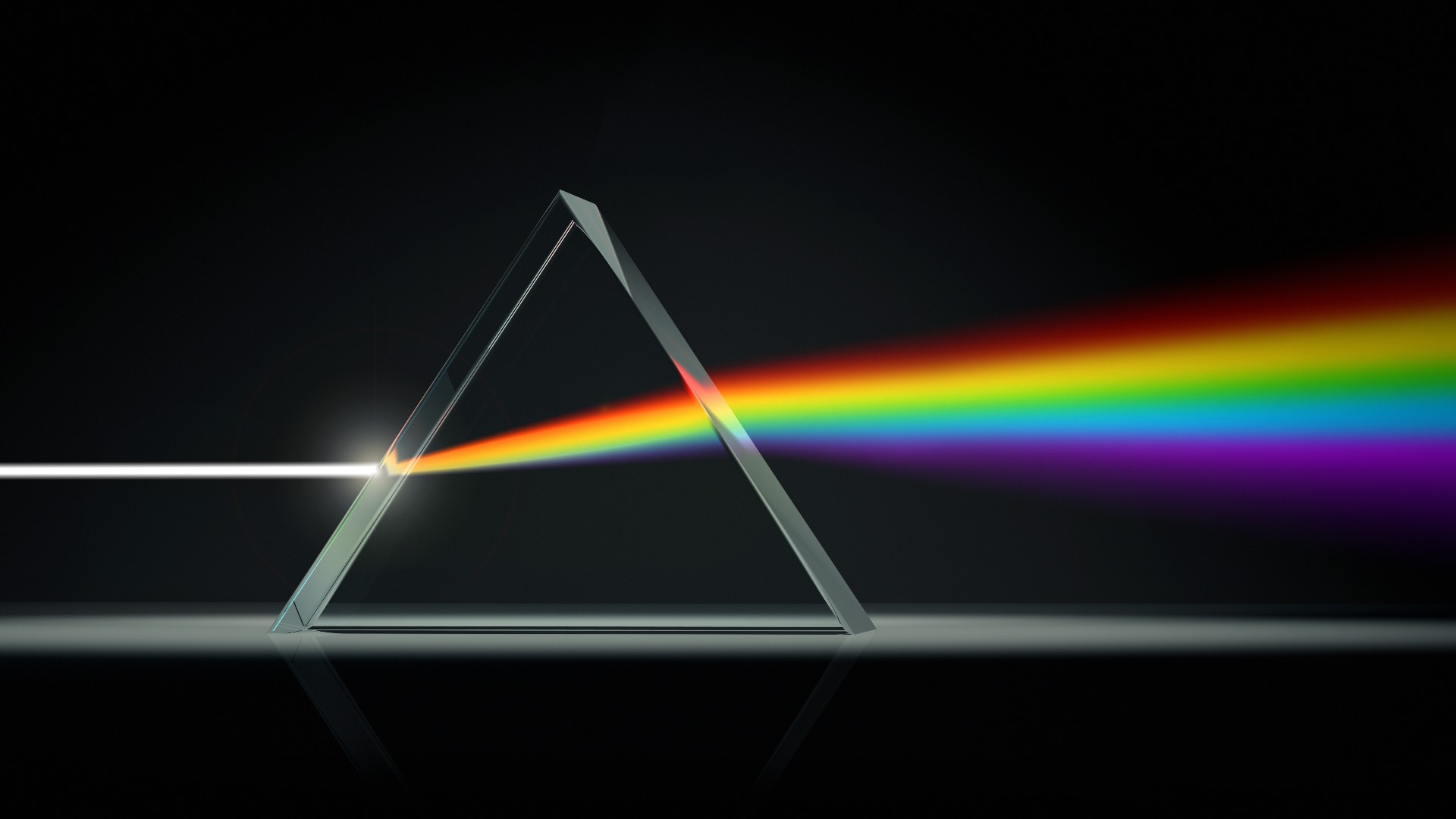
Reference Visible light is a type of electromagnetic radiation between the infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths, and it can be detected by cells in the human eye.
What is electromagnetic radiation?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays and gamma rays, as well as visible light.

