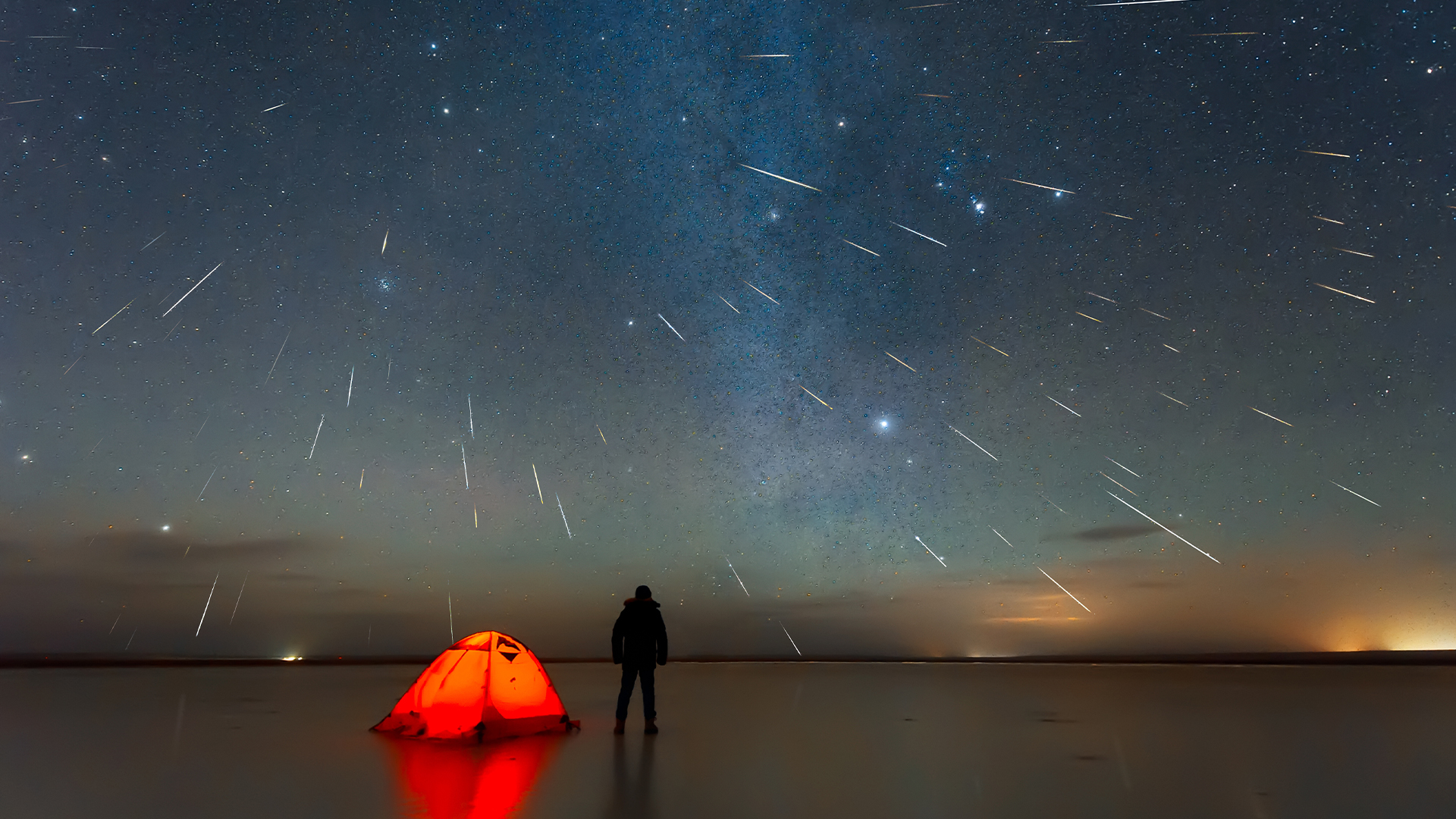
Beginner's guide to astrophotography
Learn how to capture the night sky — tips on choosing the best camera and lens, plus advice on camera settings, choosing a good location and apps to help plan your shoot.
