King Tut's father revealed in stunning facial reconstruction
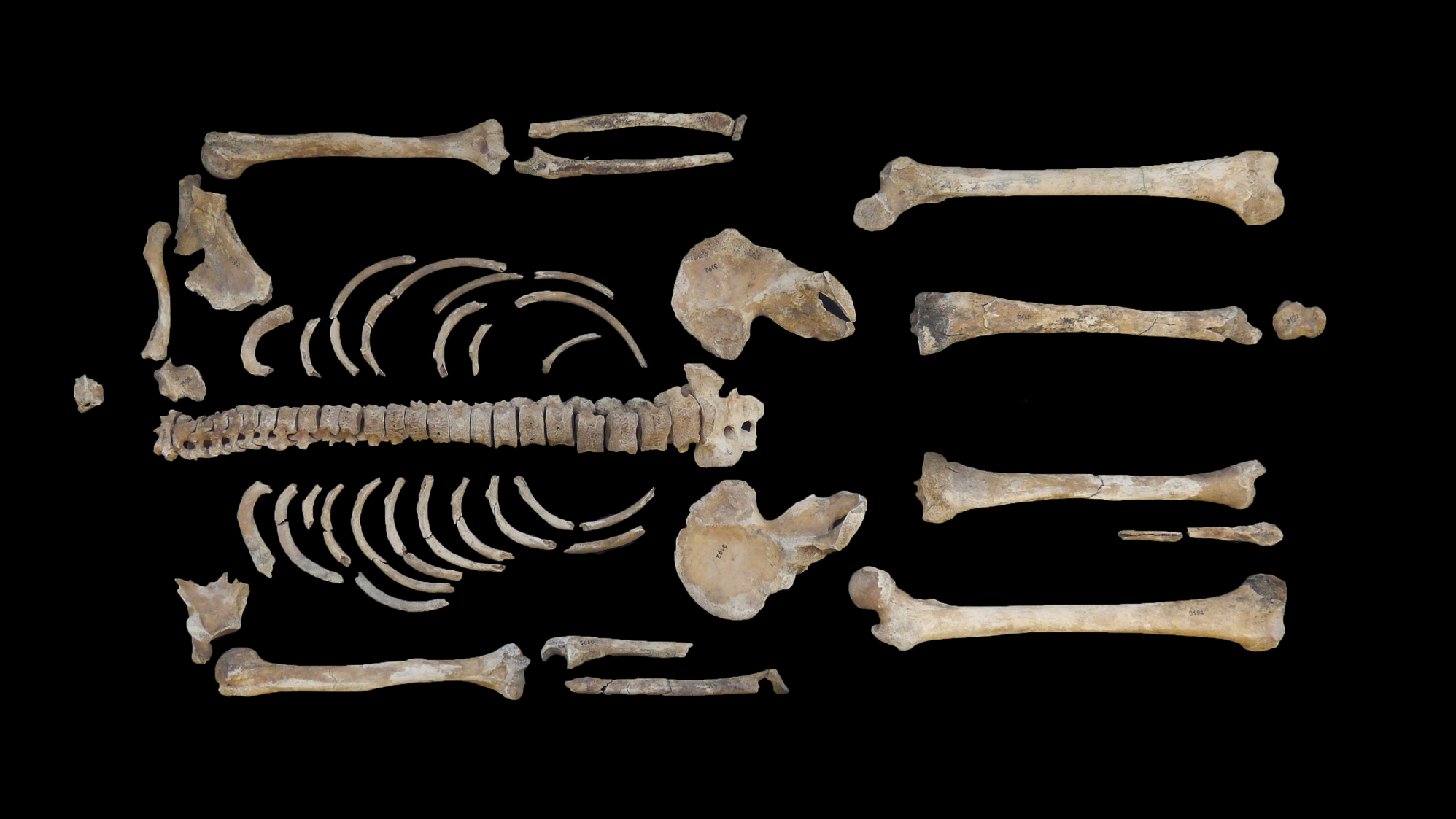
Known as KV 55, the remains were found in 1907 in the Valley of the Kings.
