Rebecca Sohn
Rebecca Sohn is a freelance science writer. She writes about a variety of science, health and environmental topics, and is particularly interested in how science impacts people's lives. She has been an intern at CalMatters and STAT, as well as a science fellow at Mashable. Rebecca, a native of the Boston area, studied English literature and minored in music at Skidmore College in Upstate New York and later studied science journalism at New York University.
Latest articles by Rebecca Sohn

Could allergies be 'deleted' someday?
By Rebecca Sohn last updated
Two studies pinpoint long-lived immune cells that "remember" allergies and likely sustain them through time.

'You could feel the energy and wonder': Despite clouds, totality wows crowds during solar eclipse in Syracuse
By Rebecca Sohn published
The total solar eclipse on April 8 plunged Syracuse, New York's Milton J. Rubenstein Museum of Science & Technology into darkness for 90 seconds, creating a wondrous and memorable totality.
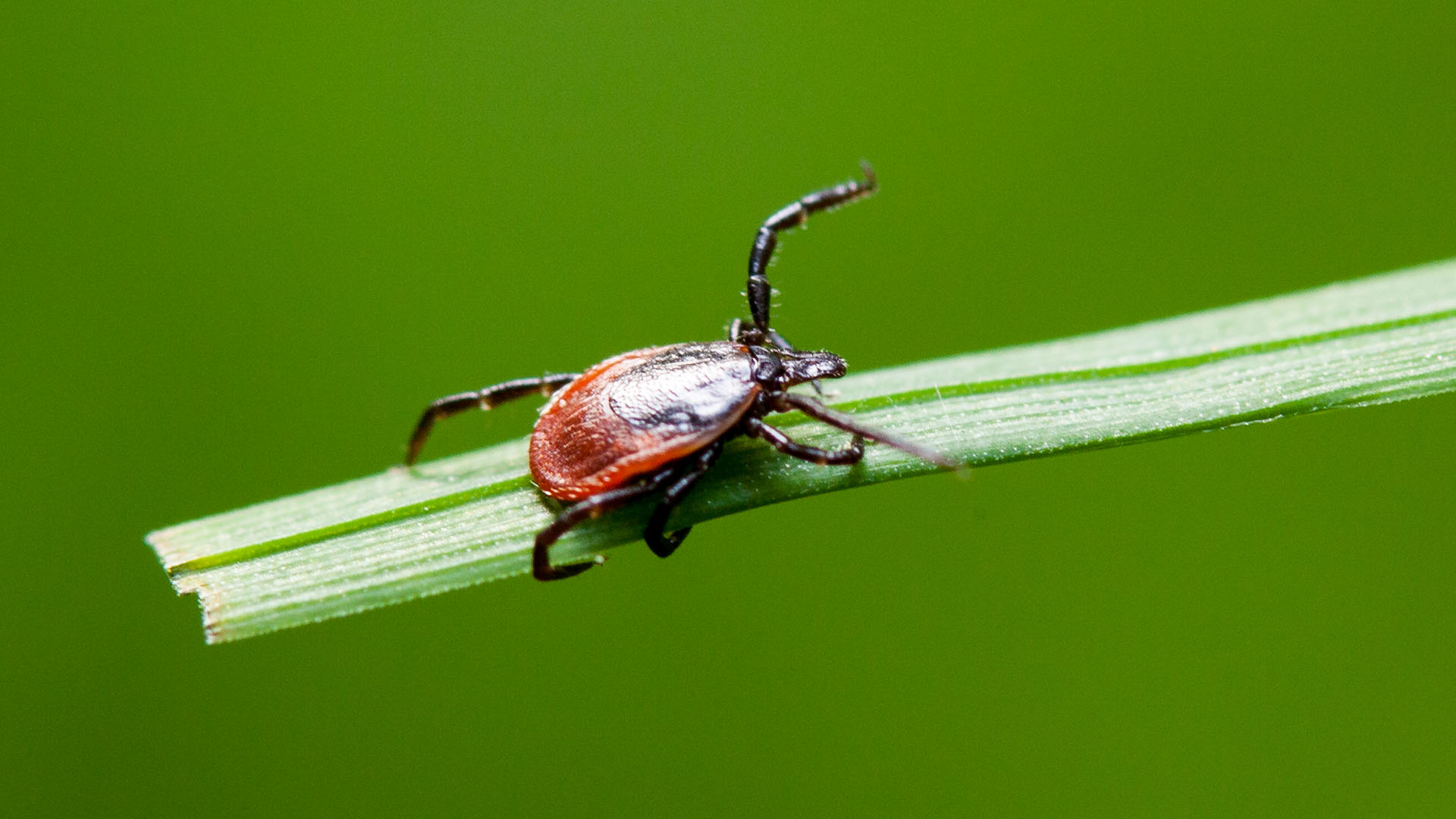

