Newly discovered 'einstein' tile is a 13-sided shape that solves a decades-old math problem
A new 13-sided shape is the first example of an elusive "einstein" — a single shape that can be tiled infinitely without repeating a pattern.
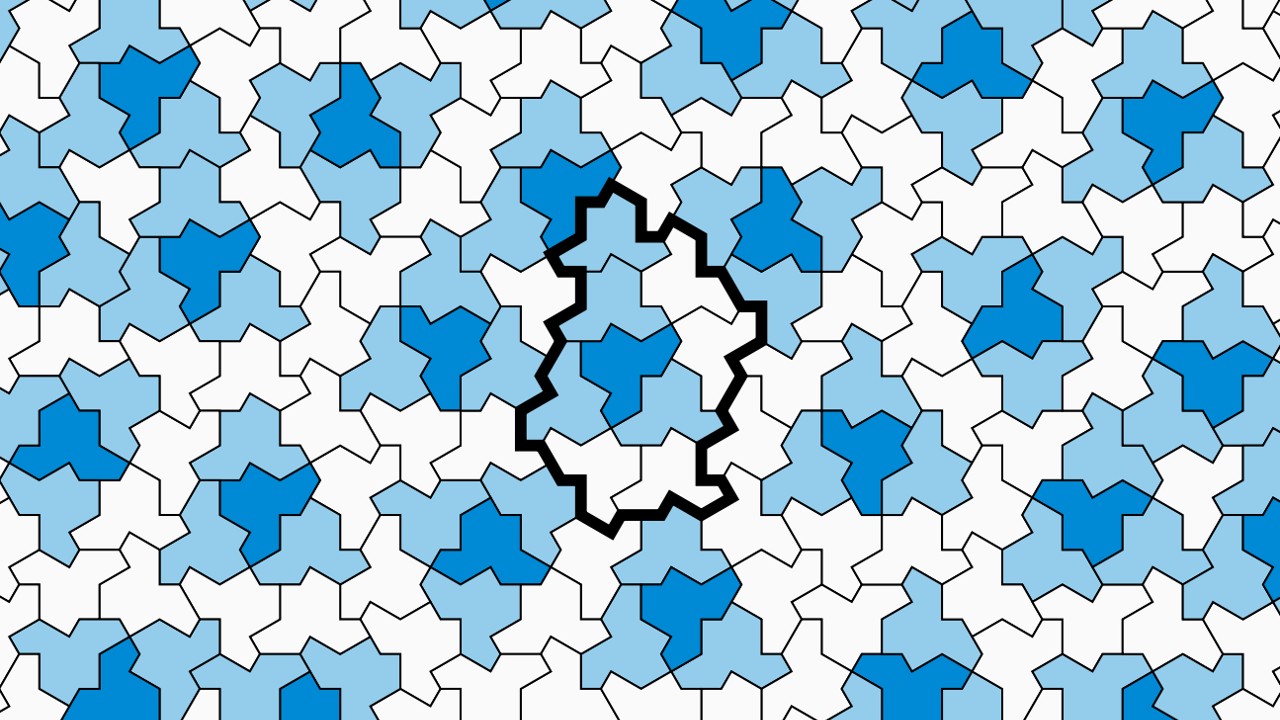
Look carefully! Mathematicians have invented a new 13-sided shape that can be tiled infinitely without ever repeating a pattern. They call it "the einstein."
For decades, mathematicians wondered if it was possible to find a single special shape that could perfectly tile a surface, without leaving any gaps or causing any overlaps, with the pattern never repeating. Of course, this is trivial to do with a pattern that repeats — just look at a bathroom or kitchen floor, which is probably made up of simple rectangular tiles. If you were to pick up your floor and move it (called a "translation" in mathematics), you could find a position where the floor looks exactly the same as before, proving that it's a repeating pattern.
In 1961, mathematician Hao Wang conjectured that aperiodic tilings, or tilings that never become a repeating pattern, were impossible. But his own student, Robert Berger, outwitted him, finding a set of 20,426 shapes that, when carefully arranged, never repeated. He then slimmed that down to a set of 104 tiles. That means that if you were to buy a set of those tiles, you could arrange them on your kitchen floor and never find a repeating pattern.
In the 1970s, Nobel prize-winning physicist Roger Penrose found a set of only two tiles that could be arranged together in a nonrepeating pattern, now known as a Penrose tiling.
Since then, mathematicians around the world have searched for the aperiodic tiling holy grail, called "the einstein." The word doesn't come from the famous Albert but from the German translation of his last name: one stone. Could a single tile — one "stone" — fill a two-dimensional space without ever repeating the pattern it creates?
The answer was just discovered by David Smith, a retired printing technician from East Yorkshire, England. How did he come across this remarkable solution? "I'm always messing about and experimenting with shapes," Smith told The New York Times. “It's always nice to get hands-on. It can be quite meditative."
