Rare mud volcano explodes into towering inferno in Caspian Sea
The enormous flames were visible from the mainland.

A towering inferno, hundreds of feet tall, burned above the Caspain Sea on Sunday (July 4) after a massive explosion in Azerbaijan's oil and gas fields. The culprit? A mud volcano, authorities now say.
The blast occurred around 9:30 p.m. local time (1:30 p.m. ET) around 6 miles (10 kilometers) from the Umid gas field, which is 45 miles (75 km) off the coast of Azerbaijan's capital Baku, and it continued to burn into Monday morning, according to the BBC.
Local authorities initially suspected an accident at one of the multiple oil and gas rigs in the area, but the state oil company SOCAR later announced that preliminary investigations had deemed the cause of the explosion to be a mud volcano, and that none of its platforms had been damaged, according to The Guardian.
Related: The world's five most active volcanoes
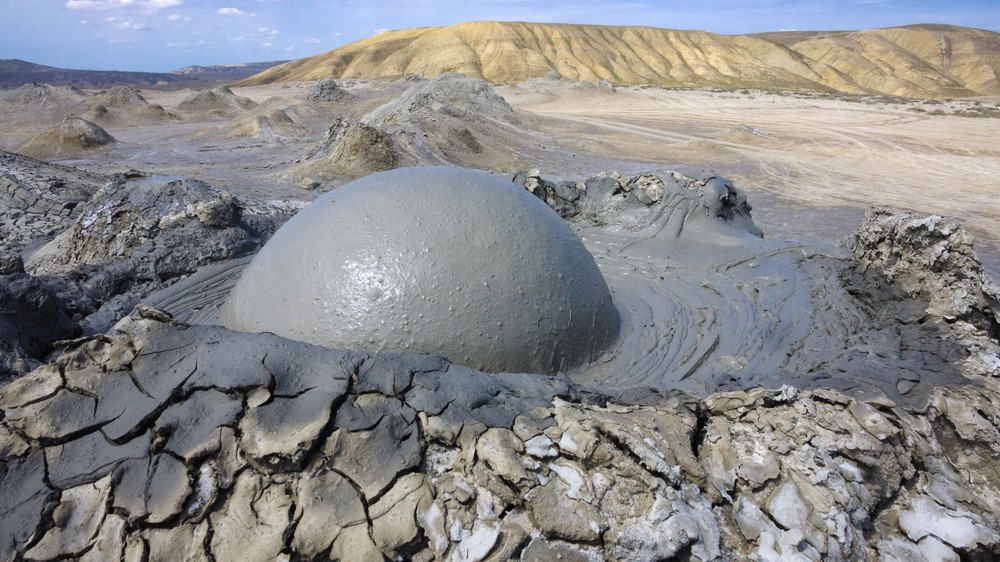

Mud volcanoes are a rare type of volcano that erupt a superheated slurry of mud and water instead of lava, which means they don't get as hot as regular volcanoes. However, they also contain high concentrations of natural gases that build up inside them, which can be ignited by sparks created by fast-moving rocks and boulders beneath the surface during eruptions. This is believed to be what caused the recent inferno in the Caspian Sea.
Azerbaijan has around 400 of the roughly 1,000 mud volcanoes on Earth, which, along with its abundance of oil and gas reserves, has earned the country the nickname "Land of Fire," according to the BBC.
"The mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan are some of the biggest and most violent in the world," Mark Tingay, a geophysicist and mud volcano expert at the University of Adelaide in Australia, said on Twitter. "There are, on average, several large mud volcano eruptions each year, and many of them can have big fires."
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Most mud volcanoes are situated on small islands created by their eruptions, but some are hidden below the surface and form temporary peaks above the water when active, Tingay said.
The most recent explosion is now confirmed to have occured at the Dashly Island mud volcano, also known as Ignatiy Stone Bank, Tingay said.
Originally published on Live Science.

Harry is a U.K.-based senior staff writer at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to become a journalist. He covers a wide range of topics including space exploration, planetary science, space weather, climate change, animal behavior and paleontology. His recent work on the solar maximum won "best space submission" at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the "top scoop" category at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He also writes Live Science's weekly Earth from space series.