Protein in human sweat may protect some people against Lyme disease
By Rebecca Sohn published
A mutant gene that produces proteins in sweat may raise some people's risk of Lyme disease, while the standard version of the gene may protect against infection.
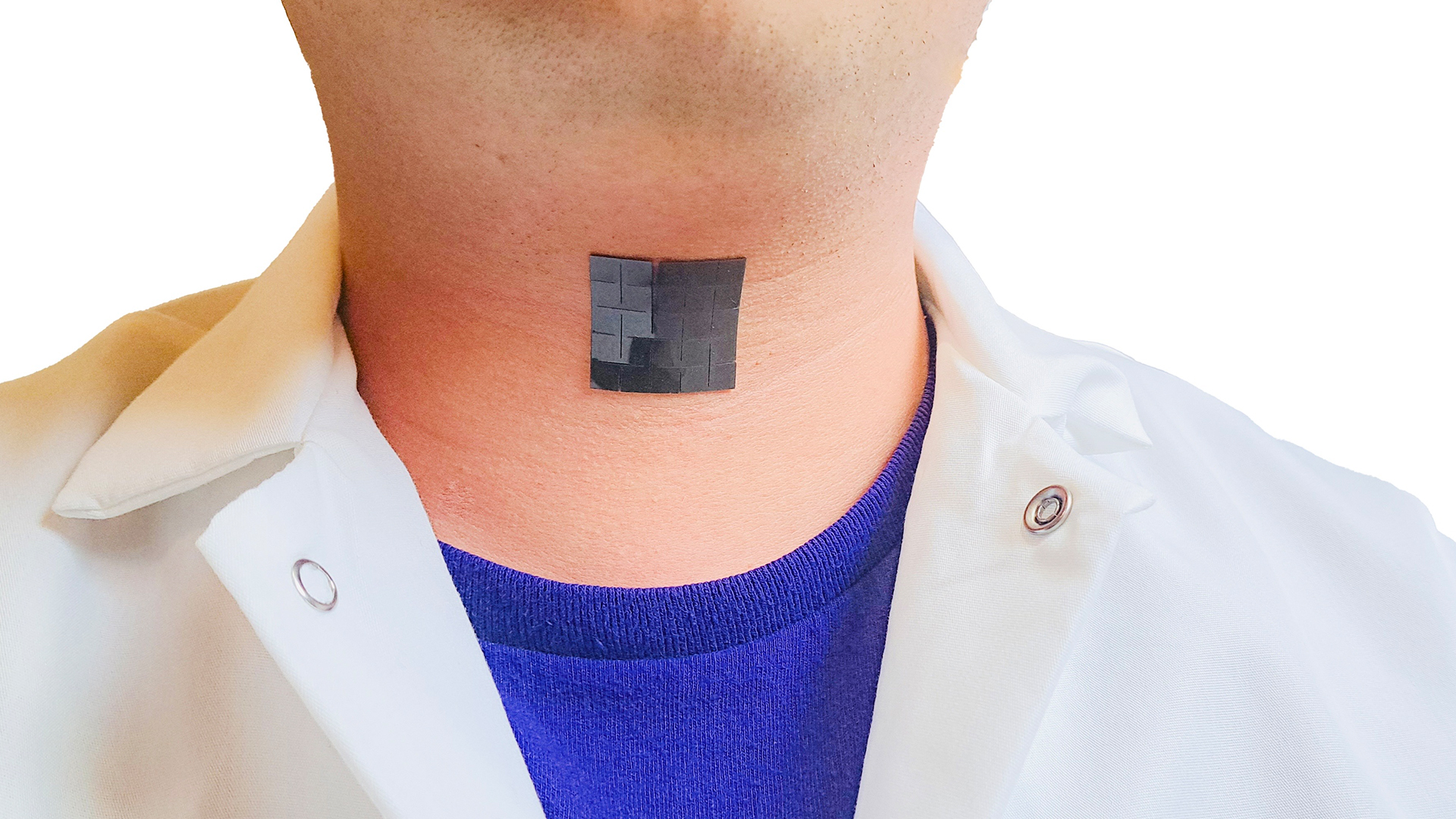
New self-powered throat patch could help people speak without vocal cords
By Rebecca Sohn published
The patch might offer a non-invasive communication tool for people who cannot speak due to vocal cord problems.
What would happen if you moved at the speed of light?
By Rebecca Sohn published
There's nothing faster than the speed of light. So, what would happen if a human managed to move at this universal speed limit?
'Mini placentas' may reveal roots of pregnancy disorders like preeclampsia
By Rebecca Sohn published
Tiny models of the human placenta are helping scientists study which proteins and genes are key to maintaining a healthy pregnancy.