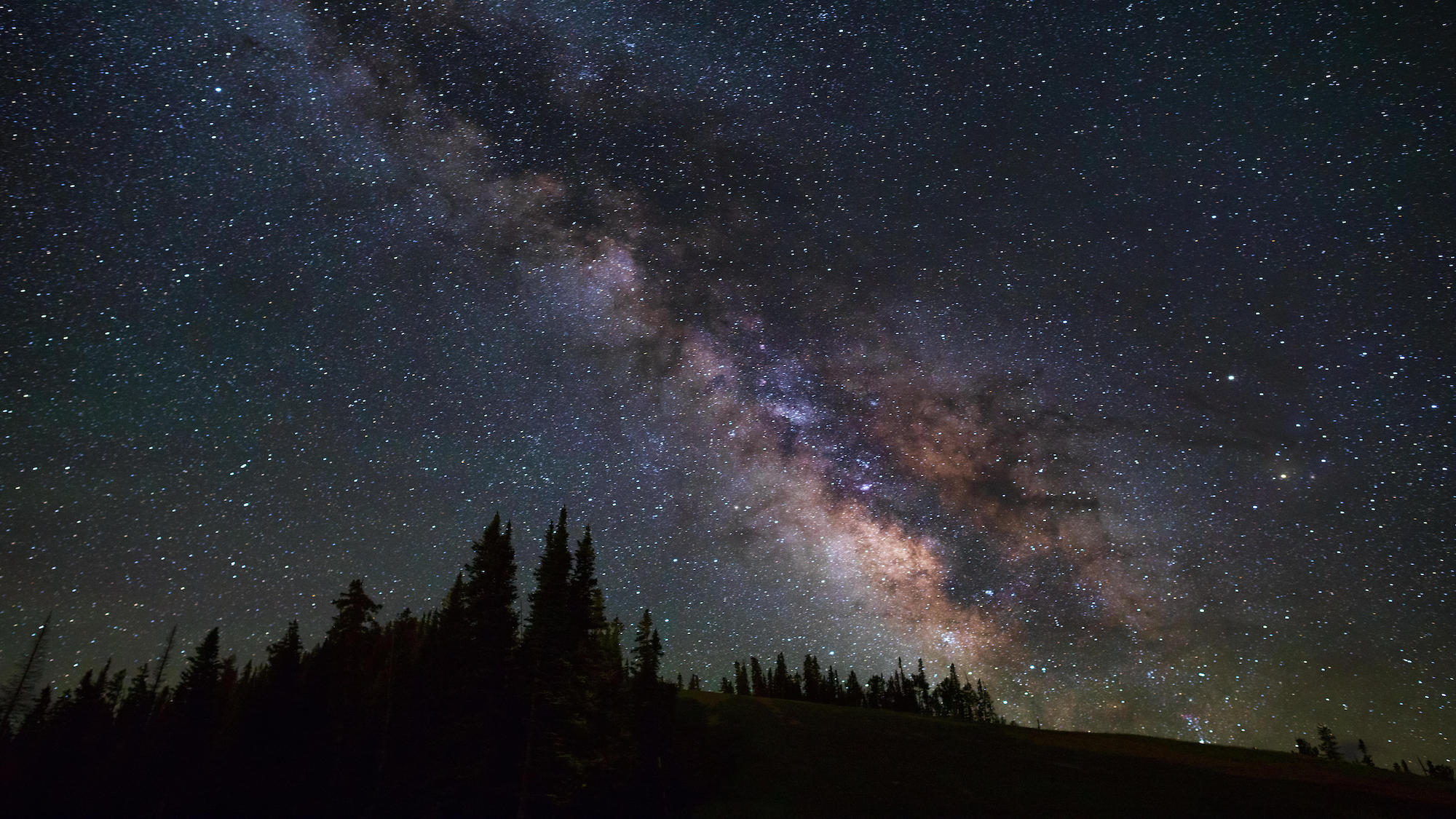

Astrophotography is a rewarding but time-consuming affair, but if you master the basics, soon you'll become confident in capturing breathtaking night sky pictures. Getting the right camera settings, depending on what you’re trying to shoot, can be a process of trial and error. This, combined with the fact there are lots of other elements to making sure you take decent night sky photographs, means you need to do your research before heading out and reading one of the best astronomy books may prove helpful.