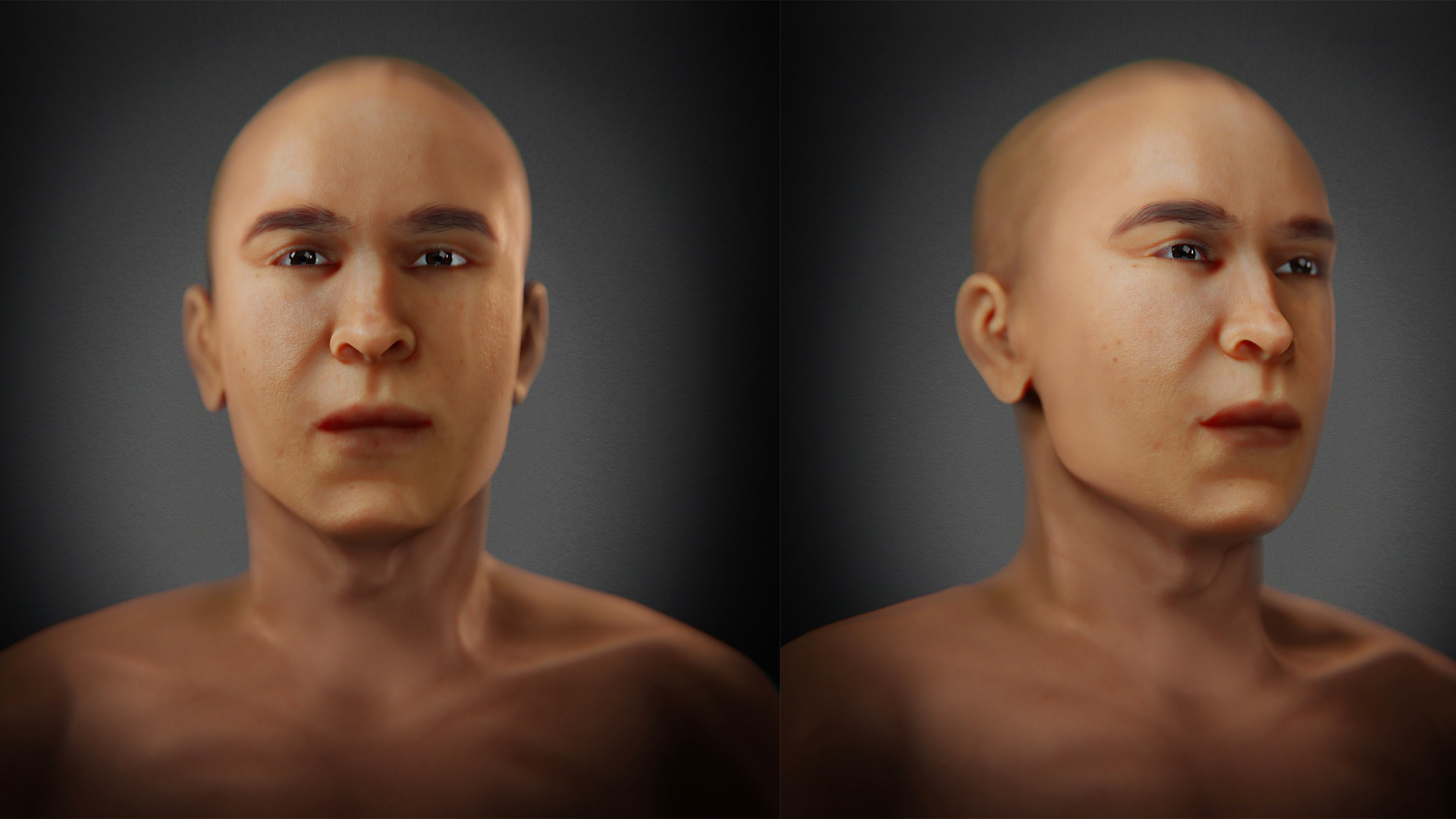
An ancient Egyptian pharaoh that may be King Tut's father has a new face, with regal features and a serene expression shaped by digital reconstruction. Though this is the most accurate reconstruction of the man to date, long-standing questions about his identity remain unanswered.
