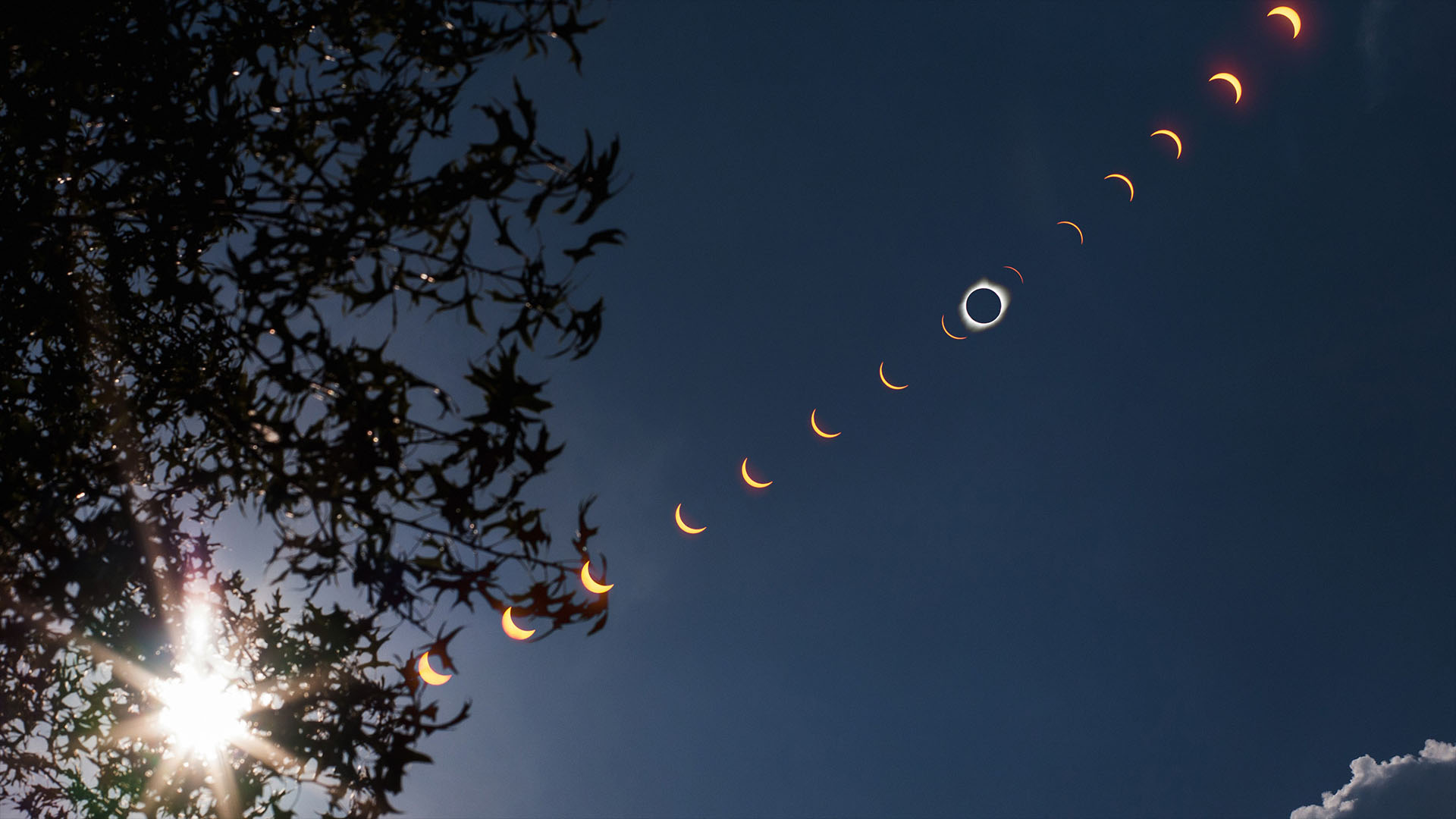
For the total solar eclipse on April 8, many people will strive to be within the path of totality, where the sun's face will be completely blocked by the moon's shadow. But even if you're within this path, it doesn't guarantee you'll have clear skies on eclipse day.
So what happens if it's cloudy where you are on April 8? Will you notice anything as the moon's shadow sweeps over you?
