Chemistry news, features and articles
Explore Chemistry
Editor's Picks
Latest about Chemistry

Can foxgloves really give you a heart attack?
By Victoria Atkinson published
Foxgloves contain digoxin, a drug used to treat cardiac arrhythmia and heart failure that can also be toxic. But can ingesting it cause a heart attack?

Is hydrogen a metal?
By Hannah Loss published
Hydrogen is not a metal on Earth, but scientists keep trying to create metallic hydrogen under high pressure to unlock a new superconductor.

States of matter: Definition and phases of change
By Mary Bagley last updated
Reference The four fundamental states of matter are solid, liquid, gas and plasma, but there others, such as Bose-Einstein condensates and time crystals, that are man-made.
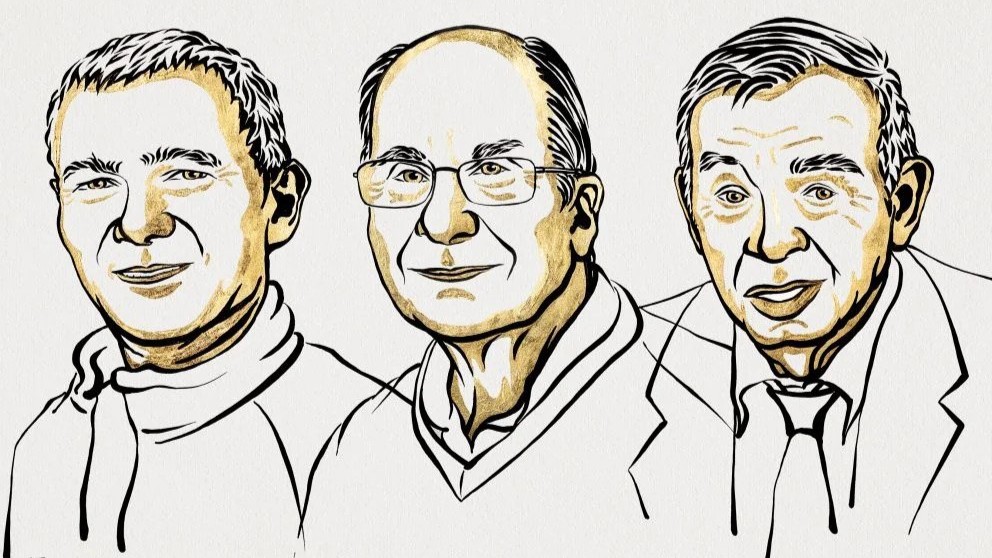

