Michael Schubert
Michael Schubert is a veteran science and medicine communicator. He writes across all areas of the life sciences and medicine but specializes in the study of the very small — from the genes that make our bodies work to the chemicals that could support life on other planets. Mick holds graduate degrees in medical biochemistry and molecular biology. When he's not writing or editing, he is co-director of the Digital Communications Fellowship in Pathology; a professor of professional practice in academic writing at ThinkSpace Education; an inclusion and accessibility consultant; and (most importantly) dog-walker and ball-thrower extraordinaire.
Latest articles by Michael Schubert

Recycled black plastic can contain flame retardants, viral study found. That's still true — but their math was off
By Michael Schubert last updated
Researchers detected flame retardants in household items made from recycled black plastic. The study later received a correction — but regardless of this paper, the chemicals' health effects remain unclear.
Radiation-resistant 'extremophile' microbe dubbed 'Conan the Bacterium' inspires new antioxidant
By Michael Schubert published
A three-part complex based on the molecules that give "Conan the Bacterium" its radiation resistance may protect humans against damage from ionizing radiation.
Twin study reveals signs of MS that might be detectable before symptoms
By Michael Schubert published
Changes in the gene activity of immune cells may help flag people who have multiple sclerosis or are likely to develop it, a study of twins hints.

More people are surviving avalanches than decades ago — here's why
By Michael Schubert published
A study of avalanche survival data shows that survival rates have increased and rescues are faster, but time is still critical for buried victims.

Saline nose drops may shorten colds and cut transmission, trial hints
By Michael Schubert published
Giving children saline nose drops at the start of a cold may shorten its duration and reduce the likelihood that they will pass the illness to others, a study hints. But it has some caveats.

Why are some people's mosquito bites itchier than others'? New study hints at answer
By Michael Schubert published
A previously unrecognized type of immune cell may be responsible for the itchy feeling brought on by bug bites and other allergic reactions.
For C. diff, antibiotic resistance comes at a cost
By Michael Schubert published
Researchers have identified two distinct mechanisms of drug resistance in C. difficile, but its ability to withstand antibiotics comes with downsides for the bacteria.
Virus that causes COVID-19 uses a secret 'back door' to infect the brain
By Michael Schubert published
A mutation on the spike protein of the virus that causes COVID-19 could help it infect the brain by forcing it to use a cellular "back door."

Single-shot HIV treatment suppresses virus 10,000-fold for months, animal study finds
By Michael Schubert published
Engineered virus-like particles can outcompete HIV in the body, potentially offering long-term viral suppression after a single dose, a monkey study suggests.
Scientists finally explain MIS-C, the rare post-COVID sydrome seen in kids
By Michael Schubert published
MIS-C, a rare post-COVID inflammatory syndrome in children, may be triggered when the immune system mistakes its own proteins for those of the virus.