What is engineering?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference Engineering is the application of science and math to solve problems. Here we explore the different types of engineering.
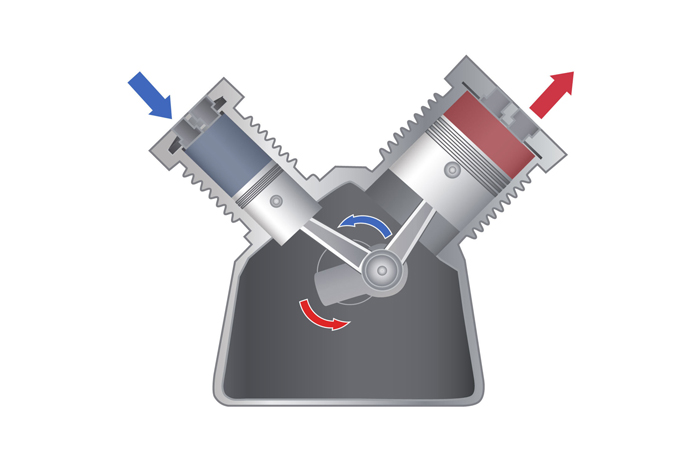
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transferred from one location to another and converted to and from other forms of energy.

What is Faraday's law of induction?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference Faraday’s law of induction describes how an electric current produces a magnetic field and, conversely, how a changing magnetic field generates an electric current in a conductor.

What is the second law of thermodynamics?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference The Second Law of Thermodynamics says, in simple terms, entropy always increases. This principle explains, for example, why you can't unscramble an egg.
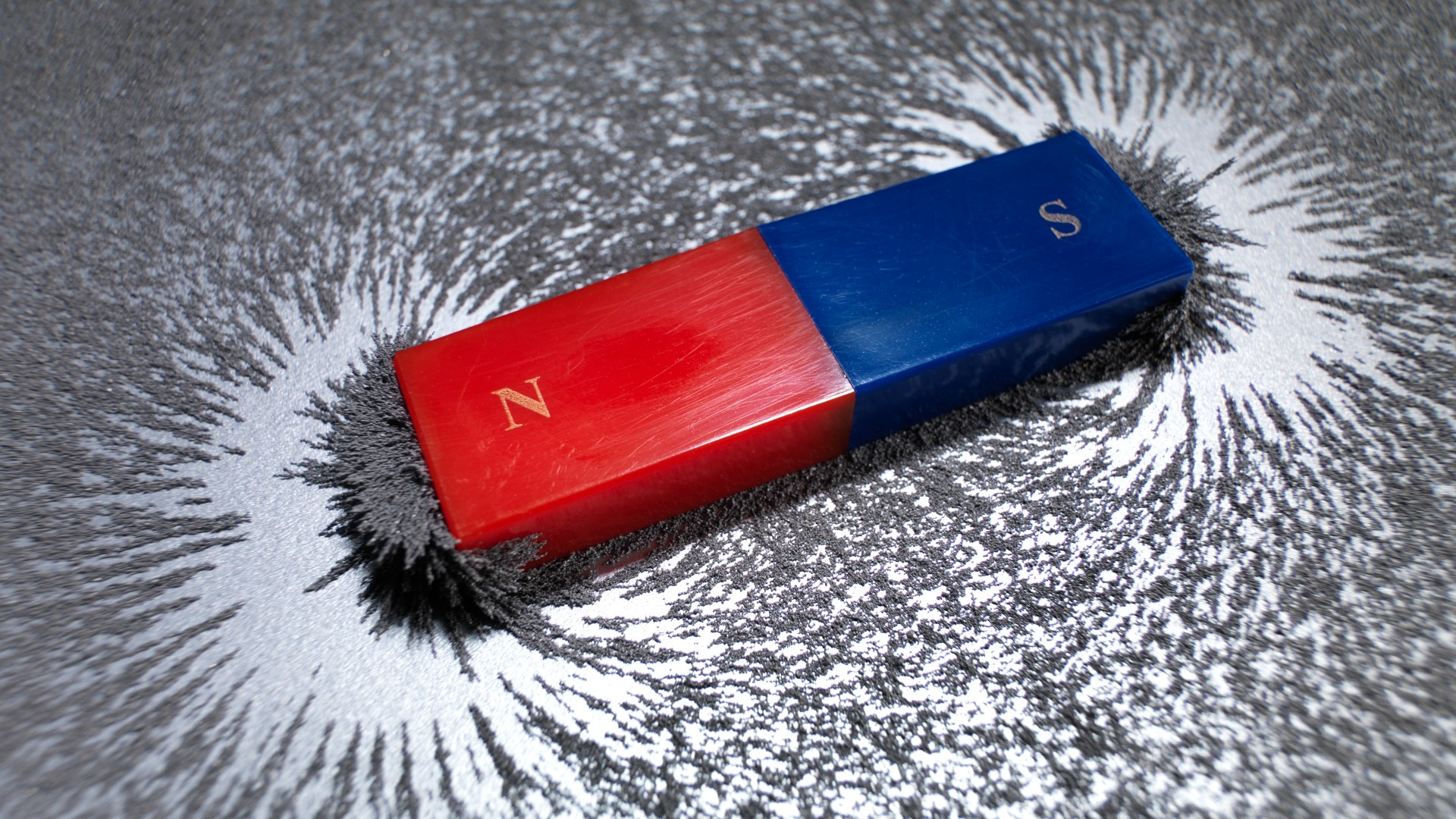