Tinnitus often causes distress. A new app could help.
By Rebecca Sohn published
A new app could help make behavioral therapies aimed at easing distress from tinnitus more accessible, a small study suggests.

Biased AI can make doctors' diagnoses less accurate
By Rebecca Sohn published
AI systems have the potential to help improve doctors' diagnoses, a new study suggests. But if bias is baked into the system, their diagnostic accuracy falls.
In a 1st, scientists combine AI with a 'minibrain' to make hybrid computer
By Rebecca Sohn published
Researchers plugged a "brain organoid" into an artificial intelligence system, using the neural tissue to help complete computational tasks. The experiment could mark a step toward "biocomputers."

Injection might help long COVID patients smell normally again
By Rebecca Sohn published
Early studies hint that a nerve block in the neck could help restore long COVID patients' normal sense of smell, but more research is needed.

The brain may interpret smells from each nostril differently
By Rebecca Sohn published
There might be an advantage to separating scent information from each nostril, a new study hints.
Menstrual cycle linked to structural changes across whole brain
By Rebecca Sohn published
A study of 30 women with regular menstrual cycles suggests that the structure of the brain fluctuates in time with hormonal shifts.

Meet the 'exclusome': A mini-organ just discovered in cells that defends the genome from attack
By Rebecca Sohn published
A newly described organelle in mammal cells may serve as a genome defense system and its function may reflect how the early nucleus formed.
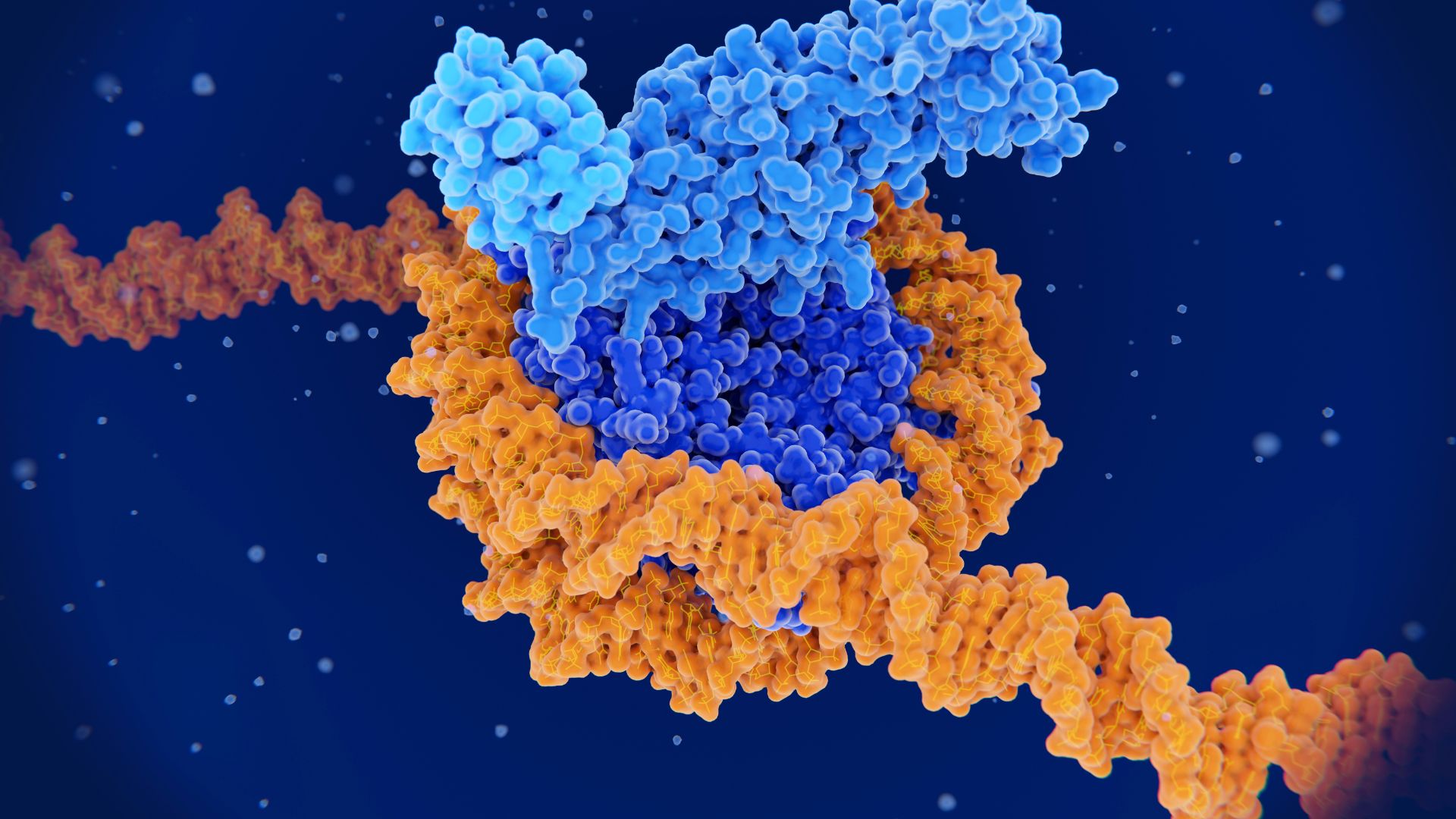
DNA's 'topography' influences where cancer-causing mutations appear
By Rebecca Sohn published
The topographical features of DNA in the body may dictate where and when cancer-causing mutations appear in its code.