In this guide, we are going to cover what to look for in the best cameras for astrophotography and which lenses are best suited to capturing the cosmos. We also take you through the best settings to use and offer suggestions on other must-have accessories. There are tips on finding a good location and targets for beginners to focus on as well as handy apps and software to help you plan your shoot.
Over the next couple of months, there are a host of exciting things to spot in the night sky. The planetary parade has Mercury joining the view in March as well as the total lunar eclipse on March 13 which will turn the moon’s surface red, known as the ‘blood moon’. Of course, despite these special events, space remains interesting on any clear night where you can observe nebulas, constellations and shooting stars, so now’s the time to pick up your camera and give it a go.
Choosing the right camera

Generally speaking, when it comes to astrophotography the lens is usually more important than the camera. The main factors to consider in a camera are its ISO sensitivity, sensor size and resolution.
ISO
ISO refers to your camera's sensitivity to light. When you're shooting in dark conditions, you need to be able to increase the ISO enough to capture enough detail in your image, but setting it too high can result in too much noise in your image — which can ruin your shot. The 'sweet spot' will vary between cameras, but start at around ISO 2,000 and increase or reduce as necessary.
Sensor size and resolution
Full-frame cameras are typically favored for astrophotography as they have a bigger sensor, but crop sensor and micro four-thirds cameras can be a good starting point for beginners — this is going to depend on how much budget you have to spend. One thing to be wary of is the megapixel count. While a higher-resolution sensor is great in theory, these tend to produce more noise in the images, so if you're only going to be shooting astro, opt for something a bit lower.
If you want to take a lot of shots and stack them to create more detailed images, choosing a camera that has “interval shooting” will save you a lot of time and stress when you’re shooting. Most newer cameras have this setting, but it's something to consider if you're buying an older or second-hand model.
Special astro features
If you have a healthy budget to play with, some cameras have some great astrophotography features. When we reviewed the OM System OM-1 Mark II, we loved its Live Composite feature for effortlessly creating star trail images, and the Starry Sky Autofocus nailed the focus on the stars every single time.
Lenses

Focal length
As a rule of thumb, astrophotography calls for wide-angle lenses to capture as much of the sky as possible and let in more light. Generally speaking, anything 20mm or lower will be great for astro. This is what we'd recommend for beginners who want to do astrophotography with a foreground, whereas as your skills advance and you want to take images of deep space, or even just the moon, a longer focal length will be needed.
Aperture
Aperture is also important when choosing a lens, as a wider aperture lets in more precious light. For astrophotography, you want an aperture of f/2.8 or lower. F/1.8 is ideal, and f/1.4 is even better, although those are even more expensive. Prime lenses with a fixed focal length are usually preferable for astrophotography because they have wider apertures than zoom lenses, and you can get more detailed shots with them. For wide prime lenses, Sony’s 20mm f/1.8 is a very popular lens for astro, or the Sony 14mm f/1.8 is also fantastic if you have the budget for it. Sigma and Tamron do some great third-party lenses to start out with that are a lot cheaper than native lenses.
