Virus
A virus is defined as any of a various number of submicroscopic parasites that can infect any animal, plant or bacteria and often lead to very serious or even deadly diseases. A virus consists of a core of RNA or DNA, generally surrounded by a protein, lipid or glycoprotein coat, or some combination of the three. No virus can replicate without the help of a host cell, and though they can be spread, viruses lack the ability of self-reproduction and are not always considered to be living organisms in the regular sense.Some of the most common or best known viruses include the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which is the virus that causes AIDS, the herpes simplex virus, which causes cold sores, smallpox, multiple sclerosis, and the human papilloma virus, now believed to be a leading cause of cervical cancer in adult women. The common human cold is also caused by a virus.Since a great deal of mystery still surrounds the origins of most modern viruses, ways to cure these viruses and the diseases they cause are still in the very early stages of development.
Latest about Viruses, Infections & Disease
-
-

Measles has long-term health consequences
By Stephanie Pappas Published
-
Oregon officials investigating 3 cases of mad cow-like disease
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
The exceptionally rare disease that causes holes to form in your brain
By Emily Cooke Last updated
-
'Flesh-eating' infections that liquefy tissues can affect the vulva, doctors warn
By Jess Thomson Published
-
Sickle cell 'crises' linked to menstrual cycle
By Jennifer Zieba Published
-

The science behind the 10 plagues of Egypt
By Live Science Staff Last updated
-

Flu: Facts about seasonal influenza and bird flu
By Mindy Weisberger Published
-
Explore Viruses, Infections & Disease
Alzheimers & Dementia
-
-

Man nearly guaranteed to get early Alzheimer's is still disease-free in his 70s — how?
By Marianne Guenot Published
-
'Reanimated' herpes viruses lurking in the brain may link concussions and dementia
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Nearly half of global dementia cases could be delayed or prevented, scientists say
By Eric B. Larson Published
-
'Look at all this we don't understand': Study unravels whole new layer of Alzheimer's disease
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Active ingredient in Viagra tied to lower Alzheimer's risk — but don't get too excited
By Emily Cooke Published
-
Alzheimer's may be caused by immune cells thinking brain cells are bacteria, expert says
By Donald Weaver Published
-
Alzheimer's is transmissible in extremely rare scenarios
By Emily Cooke Published
-

Alzheimer's comes in at least 5 distinct forms, study reveals
By Emily Cooke Published
-
Brain inflammation may drive mood changes in Alzheimer's
By Emily Cooke Published
-
Cancer
-
-

'Fingerprints of cancer' found after scientists flash infrared light pulses at blood samples
By Emily Cooke Published
-

Simple blood tests could be the future of cancer diagnosis
By Emily Cooke Published
-

When is cancer considered cured, versus in remission?
By Emily Cooke Published
-
CDC data reveal plummeting rate of cervical precancers in young US women — down by 80%
By Emily Cooke Published
-