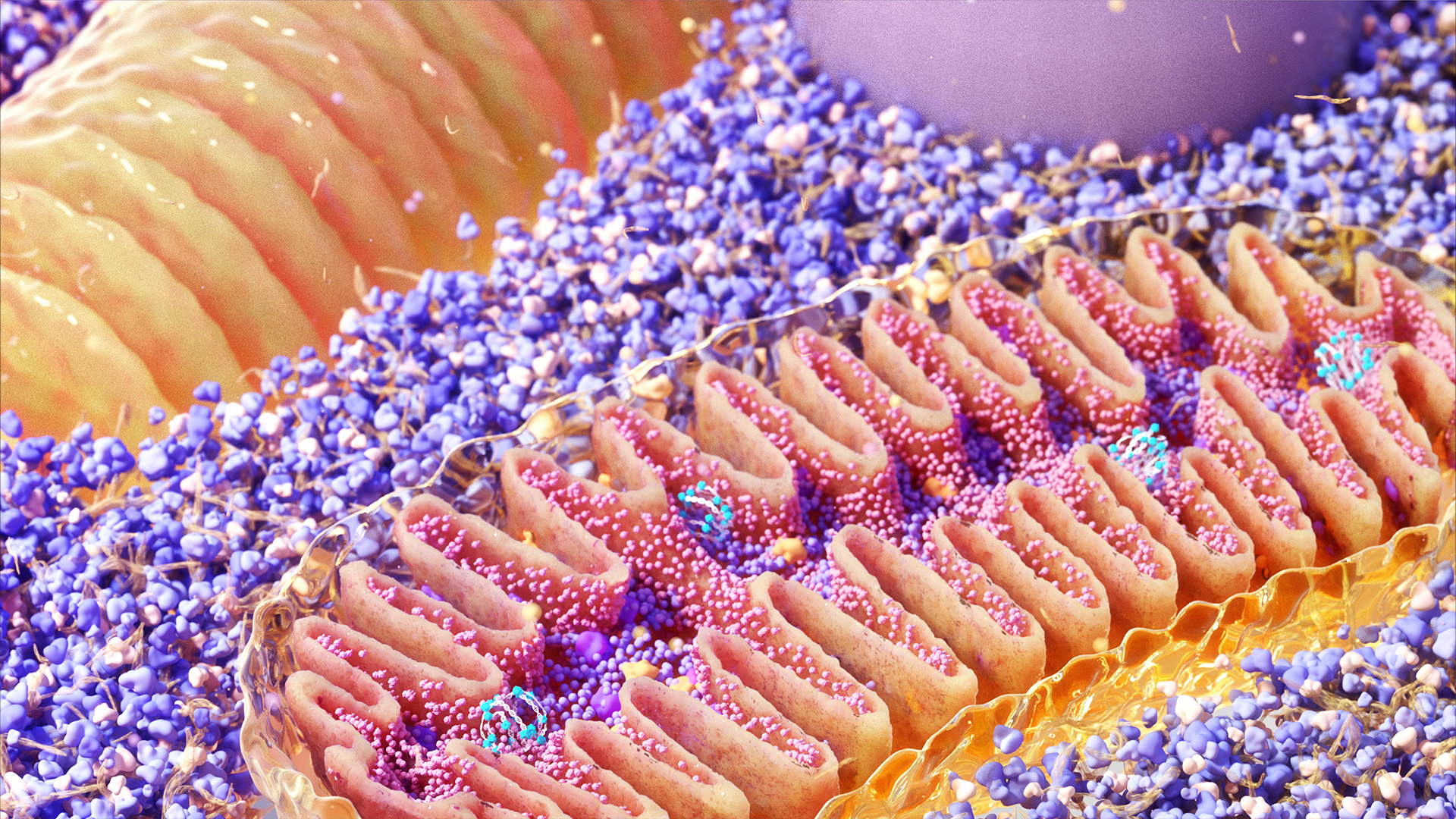
Relatives of the 1st mitochondria may be living in geothermal hot springs today
By Rebecca Sohn published
Scientists say they've identified a potential living relative of the ancient microbe that gave rise to the "powerhouse of the cell."
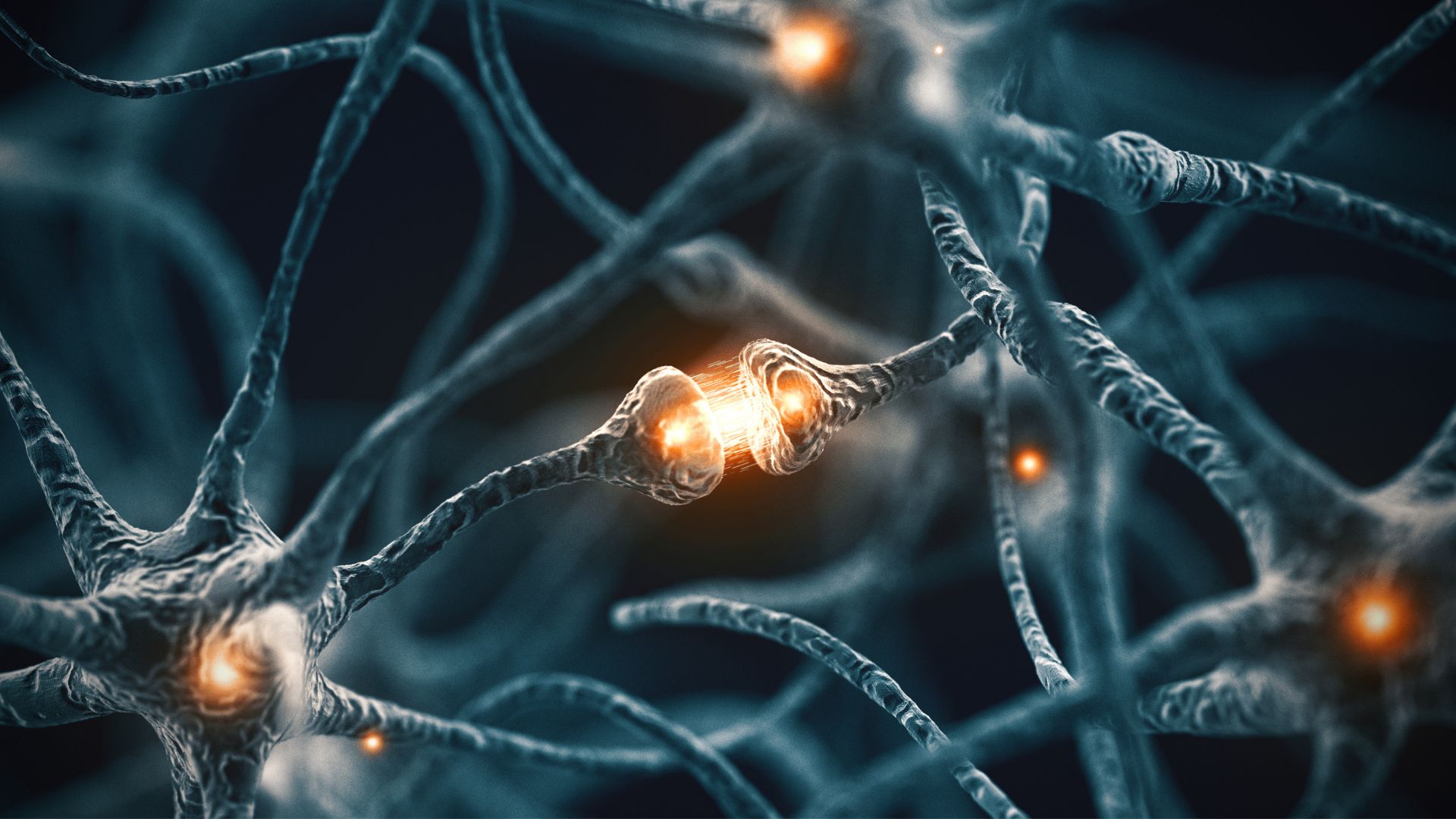
Strange, two-faced brain cells confirmed to exist, and they may play a role in schizophrenia
By Rebecca Sohn published
Researchers have confirmed the existence of an odd type of brain cell that other neuroscientists once thought might be only a technical quirk or error.