Camera settings
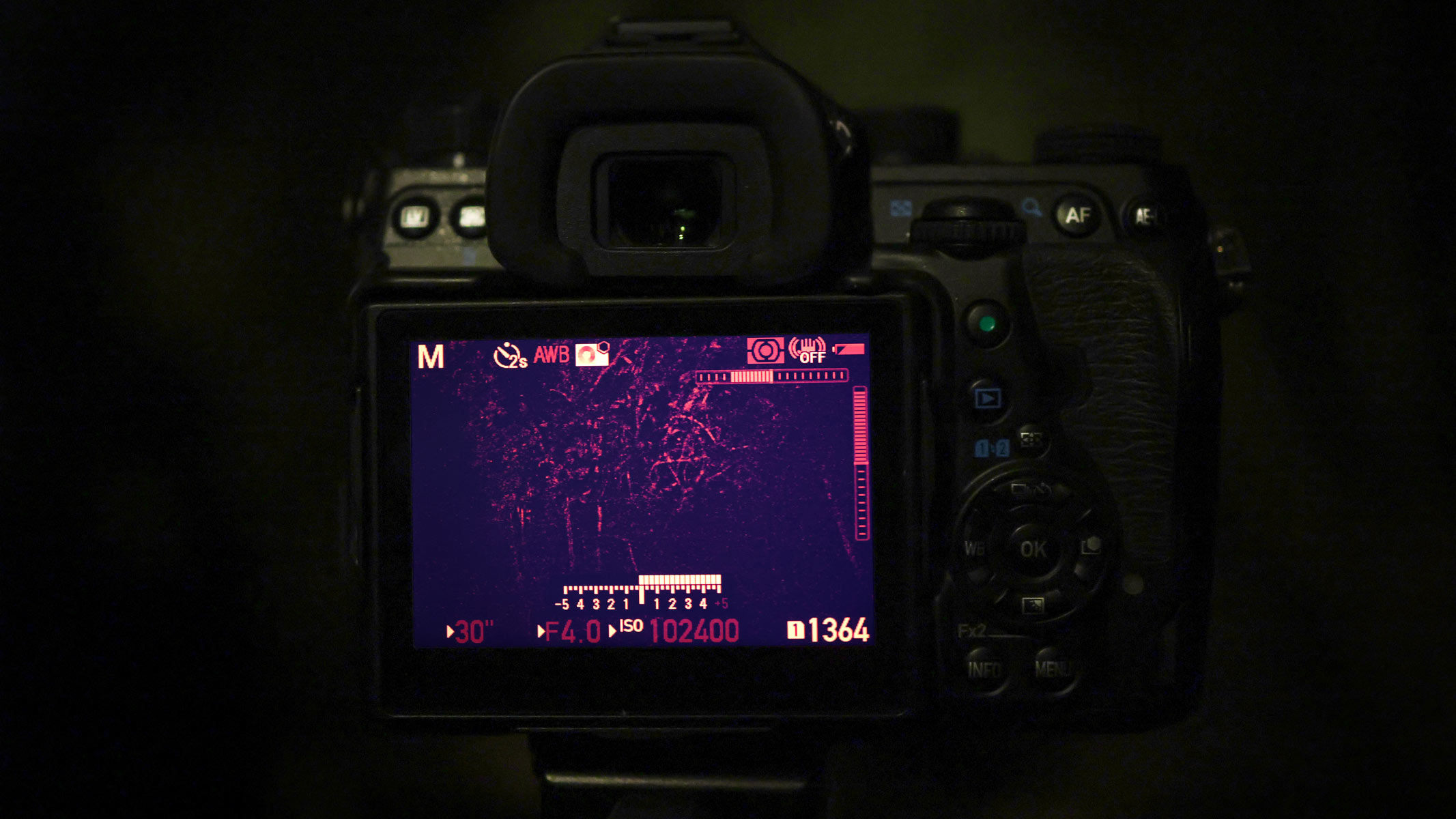

Shutter speed
When you first start out with astrophotography, there's a certain amount of trial and error involved depending on what you want to capture, and the light levels in your chosen location will also have an effect. You’ll want your shutter speed to be long enough to let as much light in as possible, but not too long where the stars begin to trail (unless star trails are what you’re going for).
How do you figure out where the sweet spot is, you ask? By using the 500 rule: you divide 500 by the focal length of the lens you’re using and that will give you the amount of time you can have your shutter open for, before everything starts to trail. So, if you’re using a 20 mm lens, 500 divided by 20 is 25, so your shutter speed can be up to 25 seconds. The 500 is the variable given for a full frame lens — if you're using a crop sensor (APS-C) camera, use 300, and 250 on a micro four-thirds.
Aperture
For aperture, you generally want it as wide as it can go to let as much light into the lens as possible — this is why prime lenses are better for astrophotography as they generally have lower apertures. For astrophotography, your aperture needs to be f/2.8 or lower.
ISO
With ISO, it largely depends on your camera’s capabilities and the ambient light levels in your area. (This is why it's better to head to a dark sky area) Setting your ISO 1,600 - 2,000 is usually a good place to start, then you can adjust it as necessary after taking a few test shots.
