Scientists accidentally create 'impossible' hybrid fish
They call it the sturddlefish.
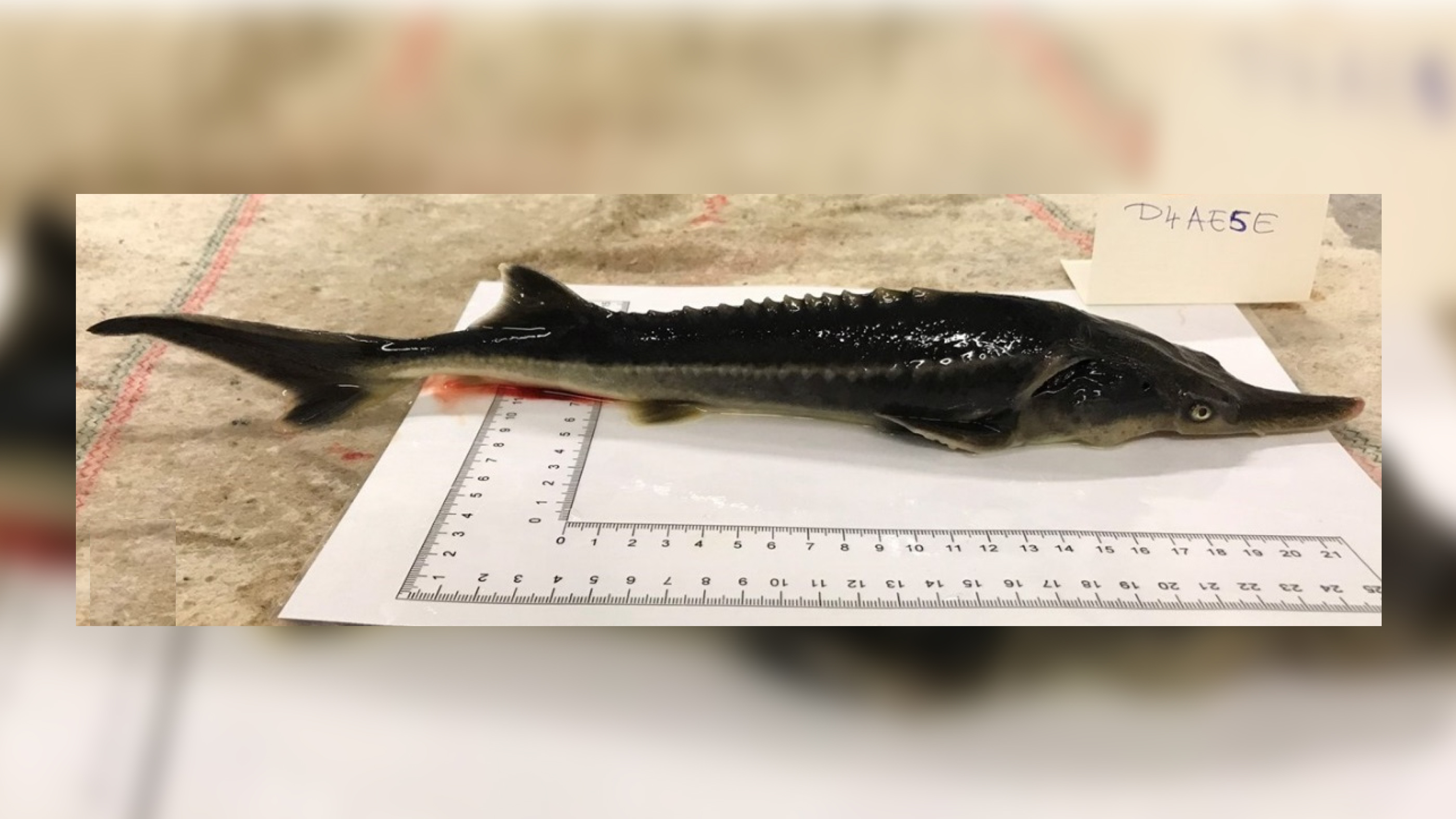

It shouldn't have been possible, but it was: The birth of long-nosed, spiky-finned hybrids of Russian sturgeons and American paddlefish.
Hungarian scientists announced in May in the journal Genes that they had accidentally created a hybrid of the two endangered species, which they have dubbed the "sturddlefish." There are about 100 of the hybrids in captivity now, but scientists have no plans to create more.
"We never wanted to play around with hybridization. It was absolutely unintentional," Attila Mozsár, a senior research fellow at the Research Institute for Fisheries and Aquaculture in Hungary, told The New York Times.
Related: Photos: The freakiest-looking fish
Russian sturgeons (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii) are critically endangered and also economically important: They're the source of much of the world's caviar. These fish can grow to more than 7 feet long (2.1 meters), living on a diet of molluscs and crustaceans. American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) filter-feed off of zooplankton in the waters of the Mississippi River drainage basin, where water from the Mississippi and its tributaries drain into. They, too, are large, growing up to 8.5 feet (2.5 m) long. Like the sturgeon, the have a slow rate of growth and development puts them at risk of overfishing. They've also lost habitat to dams in the Mississippi drainage, according to the University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. The two species last shared a common ancestor 184 million years ago, according to the Times.
Nevertheless, they were able to breed —— much to the surprise of Mozsár and his colleagues. The researchers were trying to breed Russian sturgeon in captivity through a process called gynogenesis, a type of asexual reproduction. In gynogenesis, a sperm triggers an egg's development but fails to fuse to the egg's nucleus. That means its DNA is not part of the resulting offspring, which develop solely from maternal DNA. The researchers were using American paddlefish sperm for the process, but something unexpected happened. The sperm and egg fused, resulting in offspring with both sturgeon and paddlefish genes.
The resulting sturddlefish hatched by the hundreds, and about 100 survive now, according to the Times. Some are just about 50-50 mixtures of sturgeon and paddlefish genes, and some are far more sturgeon-like. All are carnivores, like the sturgeon, and share the sturgeon's blunter nose, compared with the paddlefish's pointy snout.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Most hybrid species, such as the liger (a mix of a lion and a tiger) and the mule (a mix of a horse and donkey), can't have offspring of their own, and the sturddlefish is probably no exception. Mozsár and his colleagues plan to care for the fish, but they won't create more, since the hybrid could outcompete native sturgeon in the wild and worsen the sturgeon's chances of survival.
However, the fact that fish separated by 184 million years of evolution could cross-breed indicates that they're not so different after all.
"These living fossil fishes have extremely slow evolutionary rates, so what might seem like a long time to us isn't quite as long of a time to them," Solomon David, an aquatic ecologist at Nicholls State University in Louisiana, told the Times.
Originally published on Live Science.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.