Medicine
Explore Medicine & Drugs
Latest about Medicine & Drugs

CBD reportedly discovered in plant that's not cannabis
By Emily Cooke published
Scientists say they've discovered CBD in a shrub that belongs to the same family as cannabis, although they've yet to publish the research.

Do traditional Chinese herbs actually 'heal'? This tool aims to find out.
By Emily Cooke published
A new tool may be able to predict the effectiveness of herbs used in traditional Chinese medicines — but what do experts think of its assessments?

RSV drug shortage prompts CDC to adjust recommendations
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A new antibody shot called Beyfortus was recently approved to protect babies from RSV, but it's in short supply this season.
Will we still have antibiotics in 50 years? 7 experts weigh in
By Lori L. Burrows, Yori Yuliandra, Fidelma Fitzpatrick, Roy Robins-Browne, Raúl Rivas González, Juliana Côrrea, André O. Hudson published
Experts across public health, microbiology and biochemistry agree that we'll still have antibiotics in 50 years, but the drugs may take a different form than those we have today.
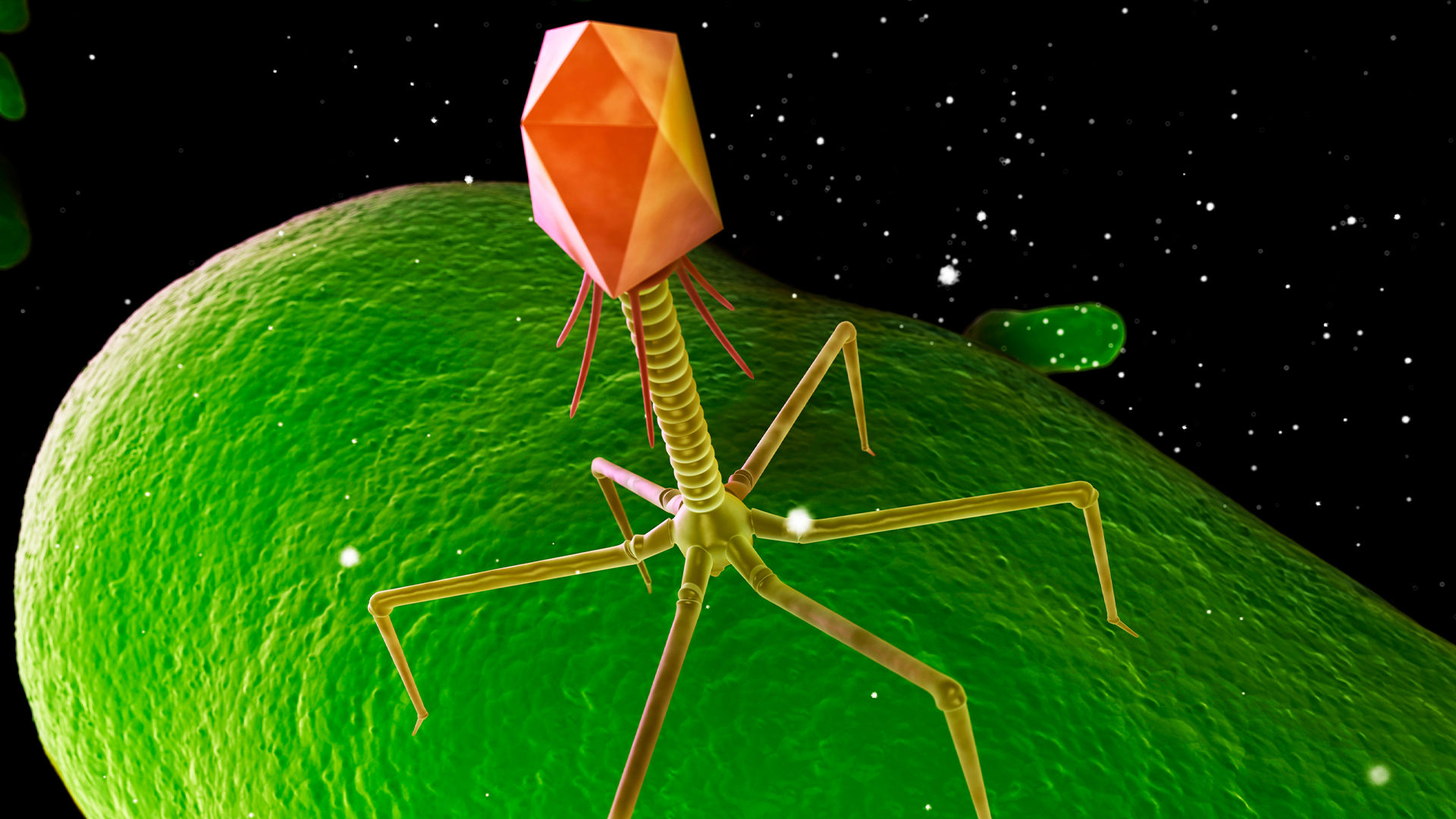
Could bacteria-killing viruses ever prevent sexually transmitted infections?
By Kamal Nahas published
The CDC will soon recommend that some people take a "morning-after" antibiotic to lower their risk of STIs. But someday, it's possible that bacteria-killing viruses could do this without driving antibiotic resistance.
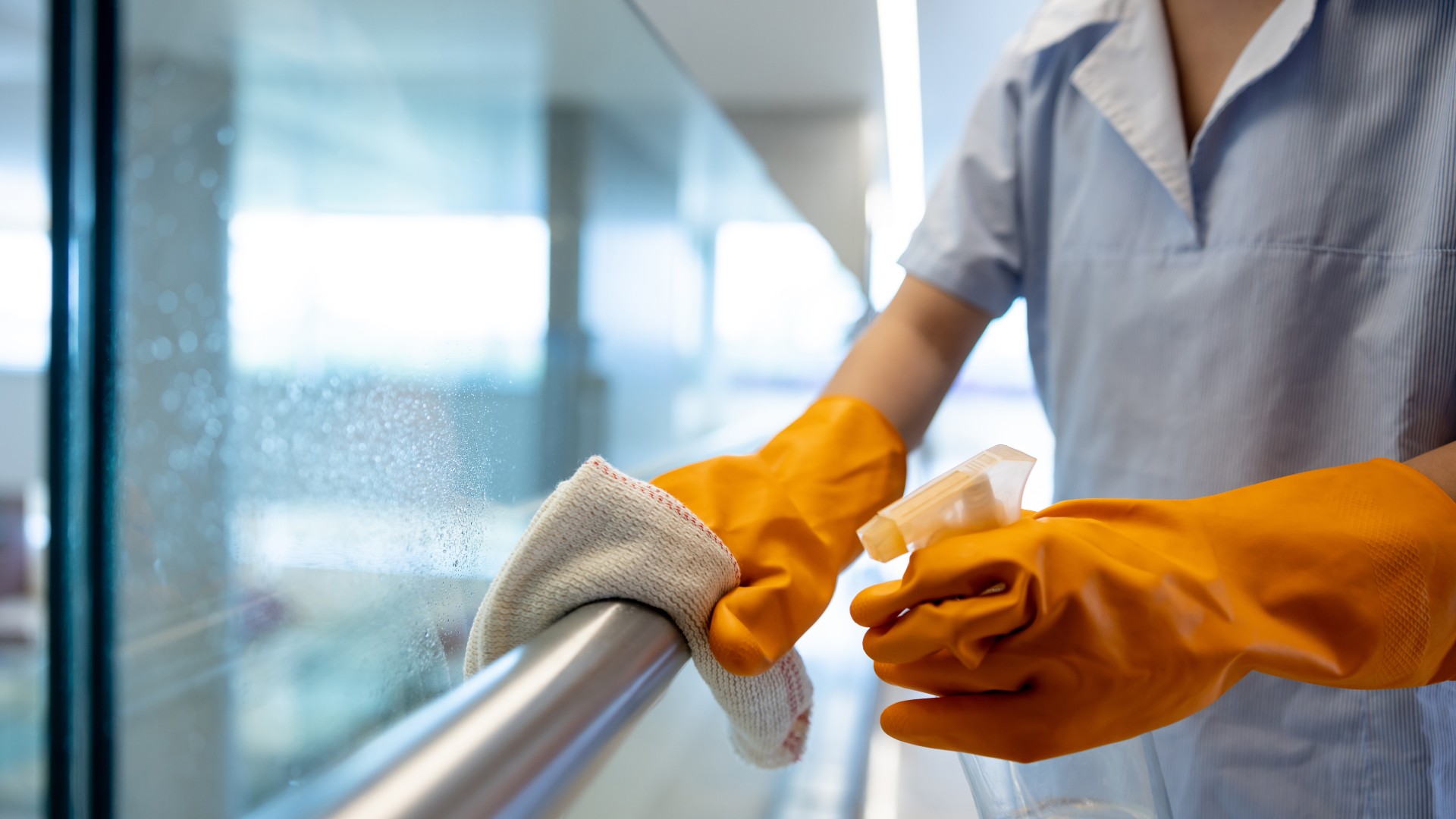

Cleaning product residues may be driving a deadly superbug's antibiotic resistance
By Emily Cooke published
When exposed to low levels of disinfectants and antiseptics in the lab, a bacterium that sickens thousands in the U.S. every year becomes more tolerant to antibiotics.
Ozempic-like meds linked to higher risk of pancreatitis, 'stomach paralysis' than other weight-loss drugs
By Nicoletta Lanese published
GLP-1 agonists like Ozempic come with a higher risk of severe GI issues than a different common weight-loss drug does.