What are cancer vaccines?
By Marilyn Perkins Published
-
Why America is losing its 50-year 'war on cancer,' according to scientist Nafis Hasan
By Nafis Hasan Published
-
The 10 deadliest cancers, and why there's no cure
By Ashley P. Taylor Last updated
-
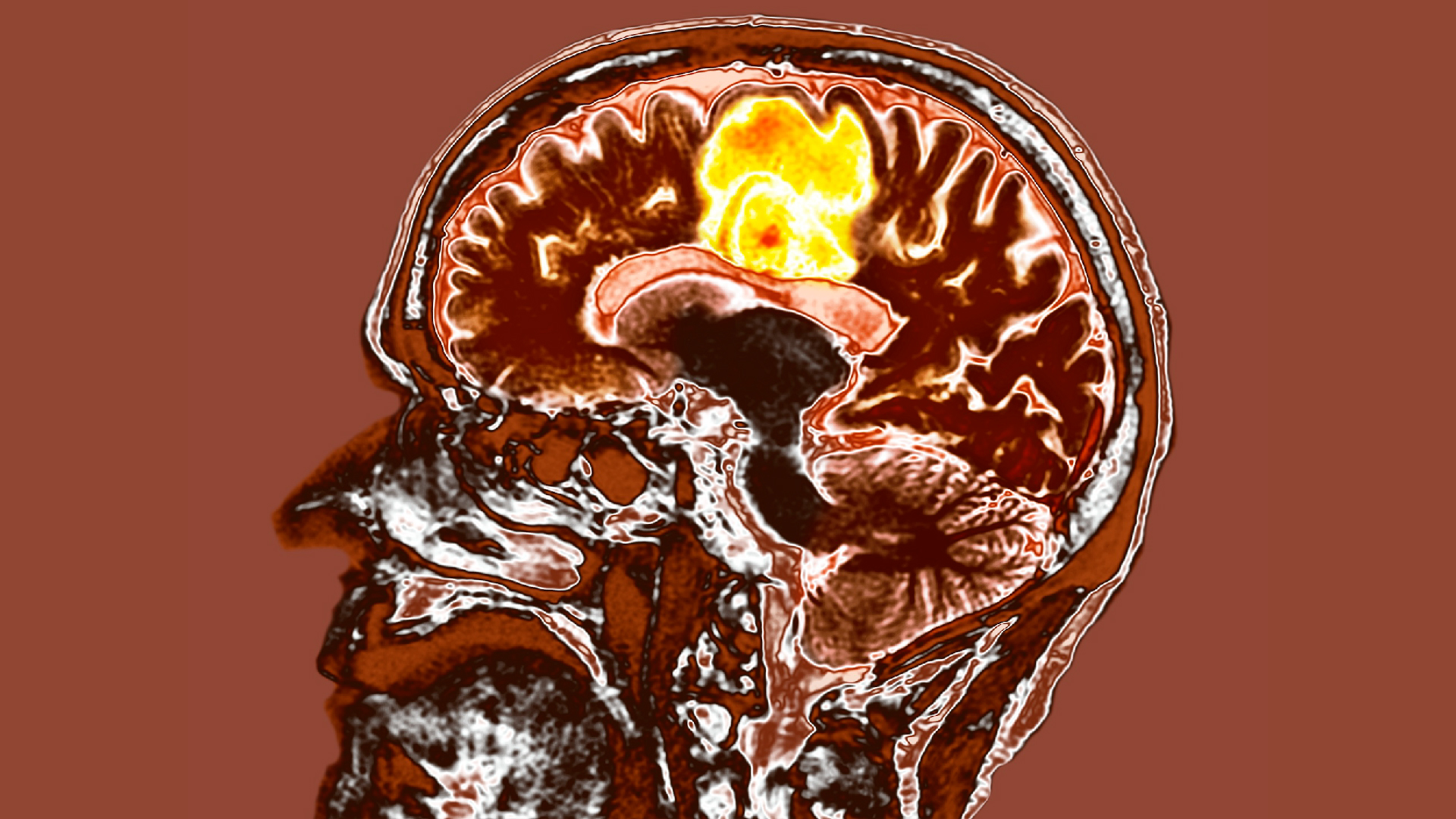
New treatment for most aggressive brain cancer may help patients live longer
By Stephanie Pappas Published
-
Healthy breast cells can look like invasive cancer, complicating early diagnosis
By Kristel Tjandra Published
-
Coronavirus
-
-

1 in 22 COVID survivors develop debilitating chronic syndrome
By Clarissa Brincat Published
-

Older adults should get 2 doses of the updated COVID shot, CDC says
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Newfound autoimmune syndrome tied to COVID-19 can trigger deadly lung scarring
By Stephanie Pappas Published
-

COVID pandemic knocked 1.6 years off global life expectancy, study finds
By Sascha Pare Published
-

Vaccines slash risk of long COVID, studies show
By Shannon Hall Published
-

Rare clotting effect of early COVID shots finally explained — what could that mean for future vaccines?
By Stephanie Pappas Published
-
Can antiviral drugs prevent long COVID?
By Ziyad Al-Aly Published
-

Injection might help long COVID patients smell normally again
By Rebecca Sohn Published
-
Who should get the new COVID vaccines? What to know about the 2023-2024 shots
By Nicoletta Lanese Last updated
-
Ebola
-
-
Ebola: Causes, symptoms, treatments & vaccines
By Alina Bradford Published
-