Could Ozempic be used to treat addiction? Studies hint yes, but questions remain
By Rebecca Sohn published
In animal studies, the weight-loss drug Ozempic has shown promise as an anti-addiction medicine. Whether it could work the same in humans remains to be seen.

NYC's air quality ranked worst of any major city on Wednesday. With climate change, will it happen again?
By Rebecca Sohn published
New York City's normally good air quality rating recently plummeted to the worst of any major city in the world, as wildfire smoke drifted over the city from Canada.

Sleep apnea linked to changes in the brain's wiring that may raise risk of dementia, stroke
By Rebecca Sohn published
Sleep apnea and a lack of deep sleep may be linked to abnormalities in the brain's white matter.

Newfound 'brain signature' linked to multiple psychiatric disorders
By Rebecca Sohn published
Researchers identified patterns of brain wiring that seem to be linked to a person's risk of having multiple psychiatric disorders.

Hormonal birth control slightly increases breast cancer risk, regardless of type
By Rebecca Sohn published
Hormonal contraceptives slightly raise users' risk of breast cancer, regardless of whether they're combination or progestogen-only.
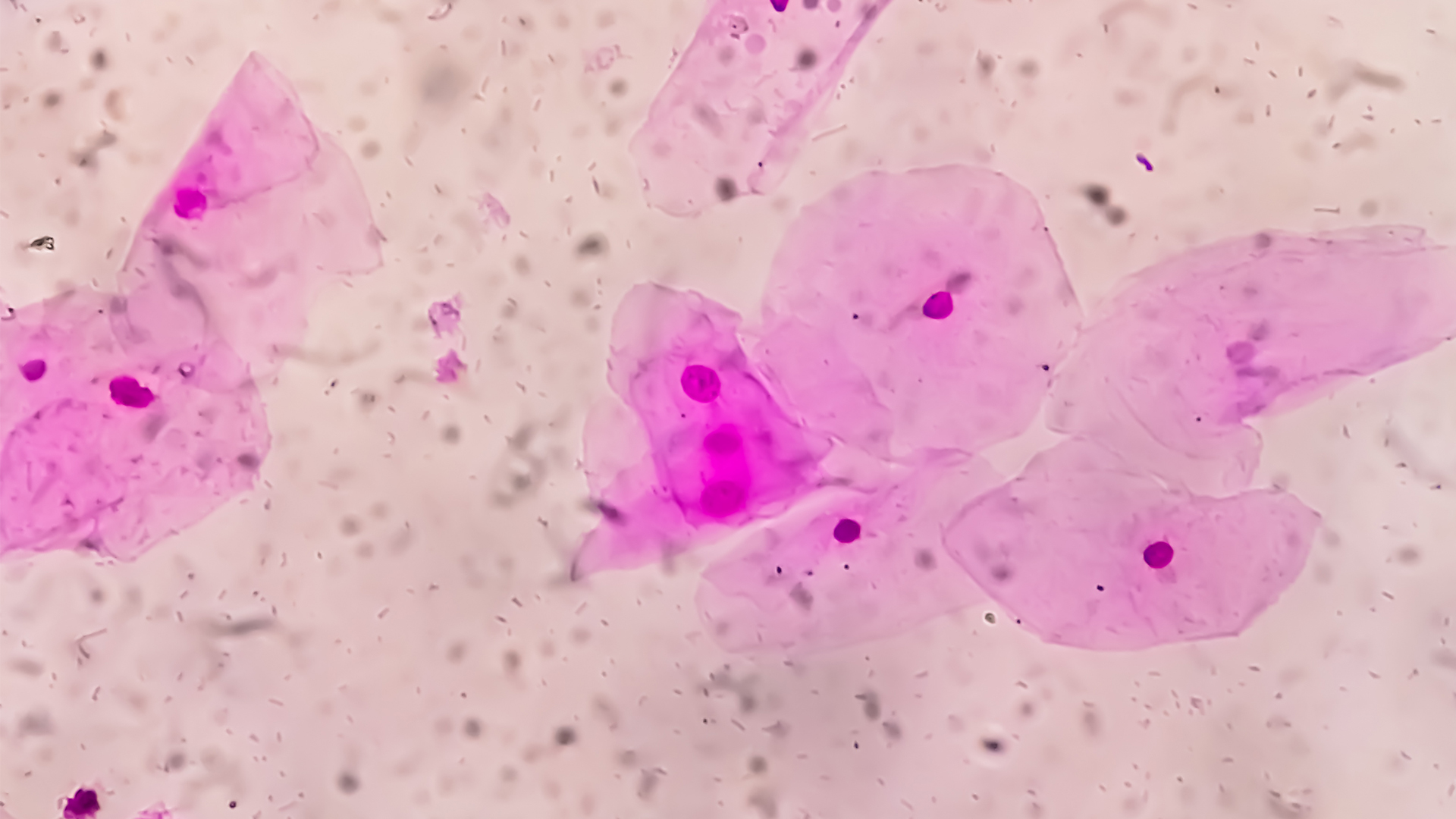
What is the vaginal microbiome?
By Rebecca Sohn published
The vaginal microbiome is made up of around 300 species of bacteria. But its links to health are still being uncovered.
What is oxidative stress?
By Rebecca Sohn published
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to counteract them.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.