Manual
Astrophotography requires full manual shooting, so you have full control over the above three settings. This applies to both manual mode on the main dial, and manual focus on the lens. You also need to be shooting in RAW format to enable you to better edit the images.
Focus
Getting pin-sharp stars takes some practice, and some cameras make it easier than others. Once you set your lens to manual focus (MF), you should see a zoomed-in view on the LCD screen once you start twisting the focus ring. From there, keep turning the focus ring until the stars look like small pin-points of light.
Locations and how to find them
Location can make or break astrophotography. I you want some sort of landscape or vista in your shot as well as the starry sky above, you’re going to need to pick your location wisely. You want to choose somewhere where there’s as little light pollution as possible — think national parks and big natural spaces, far away from towns and cities. Certified Dark Sky sites are ideal.
To get an idea of dark sky locations in your area, check out this light pollution map and dark site finder before you plan your trip so you can make sure your shot isn’t ruined by excessive light.
In terms of finding a composition in your location, try going there before it gets dark to work out a composition you like then once it's dark, you’re already in the right place. You can also check out Google Maps to scout a location before you go to give you a general idea of where you want to be.
Other accessories
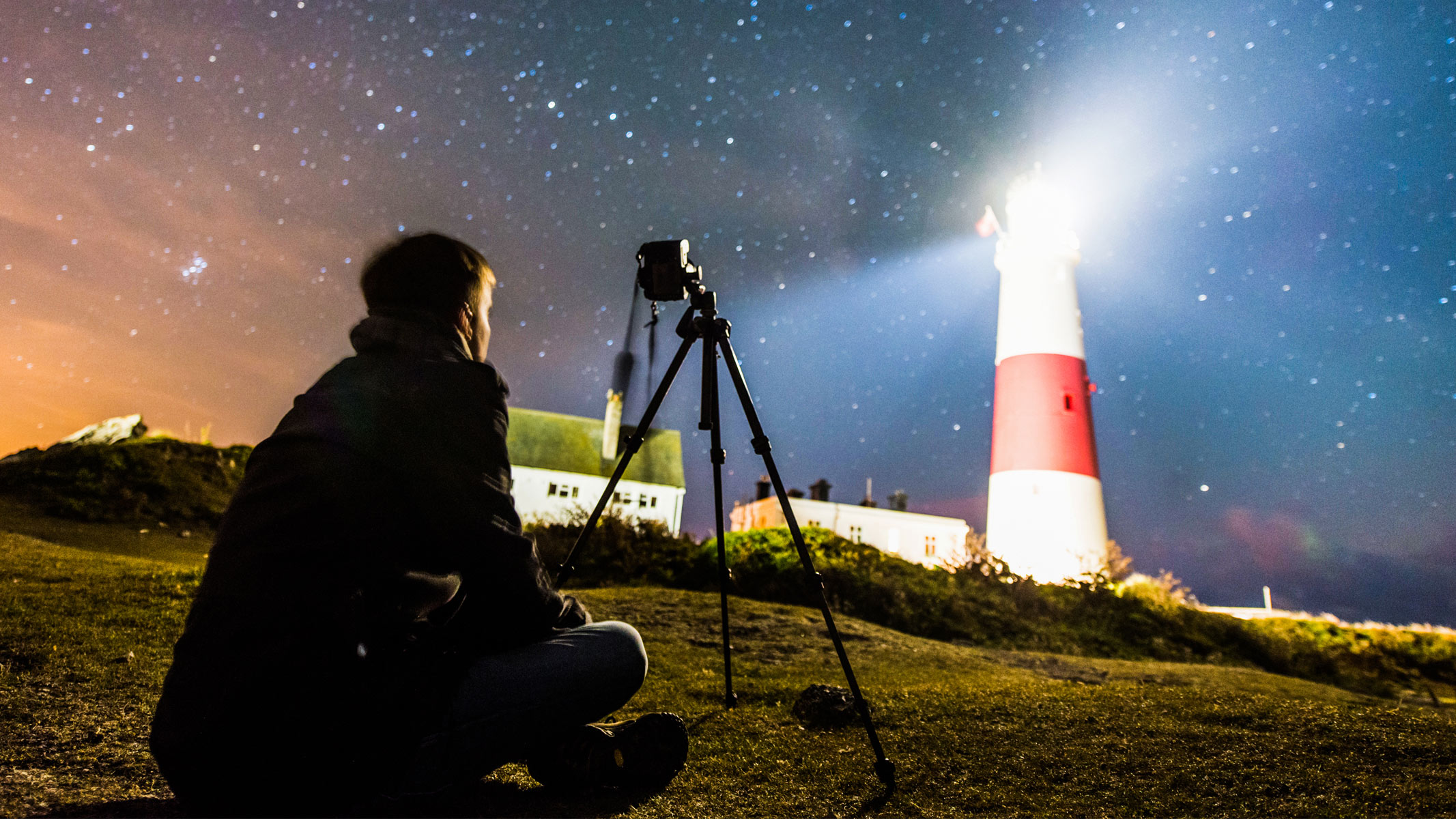

Tripod
As astrophotography requires long exposure times, a sturdy tripod is essential to produce a steady image. Manfrotto and Lowepro make some pretty good and affordable tripods for beginners.
