Space photo of the week: The chaotic heart of the Milky Way like you've never seen it before
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has teamed up with the MeerKAT radio telescope array to explore how magnetic fields affect star formation at the chaotic center of the Milky Way.
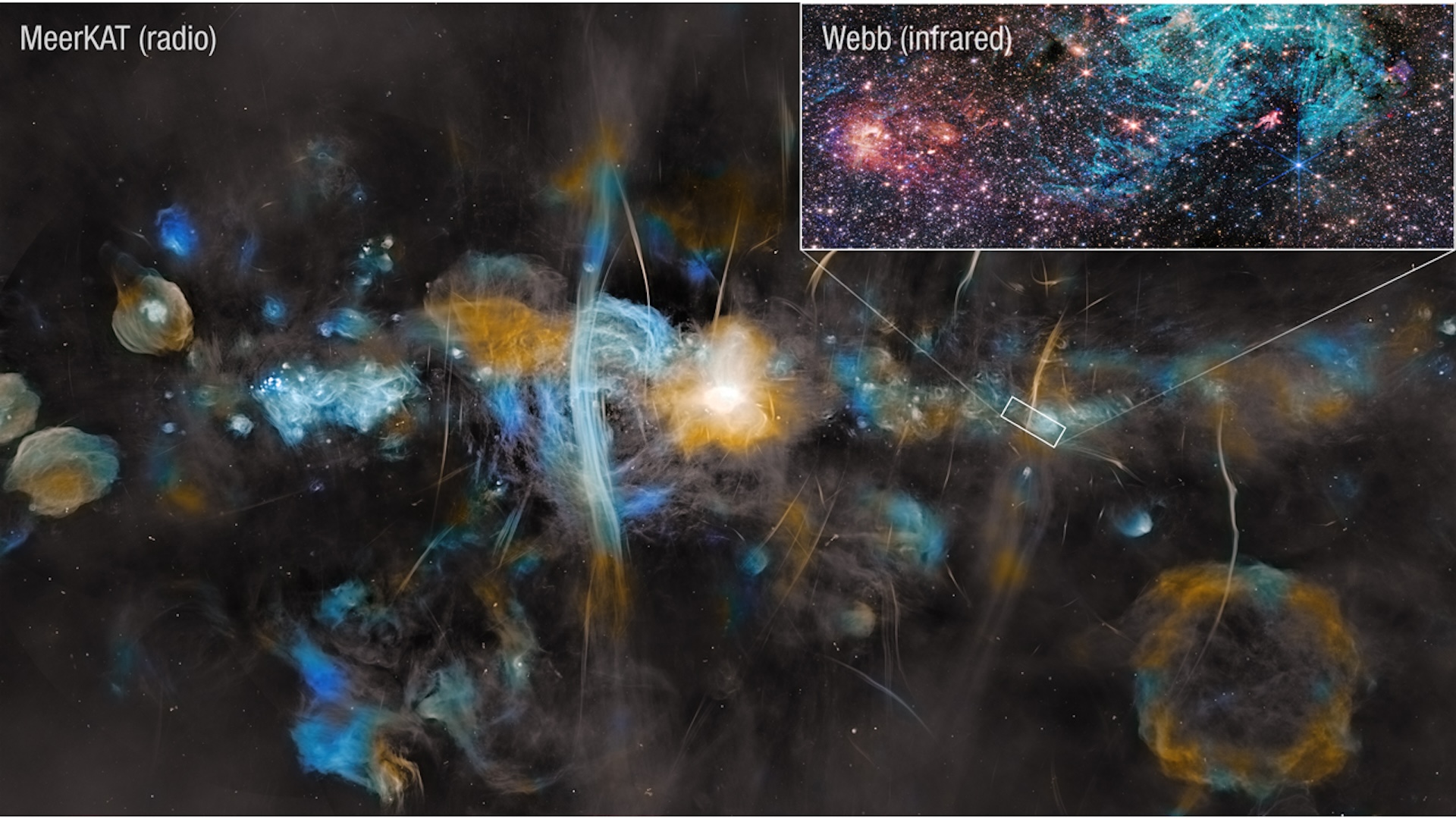

What it is: Sagittarius C (Sgr C) region of the Milky Way.
Where it is: 25,000 light-years from the solar system in the constellation Sagittarius.
When it was shared: April 2, 2025
Why it's so special: The Milky Way often appears as a reddish, pinkish and bluish-white arc across the night sky, but this new super-long exposure image from South Africa's ground-based MeerKAT radio telescope shows our home galaxy in a completely new way.
Colored in blue, cyan, yellow and white, the main image — whose many bubbles of color are remnants of supernovas — span 1,000 light-years of the Milky Way.
The new radio image helps to put in context the inset infrared image by the James Webb Space Telescope from 2023 of Sagittarius C (Sgr C). This is a 44 light-year-wide region about 200 light-years from the Milky Way's central supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A*, where stars are being formed.
JWST's image revealed more than 500,000 stars, but in this Central Molecular Zone — an extreme environment — stars are not being formed as quickly as astronomers expect. One reason may be the strong magnetic fields around that supermassive black hole, which are shaping the filaments seen by MeerKAT and JWST. These magnetic fields may also be strong enough to resist the gravity that causes dense clouds of gas and dust to collapse to create stars, thus suppressing star formation in Sgr C.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"A big question in the Central Molecular Zone of our galaxy has been, if there is so much dense gas and cosmic dust here, and we know that stars form in such clouds, why are so few stars born here?" said John Bally, an astrophysicist at the University of Colorado Boulder and one of the principal investigators of a related paper published April 2 in The Astrophysical Journal. "Now, for the first time, we are seeing directly that strong magnetic fields may play an important role in suppressing star formation, even at small scales," Bally said in a NASA statement.
MeerKAT is a radio telescope made up of 64 dishes in South Africa's Karoo region. It will eventually form part of a far larger radio telescope called the Square Kilometre Array, the world's largest and most sensitive radio telescope that will also use more than 130,000 Christmas tree-shaped antennas on the traditional lands of the Wajarri Yamaji, in Murchison, Western Australia.
For more sublime space images, check out our Space Photo of the Week archives.

Jamie Carter is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor based in Cardiff, U.K. He is the author of A Stargazing Program For Beginners and lectures on astronomy and the natural world. Jamie regularly writes for Space.com, TechRadar.com, Forbes Science, BBC Wildlife magazine and Scientific American, and many others. He edits WhenIsTheNextEclipse.com.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.