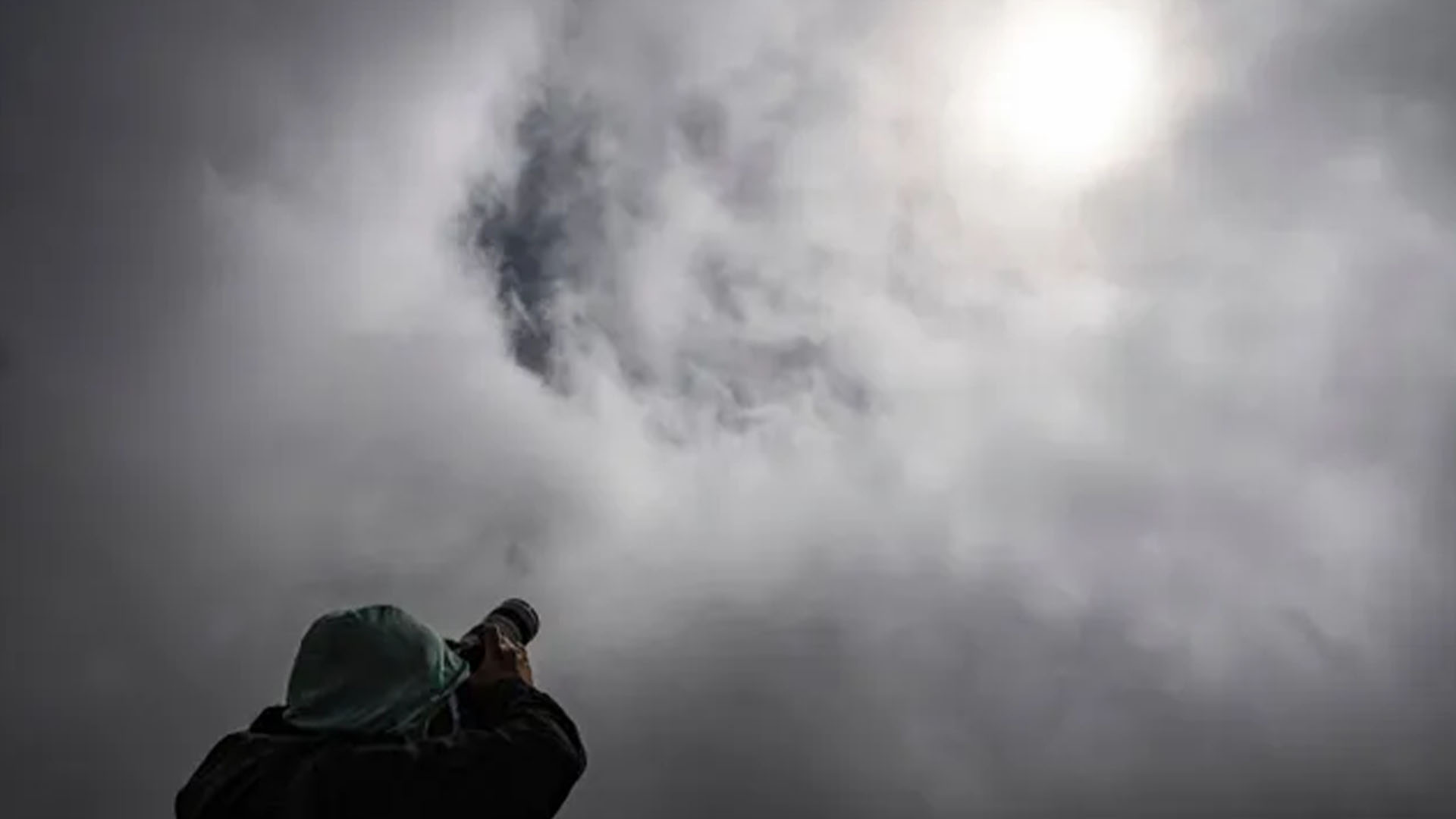
That depends on how thick and how extensive the clouds are. Regardless, you will certainly notice some very unusual effects when the moon's shadow passes by. I have had the misfortune of being completely clouded out of two of the 13 total solar eclipses I have journeyed to, and in a third case, I managed to sneak in a view of the corona even though virtually the entire sky was clouded over.
So, based on those three experiences, here is what you can expect to see if the weather does not work in your favor and you ultimately must utter those two words every eclipse chaser does not want to hear: "Clouded out!"
Passage of the moon's shadow
Should there be considerable cloud cover on "E-Day," the clouds may actually have an advantage: They will provide a projection screen of sorts to view the rapid approach and departure of the moon's dark umbral shadow. Isabel Martin Lewis described the effect in her 1924 book "A Handbook of Solar Eclipses."
"At the time of eclipse when the shadow of the moon sweeps over us we are brought into direct contact with a tangible presence from space beyond and we feel the immensity of forces over which we have no control," Lewis wrote. "The effect is awe-inspiring in the extreme. In fact, the passing of the moon's shadow, if one is fortunate to observe it, will be one of the most impressive features of the eclipse."