Nobel Prize in chemistry awarded to trio who discovered bizarre quantum dots
By Ben Turner published
Moungi Bawendi, Louis Brus and Alexei Ekimov will share the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their discovery of strange nanoparticles that change color according to their size.
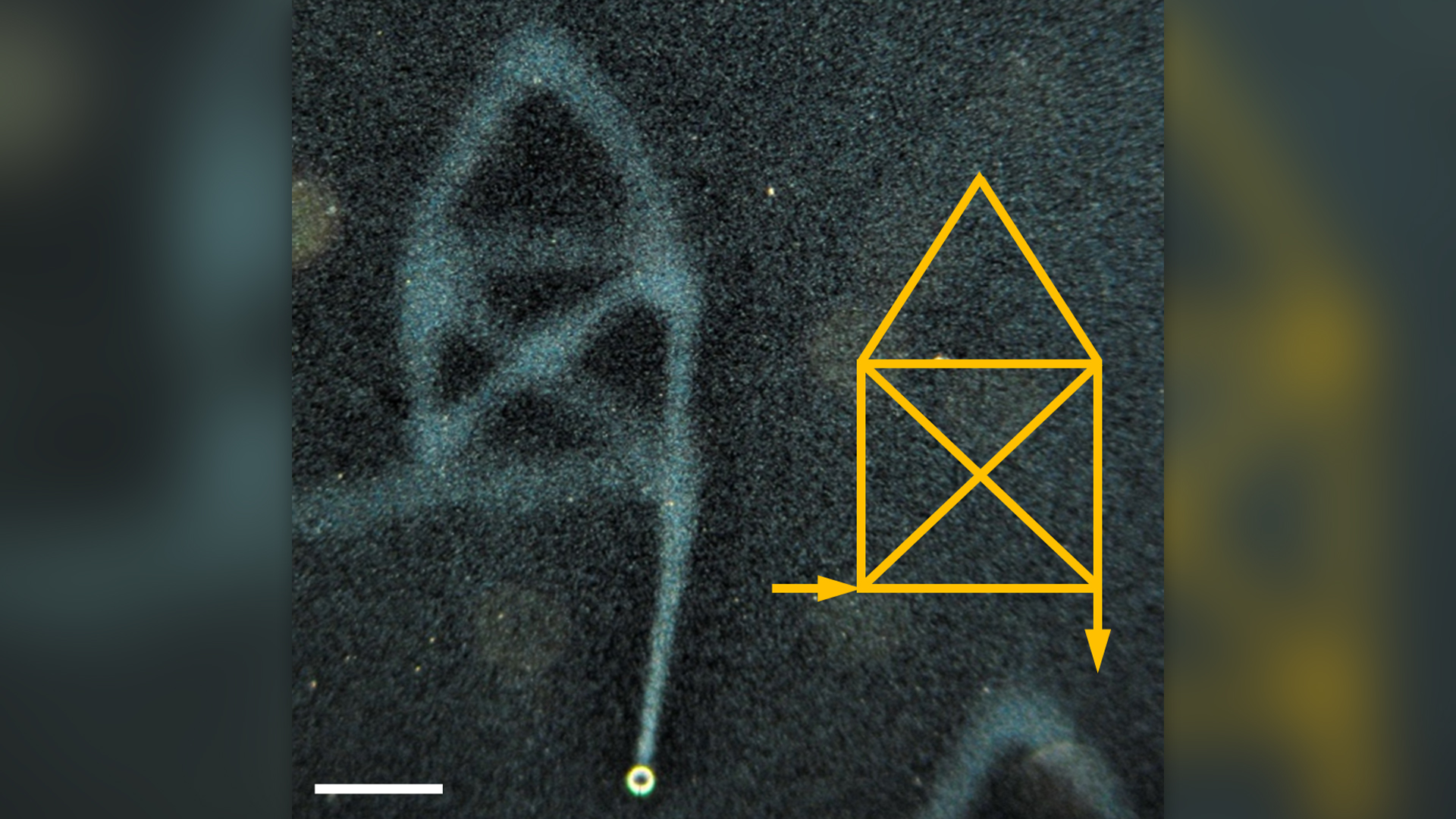
For 1st time, scientists write words in liquid water
By Victoria Atkinson published
Scientists used a process called 'diffusioosmosis' to write words that lingered in liquid water.

What's the highest temperature water can freeze, and the lowest it can boil on Earth?
By Cameron Duke published
Ice can form on Earth at temperatures above 32 degrees Fahrenheit (0 degrees Celsius), and water can boil below 212 F (100 C). Here's how.

Is glass a liquid or a solid?
By Victoria Atkinson published
Glass has unique properties, but is it a solid or a liquid, or does it fall into its own scientific category?

