Rare 400-year-old ship found in German river is a stunningly preserved 'time capsule'
The ship didn't capsize, but "sank almost standing."

Maritime archaeologists in northern Germany have discovered the wreckage of a 400-year-old cargo ship that "sank almost standing," escaped decay from ravenous shipworms and still has the barrels of lime it was carrying for the stone-building industry centuries ago.
The ship, a rare discovery, is from the Hanseatic period, when a group of northern European trade guilds dominated the Baltic and North seas from the 13th to 17th centuries, Live Science previously reported. Wood quickly rots away underwater in this region, and few shipwrecks of this age have ever been found. But maritime archaeologists think the wreck survived beneath the waves because it was quickly engulfed and protected by a layer of fine mud carried there by the river Trave, which leads to the city of Lübeck about 5 miles (8 kilometers) inland.
The remains of the ship were first found in 2020 during a routine sonar survey by authorities of the navigable channel in the Trave. The vessel lies at a depth of about 36 feet (11 meters) in the predominantly saltwater outer stretch of the river, between Lübeck and the port of Travemünde at its mouth to the Baltic Sea.
The wrecked ship was between 66 to 82 feet (20 to 25 m) long and may have been a galliot, a single-masted cargo ship common during the Hanseatic period, Fritz Jürgens, the lead maritime archaeologist on the project and assistant chair of protohistory, medieval and postmedieval archaeology at Kiel University in Germany, told Live Science. At that time, the towns and guilds of northern Germany and elsewhere in Europe made up a successful bloc — the Hansa — that dominated trade throughout the Baltic and the North Sea.
Related: Treasure trove of gold and jewels recovered from a 366-year-old shipwreck in the Bahamas