Mid-to-high-level clouds
If your sky is covered with mid-to-high-level clouds — cirrostratus, altostratus and/or cirrocumulus — you will likely be able to see the forward edge of the elliptical shadow move rapidly toward you and then over you just prior to and at the onset of totality. And with its passage may come a remarkable change in the overall quality of light on the surrounding landscape and a dramatic change in the clouds' color.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
On July 10, 1972, at my very first total solar eclipse, my family and I were located just outside Cap-Chat, Quebec, a sleepy Canadian community of 2,000 whose population swelled to nearly 30,000 on eclipse day. The eclipse began under bright sunshine, mixed with some wispy high clouds. But as more and more of the sun became covered, the high cloudiness quickly increased and began to lower so that, at the onset of totality, virtually the whole sky was covered by a swath of battleship-gray clouds.
But upon the arrival of the moon's shadow, we saw its distinctly sharp edge move in. For those of a certain age who might remember the long-running television soap opera "The Edge of Night," whose opening showed an animation with a line of darkness sweeping over a city, that's exactly what I was reminded of as we were enveloped by the moon's umbral shadow. Once you actually experience it for yourself, it becomes easy to understand why this sight was so terrifying to ancient people.
Related: 'Zeus made night from mid-day': Terror and wonder in ancient accounts of solar eclipses

Along with the sudden darkness came a change in the clouds' color. Behind the forward-moving edge of the moon's shadow were strange and exotic colors. The dull gray suddenly became yellow-orange and tints you'd see while looking through a beer or iodine bottle. Indeed, along the very edge of the disappearing sun at the start and end of totality, an arc of ruby red or fuchsia associated with the solar chromosphere appeared. It looked bright red because the hydrogen in the sun was emitting a reddish light at high temperatures, and some of this light may become evident in the clouds at the beginning and end of totality.
Some final comments regarding my 1972 eclipse experience. Despite the heavy cloud cover, we managed to catch sight of the totally eclipsed sun through a fortuitous opening in the overcast sky, some 30 seconds after totality began. As totality was ending, we saw the back edge of the shadow distinctly, projected on the clouds, racing away to the northeast. I remember my grandfather calling out to my grandmother, "Inez! Look, look! It's going that way." Meanwhile, my sister Lisa, taking this all in, said simply, "That was weird!"
"Incredible sight!"
Interestingly, in March 1970, during special coverage of the total solar eclipse on CBS TV , correspondent Bill Plante (1938-2022) was stationed in Halifax, Nova Scotia, under cloudy skies. Yet he was quite attentive to the changes taking place as the lunar shadow swept in.
"In the last 30 seconds we have witnessed the most incredible sight — in spite of the fact that we cannot see the sun — for it has become as dark as night!" he said. "The light has fallen so quickly, from an acceptable twilight or reading level or cloud-cover level, to virtual night. And just off to the north and to the east, beneath this layer of dark, dark sky, there is a lovely pink and orange horizon; an orange and gold color. We say again, it was just an incredible and fascinating phenomenon, to have the skies go so suddenly dark, in less than 30 seconds, and now we have this totality of an eclipse!"
