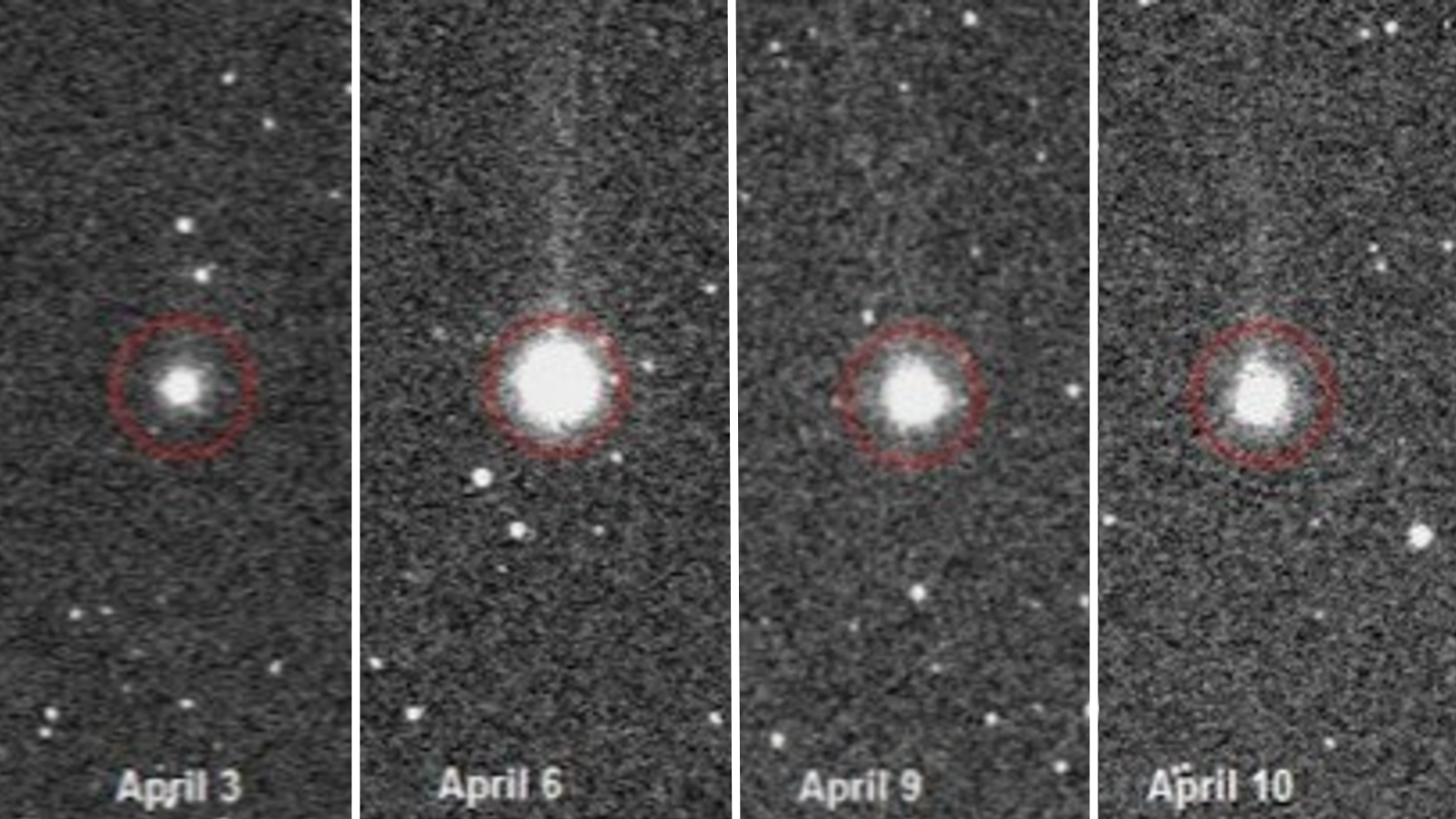
Watch 'city killer' asteroid fly by Earth today on its closest approach for centuries (Feb. 2)
A "potentially hazardous" space rock the size of a football stadium is about to reach its closest point to our planet for more than 100 years, and it won't get this close to us again for centuries more.
UPDATE: You can watch the asteroid flyby on the video above for yourself thanks to a live stream from The Virtual Telescope Project, which will begin at 1:00 p.m. ET on Feb. 2.
A "potentially hazardous" football stadium-size asteroid will zip safely past Earth on Friday (Feb. 2), and, in doing so, will reach its closest point to our planet for more than 100 years. It will also be at least several centuries before the space rock ever gets this close to us again.
The massive asteroid, named 2008 OS7, is around 890 feet (271 meters) across and will pass by Earth at a distance of around 1.77 million miles (2.85 million kilometers), according to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). For context, that is more than seven times further away than the moon orbits Earth.
As it passes by Earth, the asteroid will be traveling at a speed of around 41,000 mph (66,000 km/h), according to JPL.