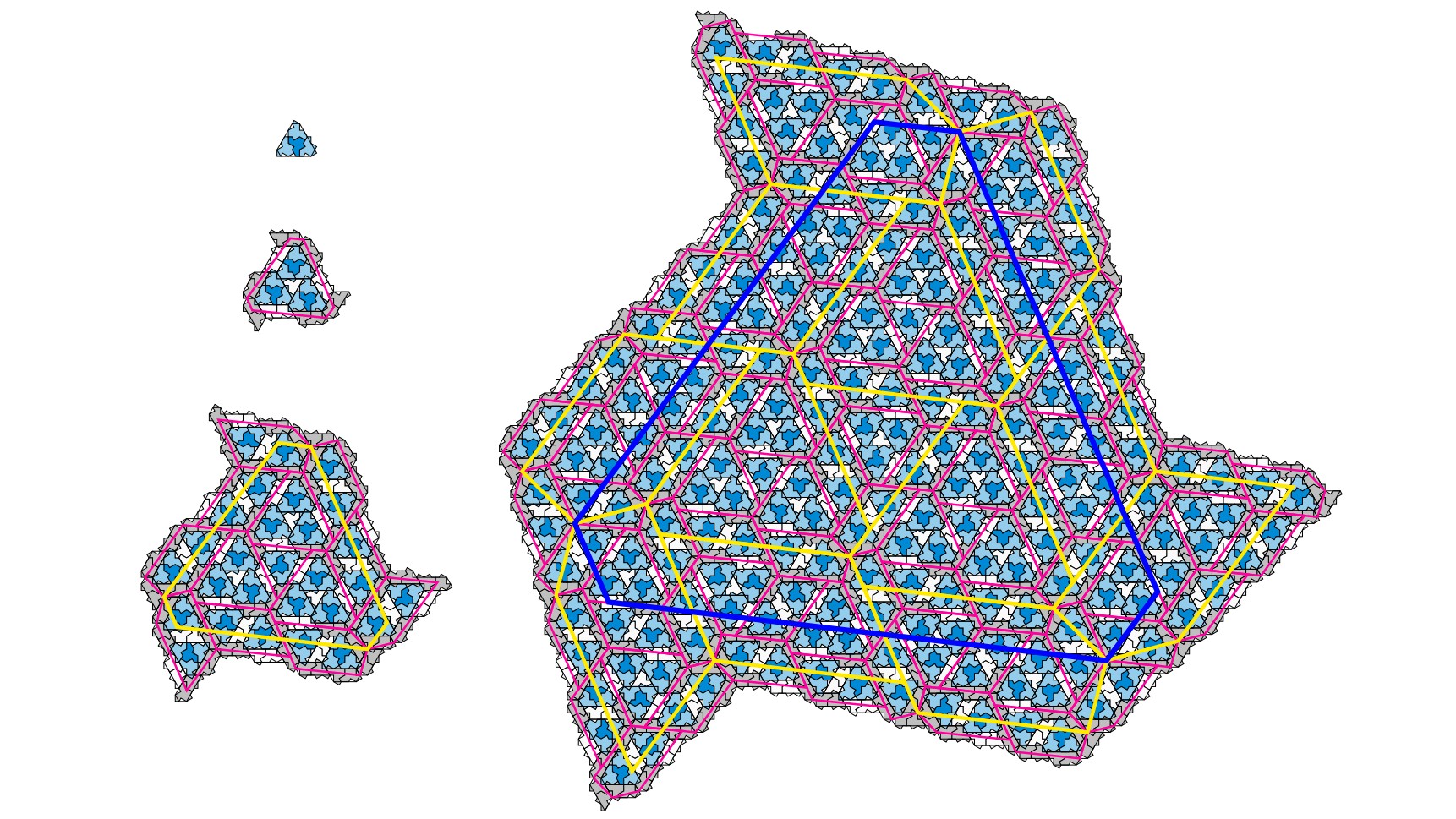
Smith and his co-authors dubbed the new shape "the hat," mostly because it vaguely resembles a fedora. Although mathematicians have known about the shape, which has 13 sides, they had never considered it a candidate for aperiodic tiling.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"In a certain sense, it has been sitting there all this time, waiting for somebody to find it," Marjorie Senechal, a mathematician at Smith College who was not part of the study, told The Times.
Smith worked closely with two computer scientists and another mathematician to develop two proofs showing that "the hat" is an aperiodic monotile — an einstein. One proof relied on building larger and larger hierarchical sets of the tiles, showing how the pattern never repeats as the surface area grows. The other proof relied on the team's discovery that there wasn't just one of these tiles, but an infinite set of related shapes that could all do the trick. The team's paper is available on the preprint server arXiv but has not yet been peer-reviewed, and the proofs have not yet been scrutinized.
These kinds of aperiodic tilings are more than mathematical curiosities. For one, they serve as a springboard for works of art, like the Penrose tiling found at the Salesforce Transit Center in San Francisco, and reveal that some medieval Islamic mosaics employed similar nonrepeating patterns.
Aperiodic tilings also help physicists and chemists understand the structure and behavior of quasicrystals, structures in which the atoms are ordered but do not have a repeating pattern.

Paul M. Sutter is a research professor in astrophysics at SUNY Stony Brook University and the Flatiron Institute in New York City. He regularly appears on TV and podcasts, including "Ask a Spaceman." He is the author of two books, "Your Place in the Universe" and "How to Die in Space," and is a regular contributor to Space.com, Live Science, and more. Paul received his PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2011, and spent three years at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, followed by a research fellowship in Trieste, Italy.