It sounds like Plante was impressed, despite the clouds.

Just a few clouds
Sometimes, you're lucky enough to get a mainly clear sky. But even then, unfortunately, one of the few clouds in the sky might happen to be in front of the sun during the total phase of the eclipse.
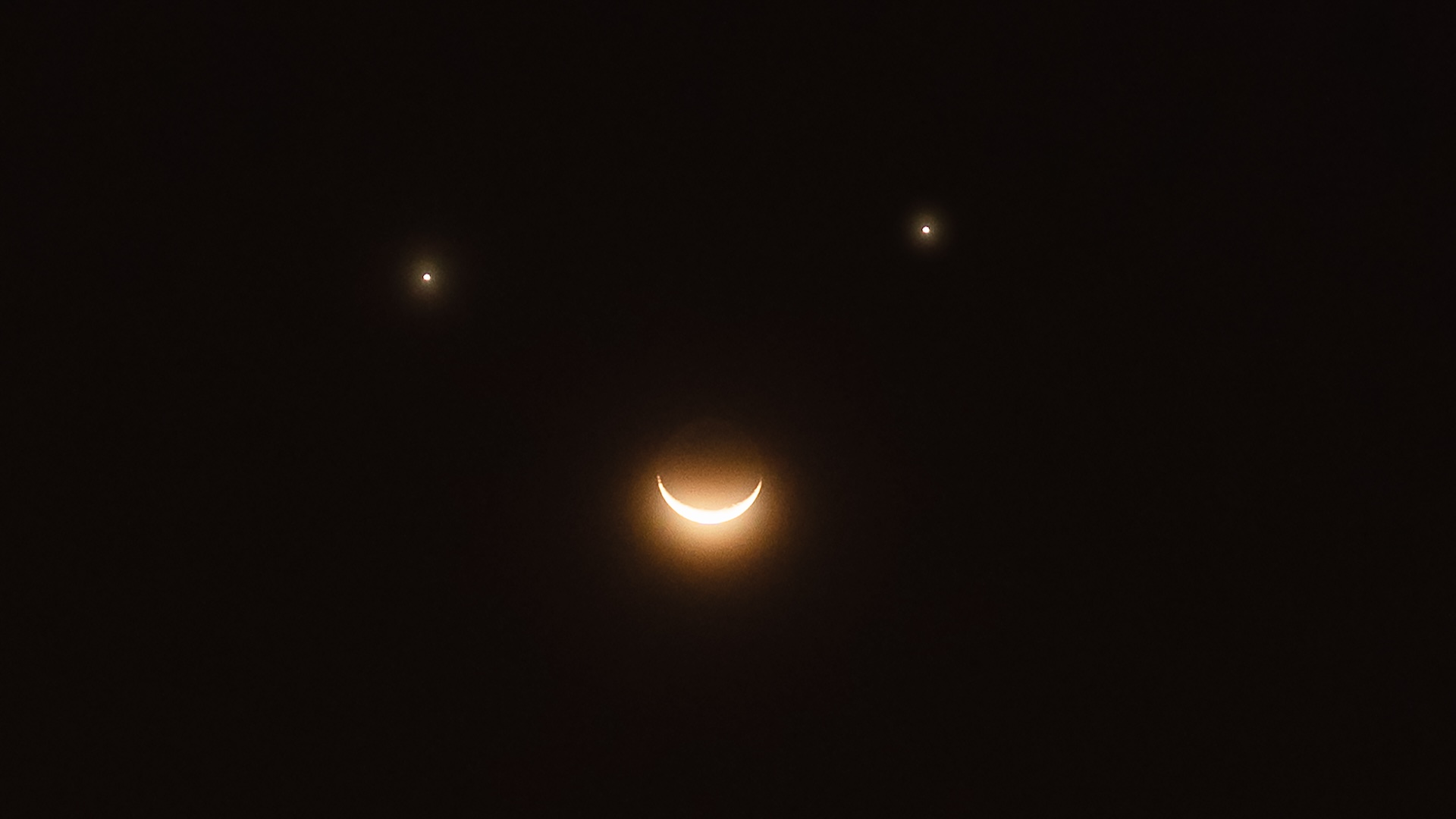
That happened to me on Oct. 12, 1977, in Colombia, South America. During the 38-second interval of totality, a single rag of cloud drifted in front of the sun. Should something like that happen to you, the best you can do is look around the darkened sky for some of the brighter stars and planets and try to watch for the passage of the moon's shadow.
As I noted in my personal journal later on, "When totality arrived, virtually the entire sky was clear and the seeing and transparency were close to excellent. We were able to easily see seven stars and were awed at third contact by the passage of the moon's umbral shadow cone retreating rapidly to the east. And in the east, part of a rainbow changed to all red just as totality began.

"There was only one thing wrong: The sun was behind a cloud! It began encroaching upon the sun a few minutes before totality and left just a minute or two after the sun began to reappear. As if to rub salt into the wound, not another cloud interfered, even as the partially eclipsed sun set behind the Andes! For me, Colombia was Cap Chat in reverse. What goes around, comes around!"
For more on this misadventure, read my colleague Glenn Schneider's comments.
Thick, low clouds
Finally, there is the possibility that on eclipse day, your view will be covered by clouds at low altitudes, generally below 6,500 feet (1,980 meters). They tend to be thick, low, flat clouds that cover large areas and often bring precipitation.
In December 2021, my wife Renate and I were on board an icebreaker, sailing off the coast of Antarctica, when we encountered the moon's shadow for a total eclipse lasting just over a minute and a half. Unfortunately, our skies were heavily overcast with low clouds and spotty, light precipitation.
In such a situation, the effects of a total solar eclipse can best be described as being in a lighted room where someone turns a dimmer switch down and then turns it back up, causing the light to return.
As I noted in my story for Space.com, "Totality lasted 97 seconds. No distinct shadow or cone of darkness was noted. Rather, just an amorphous darkening of the sky — like someone turning down a rheostat or dimmer switch. No colors were seen and the end of totality seemed more pronounced as the light seemed to come back quicker than it when it faded away. During totality, it actually began to drizzle very lightly and a few minutes after third contact it actually started to snow lightly. The air temperature hovered at around 0°C (32°F), but factoring in the winds made it feel noticeably colder."
Final thoughts
I suppose Antarctica was the most disappointing of all my eclipse experiences; aside from getting dark and light again, there really wasn't much more to see. I hope everyone who positions themselves in the path of the moon's dark shadow will get a clear view of the April 8 eclipse. But as you can see, unless the clouds are low and thick with some rain or snow falling, the moon's shadow racing by and the eerie colors accompanying it should still make for quite a show!
Originally posted on Space.com.