The layer of river mud over the wreck may have prevented it from being colonized by Teredo navalis, a type of saltwater clam called "shipworm" that rapidly eats submerged wood, Jürgens said. The bivalve quickly destroys wooden wrecks in the western Baltic region, but it doesn't live in the colder waters of the eastern Baltic; as a result, centuries-old wooden wrecks like the one in the Trave are almost never found in the west, he said.
Quicklime cargo
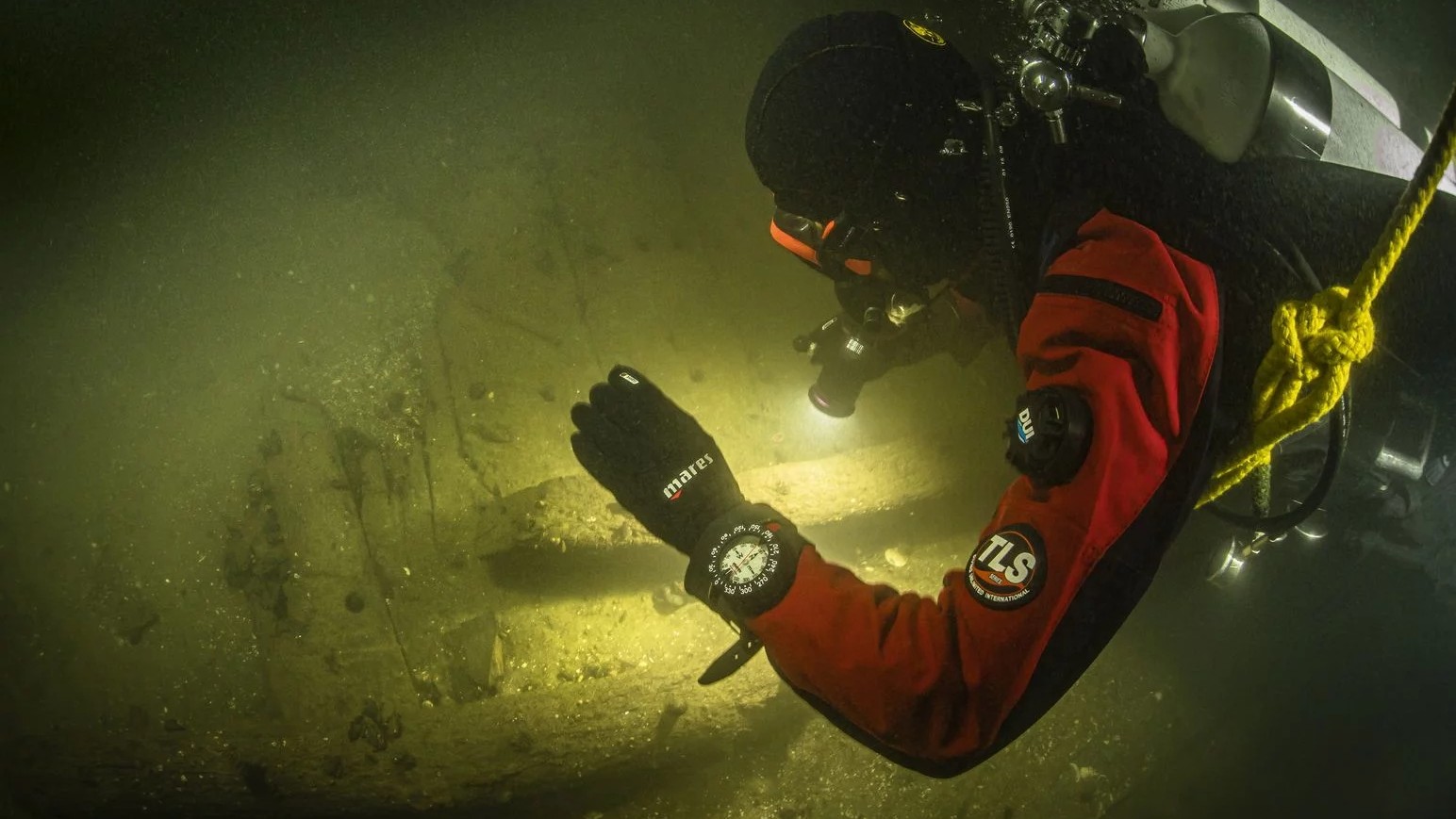

About 150 wooden barrels found almost intact on or near the wreck indicate that the ship was carrying a cargo of quicklime when it sank in the late 17th century. Quicklime is made by burning limestone and is a crucial ingredient for the mortar used in stonework.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"The source for this would have been Scandinavia — in the middle of Sweden or in the north of Denmark," Jürgens said. "We know that this cargo was coming from there, most likely to Lübeck, because northern Germany has no big sources of limestone."
Historical research may have pinpointed the date of the shipwreck to December 1680. A letter from that date in the Lübeck historical archives shows that the voight, or bailiff, of Travemünde asked an unknown recipient to recover the cargo of a galliot that had run aground in the river. That fits with what is known of the Trave shipwreck, Jürgens said, including the results of a dating technique called dendrochronology, which revealed that patterns of tree rings visible in its timbers were from trees felled in the 1650s.
It's likely that the ship had been turning before its entry into Lübeck, when it ran aground on a shoal in the river — a shallow area that still exists today and still threatens ships that don't know about it. It's possible that 17th-century workers recovered some of the ships' cargo, causing the ship to refloat; but the vessel soon sank due to leaks caused when it struck the shoal, he said.
The submerged wreck and its cargo have now been photographed in place by Christian Howe, a scientific diver based in Kiel, and the entire ship is expected to be raised from the riverbed over the next few years so that it doesn't move again and present a danger to modern shipping in the region, Jürgens said.