Shutter release
Having a remote shutter release can make life a lot easier when shooting the night sky, as you eliminate the risk of moving the camera when pressing the shutter button. These are very affordable and easy to keep in your camera bag, although you can use the timer setting on your camera if you prefer.
Star tracker
Once you get a bit more advanced, you could also consider investing in a star tracker. These are particularly useful if you want to take a lot of shots to stack them as the star tracker will move the camera in alignment with the Earth's rotation, meaning you won't have to readjust your composition.
Filters
Once you're a bit more confident, you might also want to look at astro lens filters. These can correct any weird color casts creeping into your image, help reduce light pollution and make stars look better.
Headlamp
A headlamp is an affordable lifesaver when it comes to astrophotography, particularly if it has a red light, which can help preserve your night vision. Just make sure you turn it off when the shutter is open.
Warm clothing
It's important to stay warm when you're out shooting for long hours in the dark. You'll want to wear lots of thin layers as opposed to less thick layers. We've found a combination of a moisture-wicking base layer, then a mid-layer for warmth and insulation, and an outer layer on top is a good starting point. This is in addition to a hat, scarf and gloves with which you can still operate your camera while wearing.
In regards to shoes, we spoke to our friend who lives in the Arctic Circle about how to keep your feet warm, and they said you want big shoes with a thick sole to keep you far away from the cold ground, plus thermal socks and a good pair of thick wool or cashmere socks, making sure there's enough space to wiggle your toes and warm up the air in your shoes. More socks = less space = colder feet.
Targets in the sky
Now that you’ve got your gear and your location sorted, you can start finding things in the sky to photograph. If you want to shoot wide-angle, shooting the Milky Way can be a great way to hone your astro skills. For longer focal lengths, photographing the moon is a good starting place. If you can figure out when and where the moon will be rising, you can get some fantastic images of it alongside other focal points, like trees or buildings.
This aspect of astrophotography is what takes planning as you need to know when a certain object is going to be visible in the sky and at what time of night (or even what time of year). There are a ton of great smartphone apps out there that are good for this, such as Stellarium (free), The Photographer’s Ephemeris (sign up for free) and PhotoPills ($10.99 but jam-packed full of handy features) to name a few.

Once you find an object you want to shoot, these apps can show you where exactly it’s going to be throughout the night so you can plan your composition accordingly. Milky Way season is usually somewhere between late February to late September, with July being the peak. By using one of those apps, you can wait until the exact right moment to make the Milky Way line up with any other subjects in your image.
In general, you want to make sure you’re shooting on a clear night, at either a new moon or when the moon isn’t visible in the sky as that will create more light — unless the thing you want to shoot is the moon! Be sure to keep tabs on the upcoming phases of the moon so you can get that perfect picture.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Kimberley Lane, E-commerce writer for Live Science, has tested a wide range of optics equipment reviewing cameras, lenses and tripods, and getting hands-on observations with binoculars and more. Also a landscape & seascape photographer living in South Wales, she aims to portray a feeling of calm and peaceful moments through her images. Her work has also been featured in a number of national photography magazines and she regularly contributes to our sister site Space.com.
- Kat BaylyContributing expert
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.