Roman glass keeps turning into photonic crystals. Scientists finally know why
By Ben Turner published
Analysis of the microscopic structure of an ancient shard of Roman glass has revealed how photonic crystals form, and might enable them to be grown.
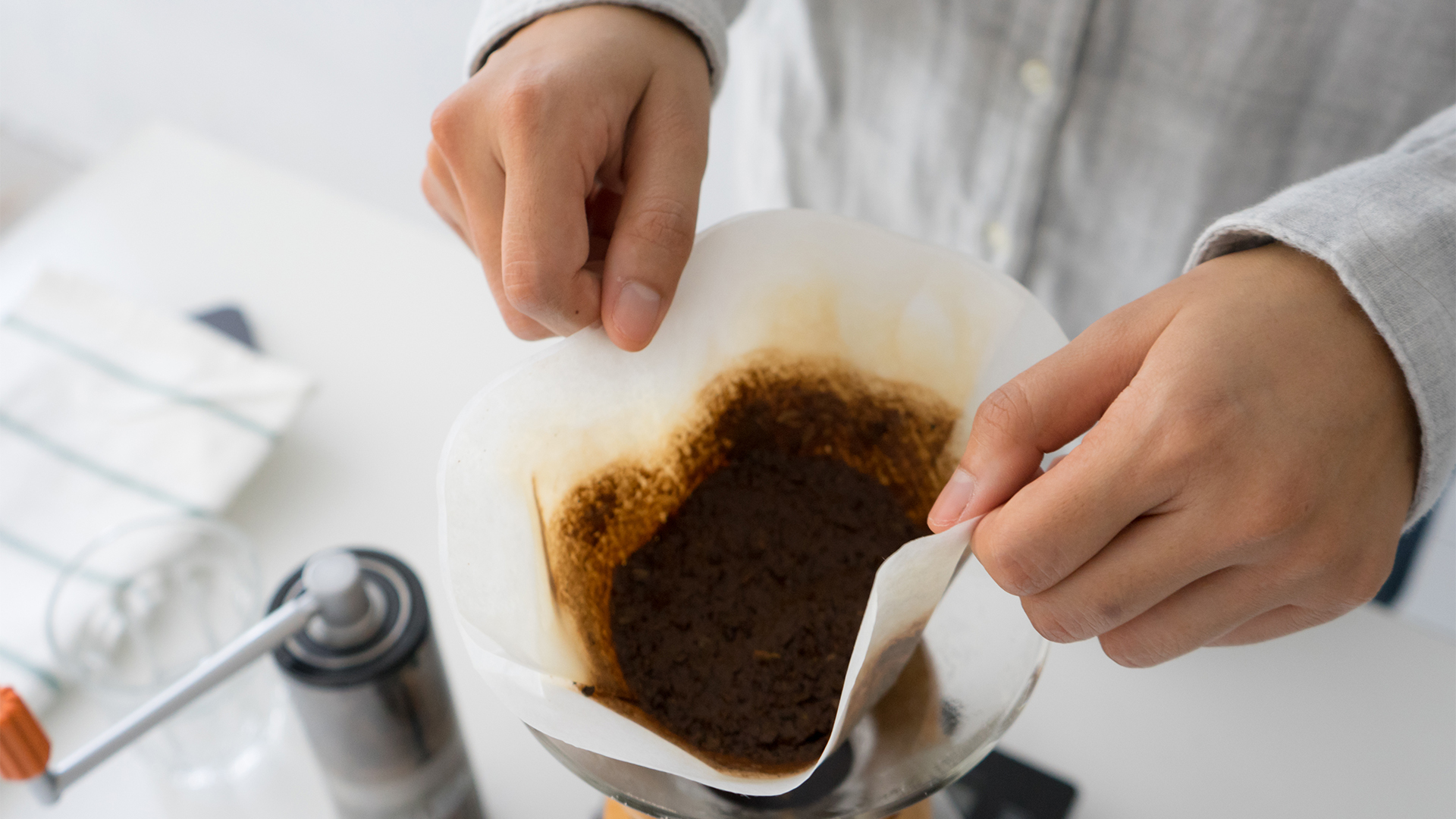

Used coffee grounds make concrete 30% stronger
By Victoria Atkinson published
Used coffee grounds that are heat treated increase the compression strength of concrete.

Scientists manipulate quantum mechanics to slow down a chemical reaction by 100 billion times
By Stephanie Pappas published
Using a quantum device, researchers have observed, for the first time, a molecular process called conical intersection that is important in reactions such as photosynthesis.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.