To compare this space rock's girth to that of other asteroids, it is around half the size of asteroid Bennu, which NASA visited and took samples of, and at least 70 times smaller than the Vredefort meteor — the largest known space rock to ever hit Earth.
Related: 'Planet killer' asteroids are hiding in the sun's glare. Can we stop them in time?
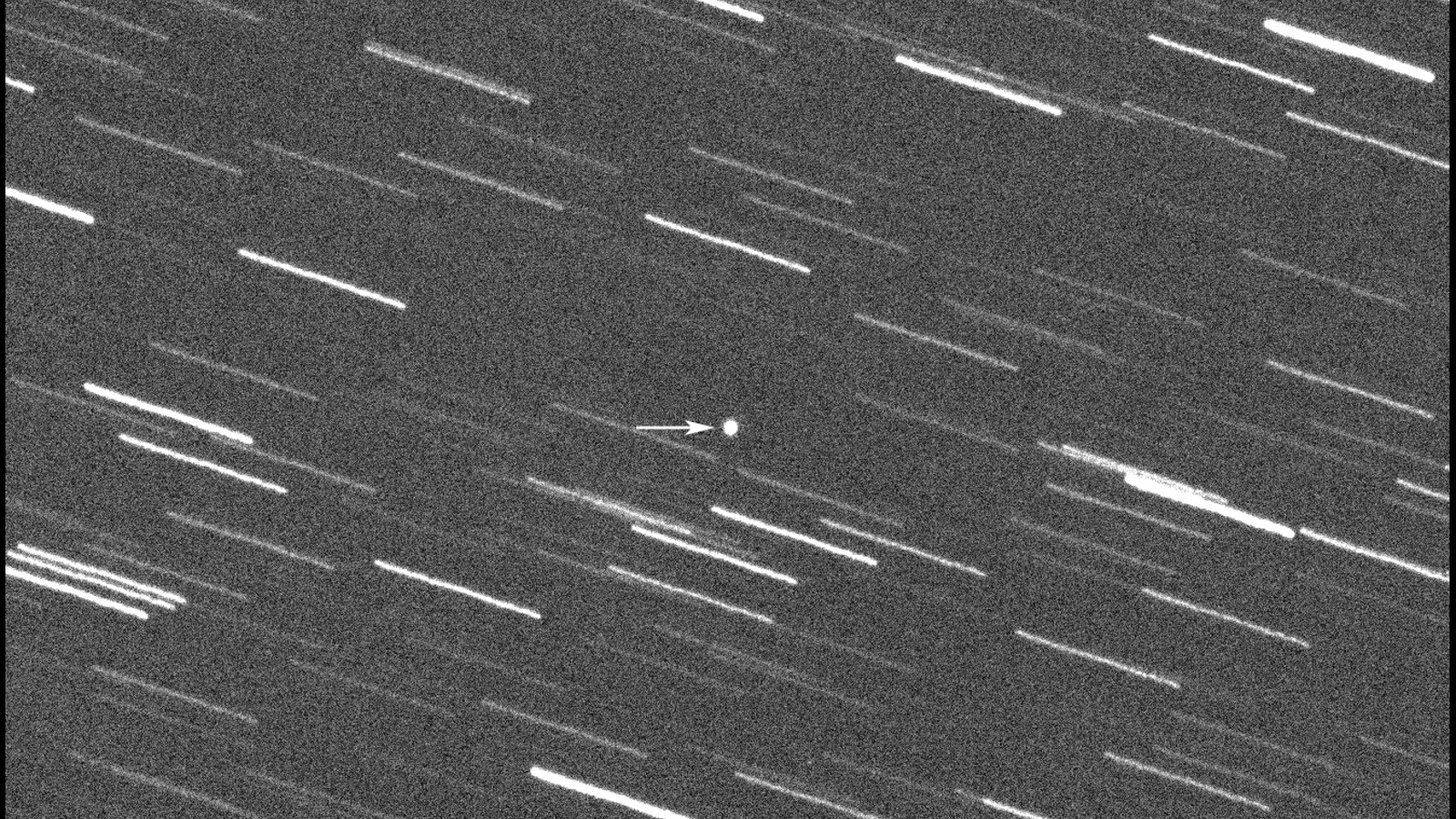

Due to its size and proximity to Earth, the asteroid is classified as potentially hazardous despite the fact it will never come close enough to impact our planet, JPL predictions show. If the space rock did ever crash to Earth, it is big enough to wipe out a large city, such as New York.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
However, the object isn't hefty enough to be considered a "planet killer" asteroid, such as the Vredefort meteor or the space rock that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago.
NASA has identified around 25,000 potentially hazardous asteroids, although a significant percentage of these are not as large as the impending space rock. One of these deadly asteroids is expected to hit Earth every 20,000 years, Live Science previously reported.