Heart attacks fell dramatically during the pandemic — and they're still dropping
By Michael Schubert published
Better prevention is driving down heart-attack rates in the U.S., but the sharp drops seen at the height of the pandemic were likely caused by people avoiding medical care.
What causes blood clots?
By Michael Schubert published
Blood clots can be dangerous, especially if all or part of them break off and then travel through the bloodstream.
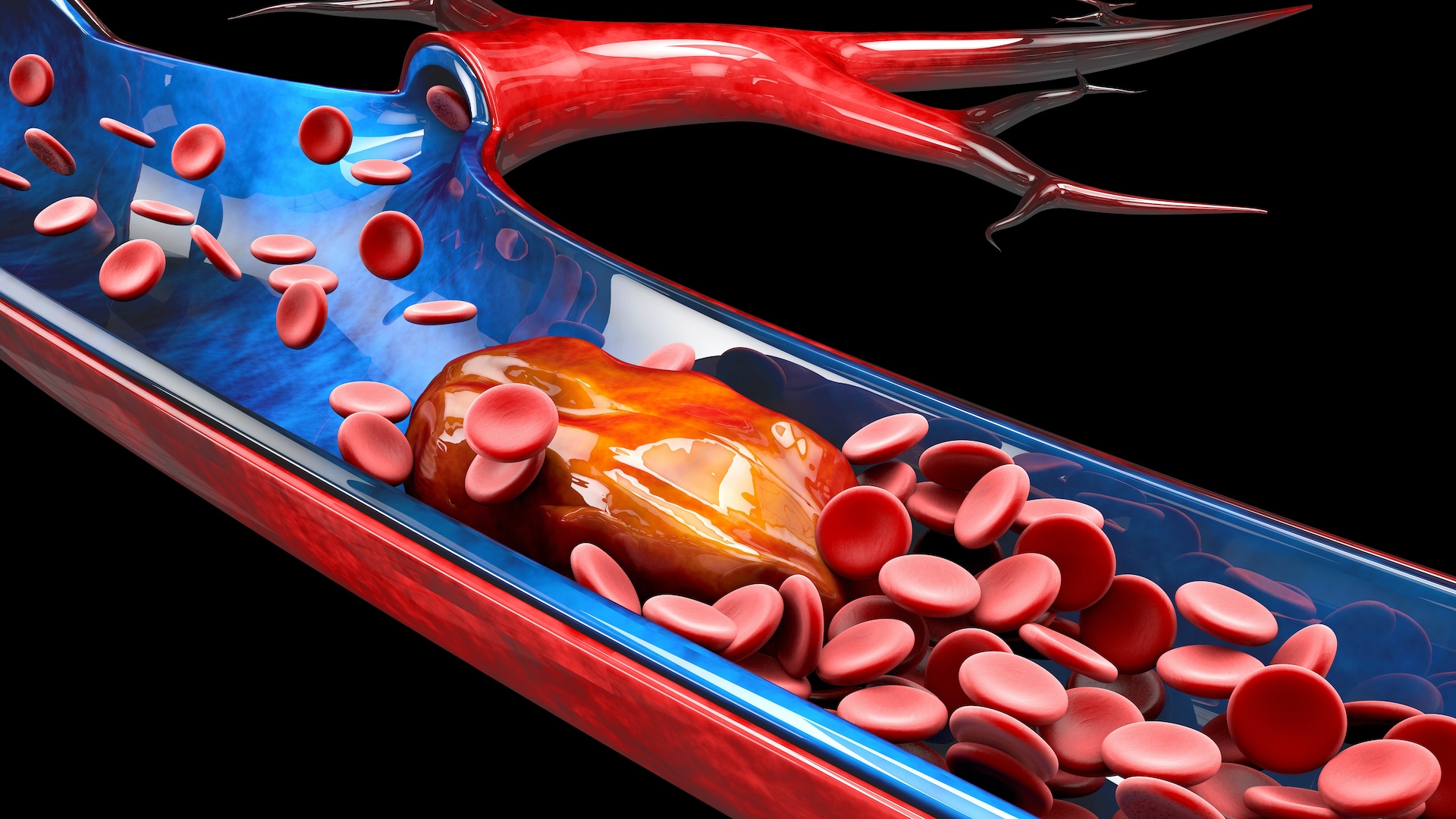
Anxiety and depression raise the risk of dangerous blood clots, study finds
By Michael Schubert published
Recent research has drawn a link between anxiety, depression and an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis.
Scientists find secret 'back door' flu viruses use to enter cells
By Michael Schubert published
Flu viruses that can use a second cellular entry point may move more effectively between animals and humans, scientists say.

'This is what drives the migraine headache': Scientists uncover 'missing link' in why some migraines happen
By Michael Schubert published
A new mouse study uncovered a previously unknown route between the brain and peripheral nerves that could explain the link between aura symptoms and migraine headaches.

New blood test could flag Parkinson's disease years before symptoms, study hints
By Michael Schubert published
By analyzing the proteins in the blood, a new blood test and AI tool can identify which at-risk patients are most likely to develop Parkinson's disease.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.


