Space photo of the week: Iconic 'Eagle Nebula' gets a major glow-up on Hubble's 35th anniversary
One of the Hubble Space Telescope's most iconic images has been reprocessed using the latest techniques.
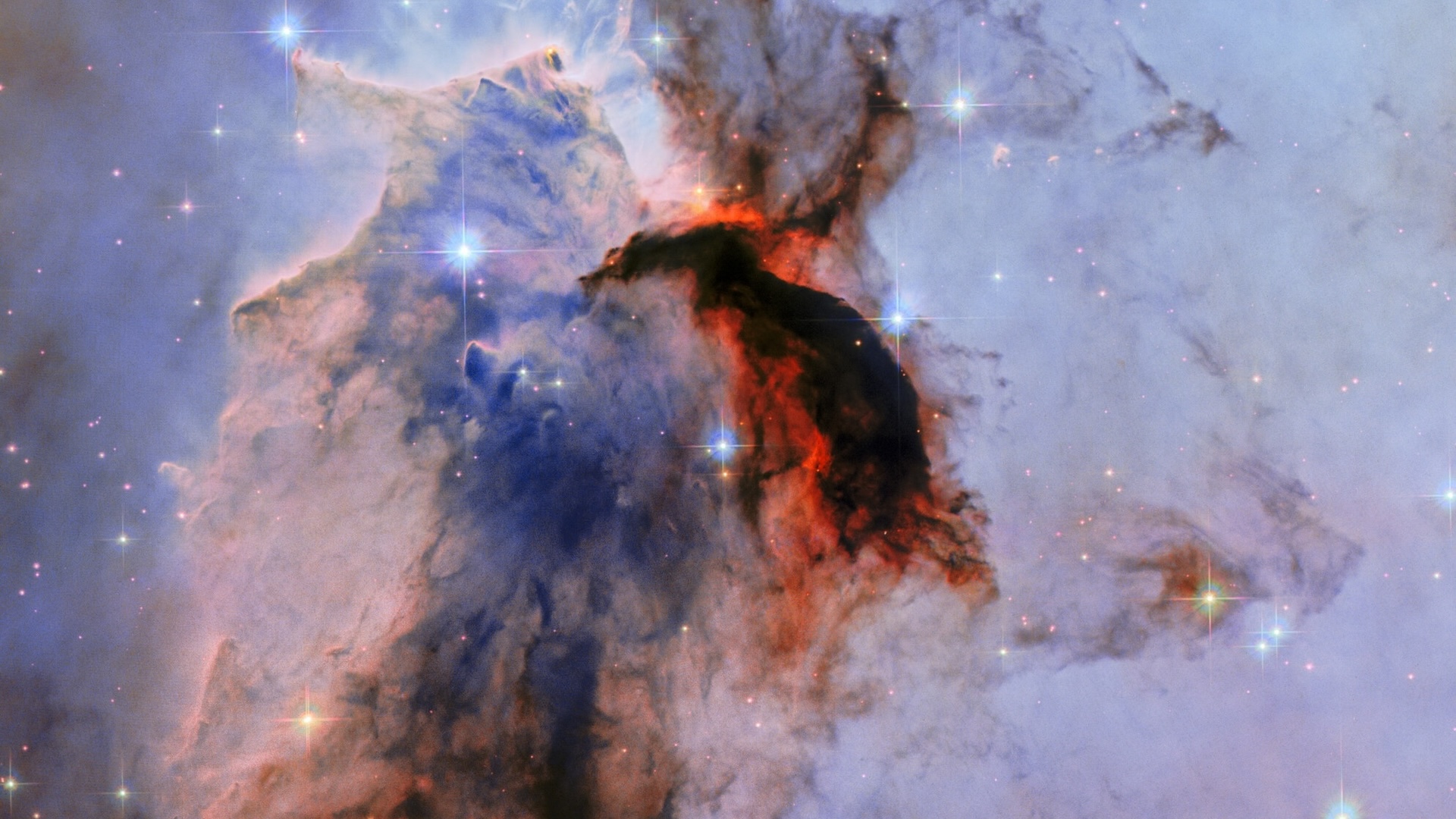