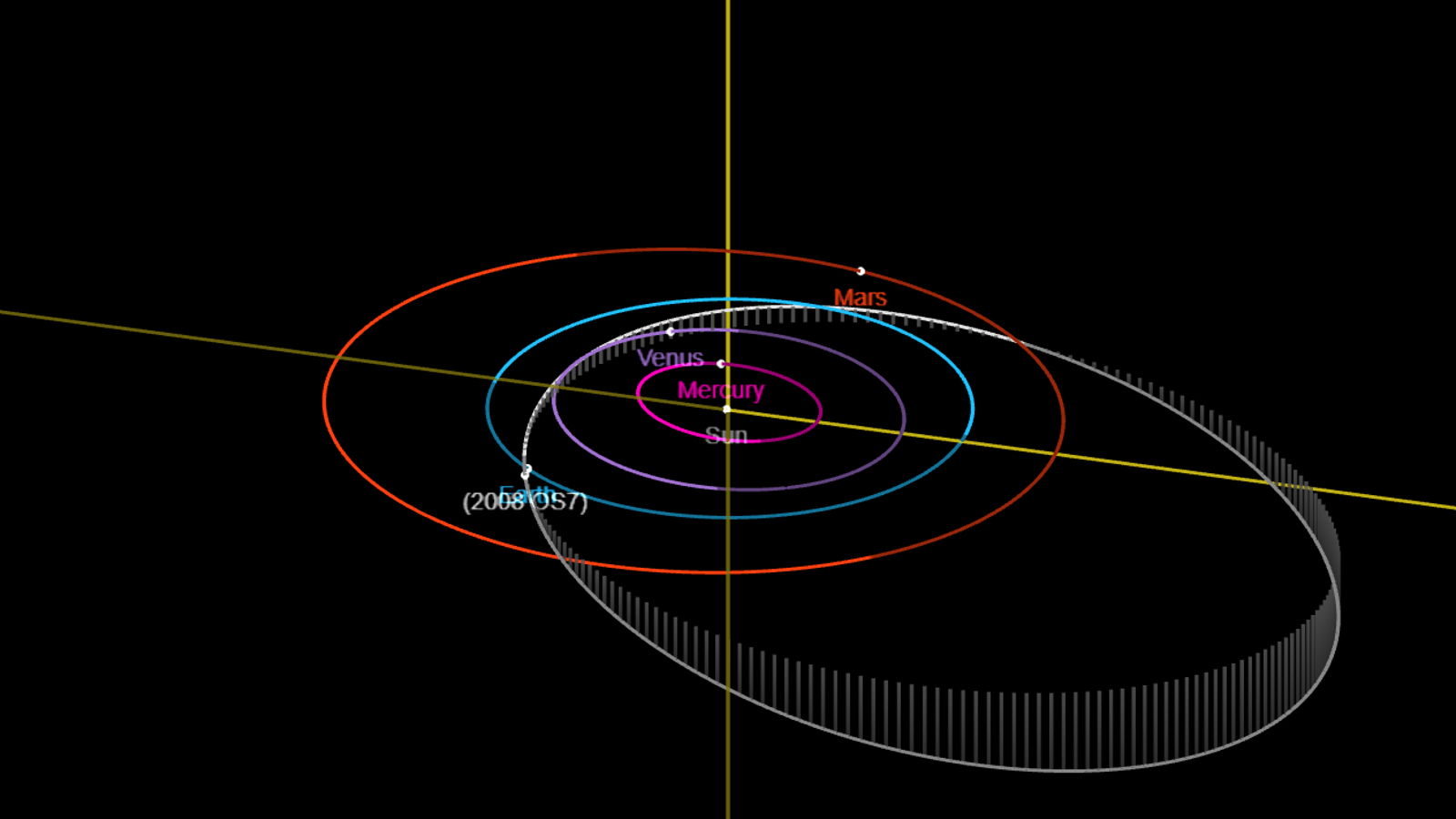
2008 OS7 has a highly elliptical orbit, meaning that it does not orbit evenly around the sun. Because of this, the distance between it and Earth varies wildly whenever the space rock makes a close approach to our planet. For example, when the asteroid approached us shortly after its discovery in 2008, it was around 55.9 million miles (90 million km) away from us, which is more than 30 times further away than it will be this week, according to JPL.
Scientists have only directly observed the asteroid fly by Earth twice before. But based on the space rock's orbital data, JPL has simulated every close approach the asteroid has made since 1900 and predicted every close approach it will make until 2198. At no other point in this nearly 300-year dataset is the asteroid expected to be closer to our planet than on Feb. 2 this year.
Several other asteroids have made close approaches to or directly hit Earth in the last few weeks.
On Jan. 27, an airplane-size asteroid passed by Earth at a distance of just 220,000 miles (354,000 km), which is slightly closer than the moon is to our planet. And on Jan. 21, a child-size asteroid was discovered by astronomers around 3 hours before it exploded in the atmosphere above Germany.

Harry is a U.K.-based senior staff writer at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to become a journalist. He covers a wide range of topics including space exploration, planetary science, space weather, climate change, animal behavior and paleontology. His recent work on the solar maximum won "best space submission" at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the "top scoop" category at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He also writes Live Science's weekly Earth from space series.