What is magnetism? Facts about magnetic fields and magnetic force
By Jim Lucas, Paul Sutter published
Reference Magnetism is a force of nature produced by moving electric charges.
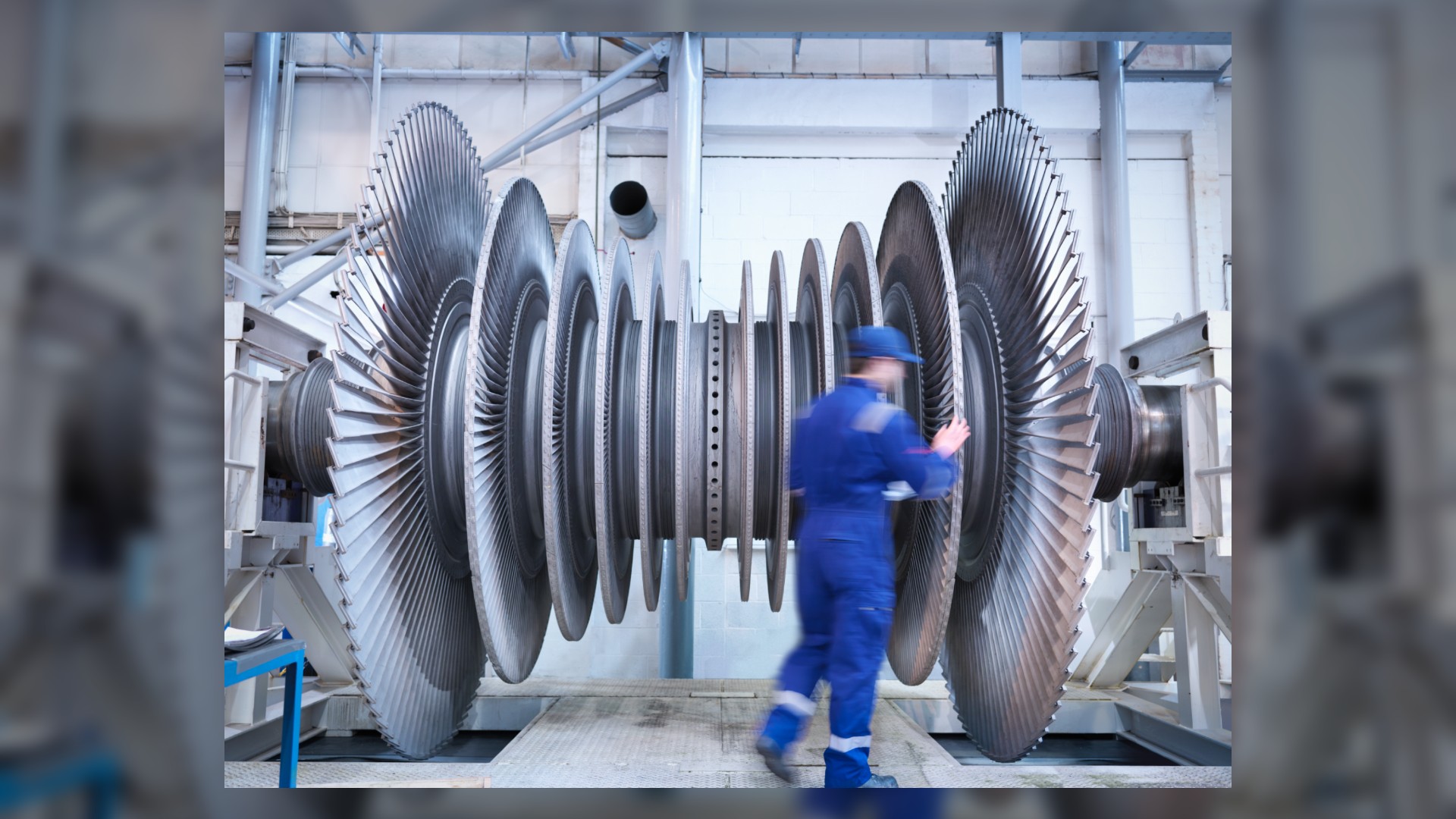
What is thermodynamics?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the relationships between heat and other forms of energy.
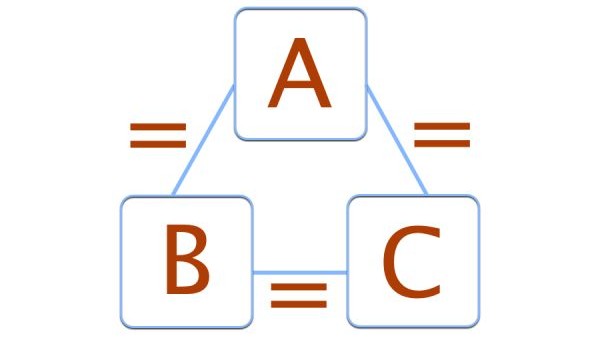
What is the zeroth law of thermodynamics?
By Jim Lucas published
Reference The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two bodies are each in thermal equilibrium with some third body, then they are also in equilibrium with each other.