What it is: The Eagle Nebula (Messier 16)
Where it is: 7,000 light-years away, in the constellation Serpens
When it was shared: April 18, 2025
There are few more iconic images from the Hubble Space Telescope than this one. A colossal pillar of gas and dust towering 9.5 light-years tall, this spectacular structure in the Eagle Nebula highlights the breathtaking beauty sculpted by the forces of star formation.
The stunning image, originally published in 2005, is an important part of why the Hubble is so loved. The photo has been newly processed using modern techniques to show the "cosmic pillar" in even more detail, with layers of cold gas and dust seen by Hubble's visible and infrared cameras.
The new image more clearly shows how the radiation from the hot, young stars in the more dramatic top half of the image is lighting up — but also eroding — the massive tower. The image covers an area equal to twice the distance from the sun to Alpha Centauri, the closest star system to our own.
Related: Stunning 'pillars of creation' shine like never before in new James Webb Telescope image
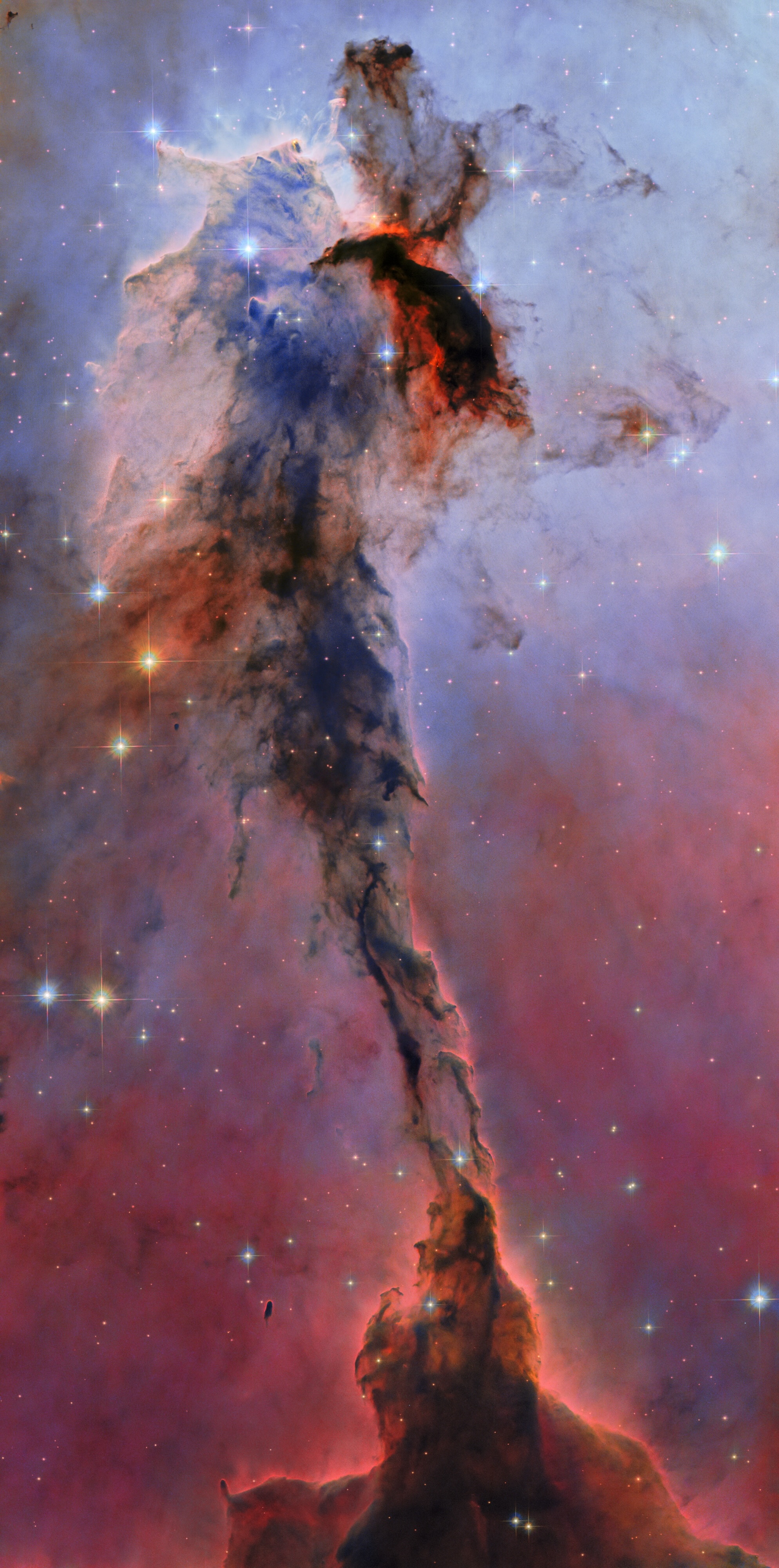

If you think this newly minted snapshot looks a bit like an even more famous Hubble image, the iconic Pillars of Creation, there's a reason for that. Hubble's images of three towers of cosmic dust and gas that resemble a pointing finger — first released in 1995 and improved upon in 2015 to mark Hubble's 25th anniversary — are relatively nearby in the Eagle Nebula (M16). In fact, both images are of dust pillars around the edge of the nebula's heart, where the radiation from a cluster of young stars called NGC 6611 has sculpted a cavity in the dusty gas.
Serpens is prominent in the night sky during the Northern Hemisphere's summer. It can be found in the south, between the bright stars Aquila and Antares and beneath the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer.
This photo of M16 is the latest redux image published to mark the 35th anniversary of the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched on the space shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 and was released from the cargo hatch the following day. Earlier this month, new images revisiting NGC 346 and the Sombrero Galaxy were published.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
For more sublime space images, check out our Space Photo of the Week archives.

Jamie Carter is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor based in Cardiff, U.K. He is the author of A Stargazing Program For Beginners and lectures on astronomy and the natural world. Jamie regularly writes for Space.com, TechRadar.com, Forbes Science, BBC Wildlife magazine and Scientific American, and many others. He edits WhenIsTheNextEclipse.com.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.