Psychedelics rapidly change the brain. Here's how.
By Edmund S. Higgins published
New research hints at how psychedelics trigger rapid, lasting change at the neuronal level.
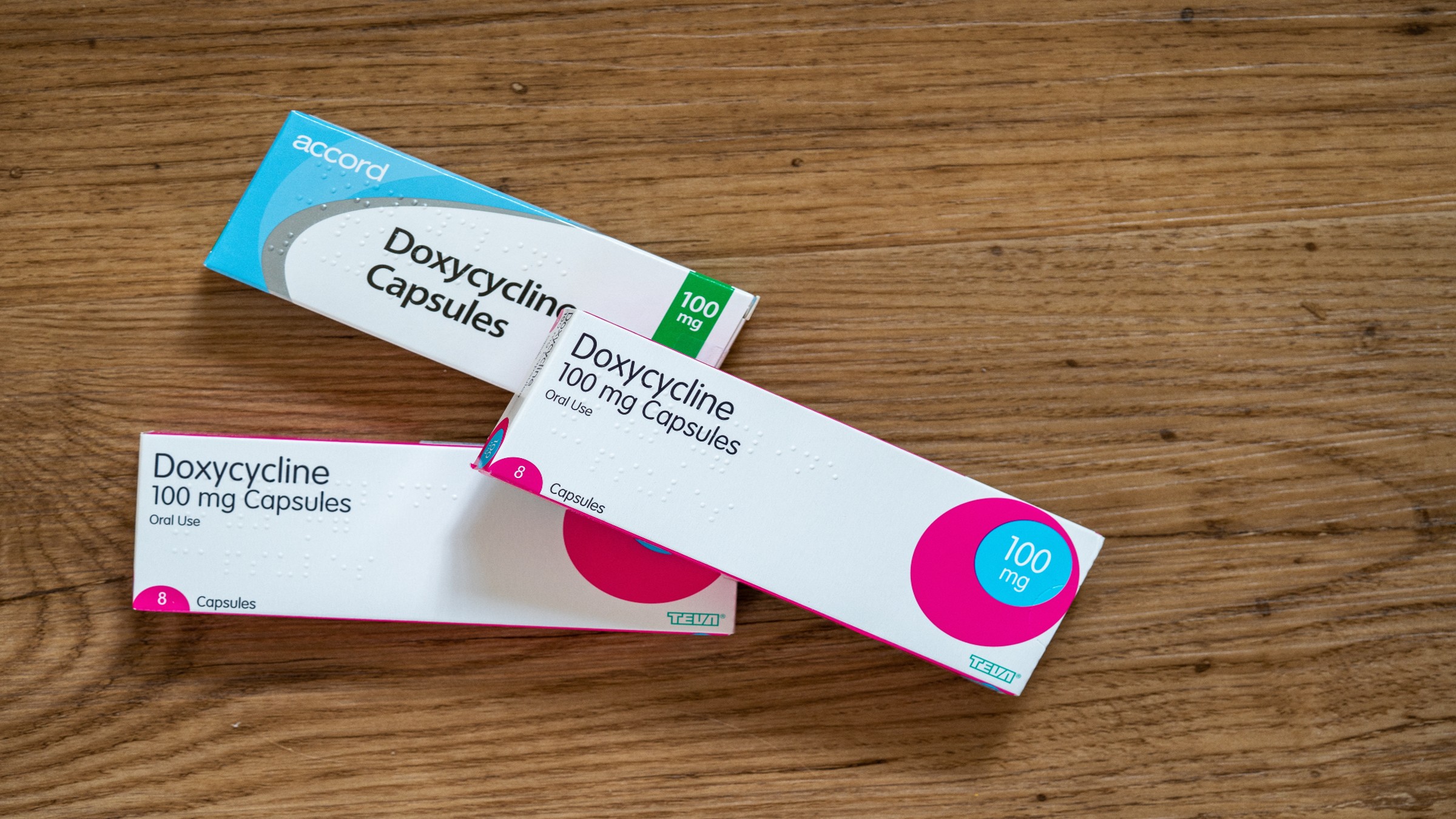
CDC to recommend some people take an antibiotic after sex to prevent sexually transmitted infections
By Nicoletta Lanese published
The CDC issued a draft of its guidance for how and when the antibiotic doxycycline should be used as a preventive treatment for STIs, a regimen known as doxy-PEP.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