Historic wreck
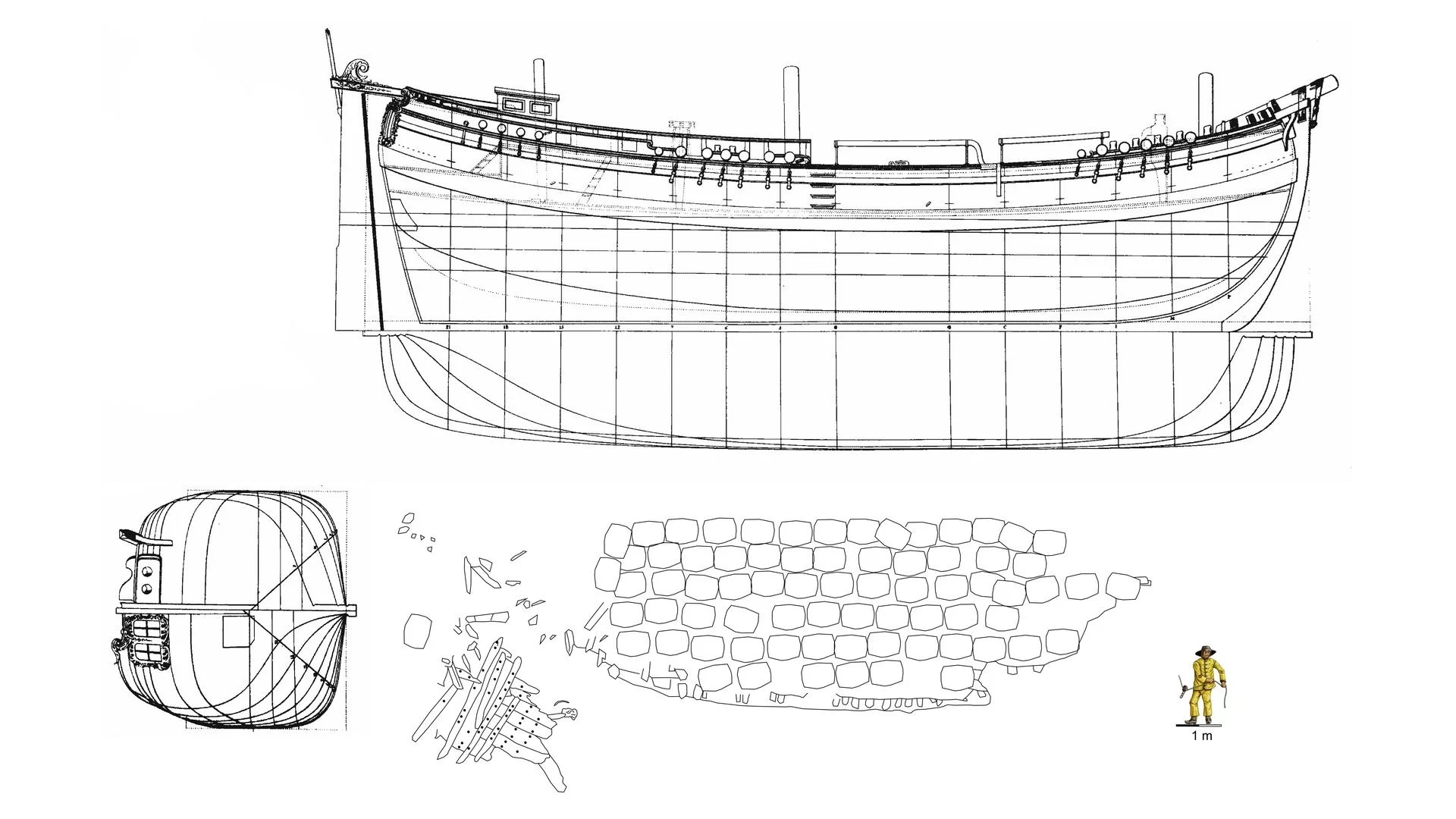
Lübeck was famous for shipbuilding in the Hanseatic period, so it's possible the ship was built there. But such vessels were common throughout the region at the time the ship sank in the Trave, so perhaps it was constructed elsewhere in Europe, said Manfred Schneider, the head of Lübeck's archaeology department and a leader on the project to salvage the ship.
Related: Head of Hercules and other treasures found on Roman 'Antikythera Mechanism' shipwreck
The wreck is notable for its remarkable state of preservation, not only due to the lack of infestation by shipworms and other marine organisms but also because of its weighty cargo.
"There are still about 70 barrels in their original location on the ship, and another 80 barrels in the immediate vicinity," Schneider told Live Science in an email. "The ship therefore sank almost standing and did not capsize." He added that archaeologists may uncover further archaeological finds in the sediment that fills the ship's interior.
Raising the ship from the riverbed will give archaeologists a chance to fully investigate the hull and its construction, and perhaps identify its origin. "The salvage will probably also uncover previously unknown parts of the wreck that are still hidden in the sediment," Schneider said, such as rooms for the ship's crew in the stern that may still hold everyday objects from the 17th century.
Although Lübeck was a center for Baltic trade during the Hanseatic period, very few authentic maritime objects from that time had survived, Schneider said, so the discovery of almost an entire ship from this era is remarkable. "We have something like a time capsule that transmits everything that was on board at that moment," he said. "It throws a spotlight on the trade routes and transport options at the end of the Hanseatic period."
Originally published on Live Science.
Tom Metcalfe is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor who is based in London in the United Kingdom. Tom writes mainly about science, space, archaeology, the Earth and the oceans. He has also written for the BBC, NBC News, National Geographic, Scientific American, Air & Space, and many others.