6 simple machines: Making work easier
By Jim Lucas, Scott Dutfield published
Reference Humans have invented six devices that combine to make work easier. These six simple machines are the wheel and axle, the lever, the inclined plane, the pulley, the screw and the wedge.

What Are Radio Waves?
By Jim Lucas published
Radio waves help us communicate across close and far distances. They also help us identify otherwise invisible objects in space.

Electricity Basics: Resistance, Inductance and Capacitance
By Jim Lucas published
Resistors, inductors and capacitors are basic electrical components that make modern electronics possible.
What are gamma rays?
By Jim Lucas published
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation. They can be used to treat cancer, and gamma-ray bursts are studied by astronomers.
What Are X-Rays?
By Jim Lucas published
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation. One of the most common uses of X-rays is for medical imaging. X-rays are also used in treating cancer and in exploring the cosmos.
What Are Microwaves?
By Jim Lucas published
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, and are useful in communications, radar and cooking.

Newton's Laws of Motion
By Jim Lucas published
Newton's laws of motion formalize the description of the motion of massive bodies and how they interact.

Inertia & Newton's First Law of Motion
By Jim Lucas published
Newton's First Law of Motion states, "A body at rest will remain at rest, and a body in motion will remain in motion unless it is acted upon by an external force."
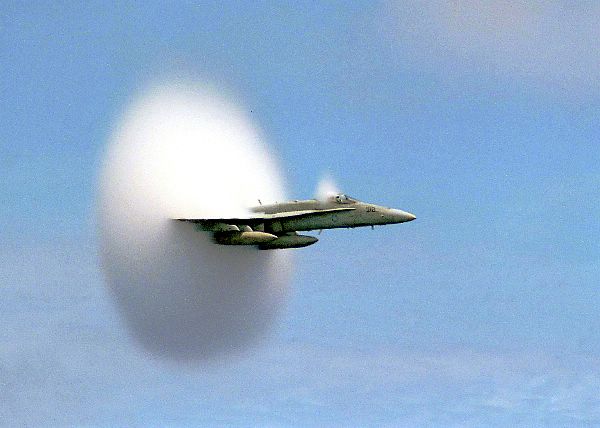

Force, Mass & Acceleration: Newton's Second Law of Motion
By Jim Lucas published
Newton’s Second Law of Motion states, “The force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object times its acceleration.”
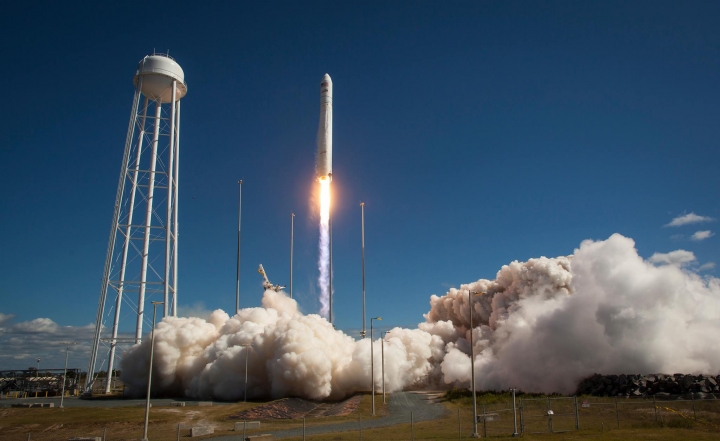

Equal & Opposite Reactions: Newton's Third Law of Motion
By Jim Lucas published
Newton's Third Law of Motion states, "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction."
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.