His remains were found in 1907 in Egypt's Valley of the Kings in tomb KV 55, just a few feet from the tomb of Tutankhamen. More than a century after the tomb's discovery, genetic analysis suggested that the skeleton inside belonged to King Tut's biological father, and other clues in the tomb told archeologists that the man was Akhenaten, who reigned from 1353 B.C. to 1335 B.C. and was the first king to introduce monotheism in Egypt. However, some experts have challenged these conclusions, claiming that the true identity of the individual is still uncertain.
The reconstruction, which took months to design, was created by scientists at the Forensic Anthropology, Paleopathology, Bioarchaeology Research Center (FAPAB) in Sicily. They worked closely with Cicero Moraes, a 3D forensic artist from Brazil who is known for his work reconstructing faces from the distant past, FAPAB representatives wrote on Facebook. Unlike previous facial reconstructions of KV 55, the new model omits hair, jewelry and other adornments, in order "to focus on the facial traits of this individual," according to the post.
Related: See photos of Egypt's majestic Valley of the Kings
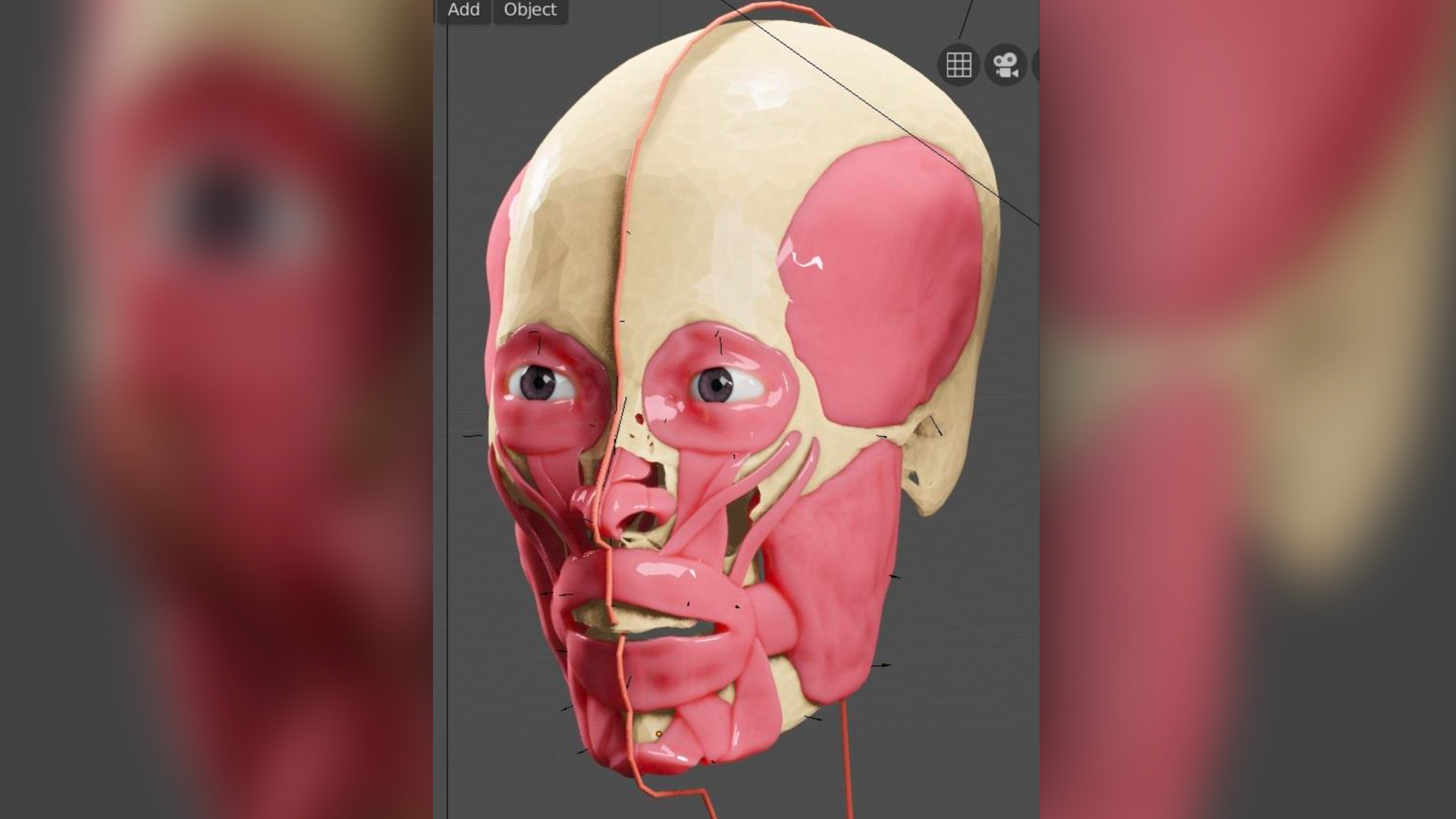
Scientists used a reconstruction process called the Manchester method to bring KV 55's face into the present "from the shadows of history," said Francesco Galassi, director and co-founder of the FAPAB Research Center, an associate professor of archaeology at Flinders University in Australia, and an adjunct professor of forensic anthropology at the Magna Graecia University of Catanzaro in Calabria, Italy.