Ebola can linger in brain fluid and trigger deadly relapse, monkey study suggests
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Ebola may have lingered in a survivor for 5 years before sparking new outbreak
By Yasemin Saplakoglu Published
-

Japan Just Imported Ebola to Prep for Possible Olympic Outbreak
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Patient Tested for Ebola in Pennsylvania
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

Anti-Vaccine Movement Joins Ebola, Drug Resistance on List of Top Global Threats
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

Scientists Discover a Sixth Species of Ebola Virus — in Bats
By Kimberly Hickok Published
-
How Bats Could Help Scientists Stop Ebola Outbreaks Before They Start
By Nidhi Sharma Published
-

Here's How Health Officials Plan to Use the Ebola Vaccine in New African Outbreak
By Tereza Pultarova Published
-
Ebola
-
-

Ebola: Causes, symptoms, treatments & vaccines
By Alina Bradford Published
-

Ebola can linger in brain fluid and trigger deadly relapse, monkey study suggests
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Ebola may have lingered in a survivor for 5 years before sparking new outbreak
By Yasemin Saplakoglu Published
-

Japan Just Imported Ebola to Prep for Possible Olympic Outbreak
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Patient Tested for Ebola in Pennsylvania
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

Anti-Vaccine Movement Joins Ebola, Drug Resistance on List of Top Global Threats
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

Scientists Discover a Sixth Species of Ebola Virus — in Bats
By Kimberly Hickok Published
-

How Bats Could Help Scientists Stop Ebola Outbreaks Before They Start
By Nidhi Sharma Published
-

Here's How Health Officials Plan to Use the Ebola Vaccine in New African Outbreak
By Tereza Pultarova Published
-
Flu
-
-

Flu: Facts about seasonal influenza and bird flu
By Mindy Weisberger Published
-

Brain damage reported in 13% of kids who have died of flu this season, CDC finds
By Patrick Pester Published
-
This year's flu shot was up to 78% effective at preventing hospitalization in kids, early data finds
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

The US is having its most active flu season in 15 years
By Hatty Willmoth Published
-

2nd form of bird flu detected in US cows
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

US reports 1st outbreak of 'highly pathogenic' H5N9 virus in poultry. Should we worry?
By Emily Cooke Published
-
1st deadly case of H5N1 bird flu reported in US
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Pet cats in Los Angeles County are catching bird flu from raw food, milk
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Avian influenza: Bird flu spread triggers state of emergency in California
By Pandora Dewan Published
-
HIV
-
-

HIV-funding cuts could lead to nearly 3 million extra deaths by 2030, study suggests
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Single-shot HIV treatment suppresses virus 10,000-fold for months, animal study finds
By Michael Schubert Published
-
HIV prevention drug found 100% effective in clinical trial
By Linda-Gail Bekker Published
-
In a 1st, HIV vaccine triggers rare and elusive antibodies in humans
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
New trial hints at a possible HIV cure approach: Wake up latent virus hiding in the body, then kill it
By Stephanie Pappas Published
-

Teens use HIV prevention meds way more if they get these simple interventions
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-

Kids under 5 with HIV are dying at high rates. Here's why.
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
We could end the AIDS epidemic in less than a decade. Here's how.
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Could CRISPR cure HIV someday?
By Jennifer Zieba Published
-
Zika
-
-

Florida releasing genetically modified mosquitoes to prevent diseases like Zika
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Ebola, Zika & More: How Many Viruses Can Get into Men's Semen?
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

About 10% of Pregnant Women with Zika Had Babies with Birth Defects
By Rachael Rettner Published
-
Zika to Weed: 8 Huge Health Stories from 2016
By Stephanie Bucklin Published
-
Men with Vasectomies Can Still Spread Zika Via Sex, Report Suggests
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

Zika Can Cause Birth Defects in Monkeys Too
By Rachael Rettner Published
-
Zika Pesticide Controversy: Is 'Naled' Dangerous to Human Health?
By Stephanie Pappas Published
-
Crying Zika: Virus Material Found in Tears
By Rachael Rettner Published
-

In Babies, Zika Can Linger for Months, Brazilian Case Suggests
By Rachael Rettner Published
-