During this process, "facial muscles and ligaments are modeled on the skull model according to the rules of anatomy," Galassi told Live Science in an email. "The skin is placed on top of this, and the tissue thicknesses are average values that have been scientifically determined."
While building the reconstruction, the researchers referred to "a massive amount of data" for KV 55, including notes from prior physical examinations of the skull, detailed measurements, scaled photographs and X-rays of the skeleton, Galassi said.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
A shadowy past
Akhenaten ascended to the throne as Amenhotep IV and took his new name, which means "the Servant of Aten" — an Egyptian sun god — early in his reign. He then began dismantling the priesthood that served Egypt's pantheon of deities, in order to establish a monotheistic worship of Aten, according to The Ohio State University's Department of History.
Archaeologists found KV 55 in an undecorated tomb that contained bricks engraved with magic spells bearing Akhenaten's name. Another coffin and canopic jars — vessels for holding mummified organs — contained the remains of a woman named Kiya, who was identified as Akhenaten's concubine, according to a FAPAB statement released on March 10.
KV 55 had been mummified, but the preserved flesh disintegrated in the excavators' hands, leaving only the skeleton behind. Based on objects in the tomb and the sex of the skeleton, some archaeologists concluded that it must represent Akhenaten. However, analysis of the teeth and bones revealed that the man was younger than expected. He was around 26 years old when he died — and possibly only 19 to 22 years old, whereas records suggest Akhenaten ruled for 17 years and fathered a daughter during the first year of his reign, Galassi said.
"Some archaeologists tend to assume that he began his reign as a young adult rather than as a child. For this reason, there have been continued attempts [to] consider KV 55 older than the actual anatomy indicates," he said.
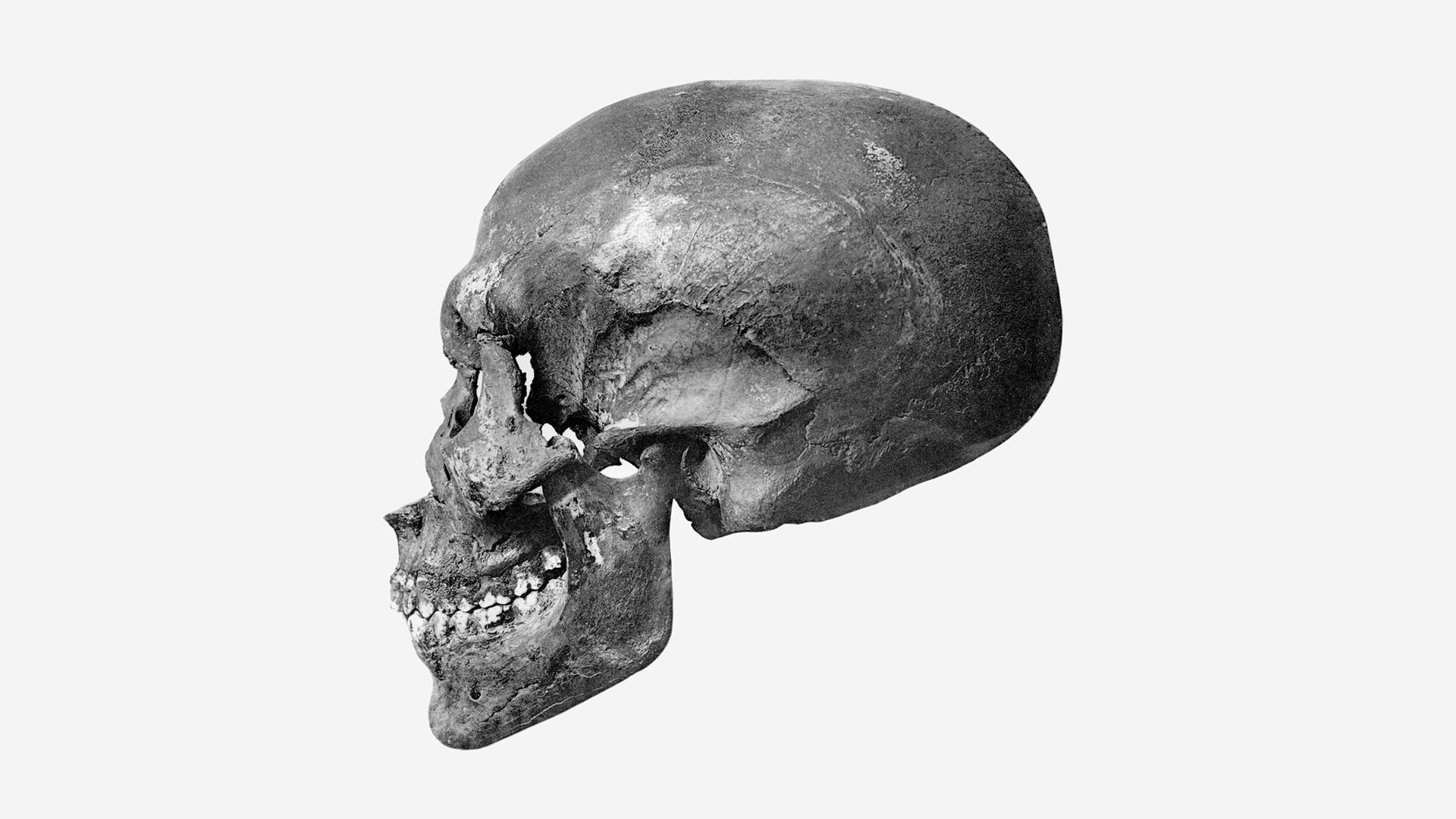
Other experts have proposed that KV 55 could be Smenkhkare, a younger brother of Akhenaten, but there is little evidence that the brother existed at all, Galassi said. Today, Smenkhkare is more commonly thought to be not a real person, but a constructed identity for Queen Nefertiti, who may have assumed this name when she ascended to the throne after Akhenaten's death. This would effectively rule out the "younger brother" hypothesis for KV 55, Galassi said.
Genetic analysis suggested that KV 55 was the son of Amenhotep III and the father of Tutankhamen, providing more evidence that he was Akhenaten, according to a study published in 2010 in the journal JAMA. However, this conclusion is also not without controversy, as genetic data for Egyptian mummies can be "complicated" by the fact that sibling incest was a common practice in royal dynasties, according to the statement.
A more detailed report of the KV 55 reconstruction will be published in 2021, FAPAB representatives said.
Originally published on Live Science.

Mindy Weisberger is an editor at Scholastic and a former Live Science channel editor and senior writer. She has reported on general science, covering climate change, paleontology, biology and space. Mindy studied film at Columbia University; prior to Live Science she produced, wrote and directed media for the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. Her videos about dinosaurs, astrophysics, biodiversity and evolution appear in museums and science centers worldwide, earning awards such as the CINE Golden Eagle and the Communicator Award of Excellence. Her writing has also appeared in Scientific American, The Washington Post and How It Works Magazine. Her book "Rise of the Zombie Bugs: The Surprising Science of Parasitic Mind Control" will be published in spring 2025 by Johns Hopkins University Press.